Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Article | 12 April 2024
WIKIMOLE—Gastrin I, human
By TargetMol
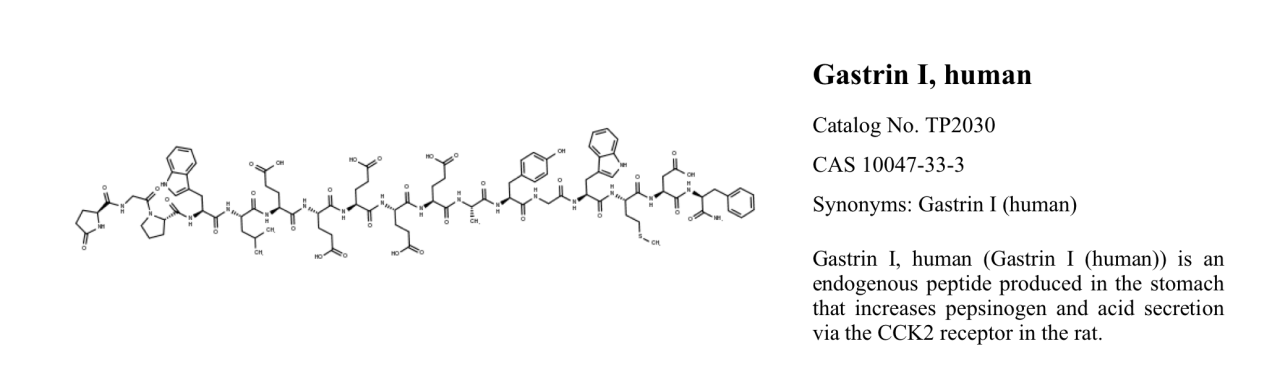
Gastrin I, human, Catalog Number TP2030, also known as Gastrin I (human) or Gastrin 1, is an endogenous peptide produced in the stomach. It increases gastric pepsinogen and gastric acid secretion in rats through the CCK2 receptor.
Function
Gastrin is an important gastrointestinal hormone mainly secreted by G cells. G cells are typical open-type cells, most abundant in the gastric antrum, followed by the gastric fundus, duodenum, and jejunum. Gastrin I is one of the earliest discovered subtypes of gastrin. Gastrin affects almost the entire gastrointestinal tract. It can promote the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the mucosa of the gastric acid gland area and duodenal mucosa, thereby promoting mucosal cell growth and proliferation. The main functions of gastrin include:
1. Stimulating the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the mucosa of the gastric acid gland area and duodenal mucosa, thereby promoting mucosal cell growth and proliferation.
2. Stimulating parietal cells to secrete hydrochloric acid and chief cells to secrete pepsinogen.
3. Stimulating gastric antrum and intestinal movement, delaying gastric emptying.
4. Stimulating the secretion of pancreatic juice, bile, and intestinal juice.
Application
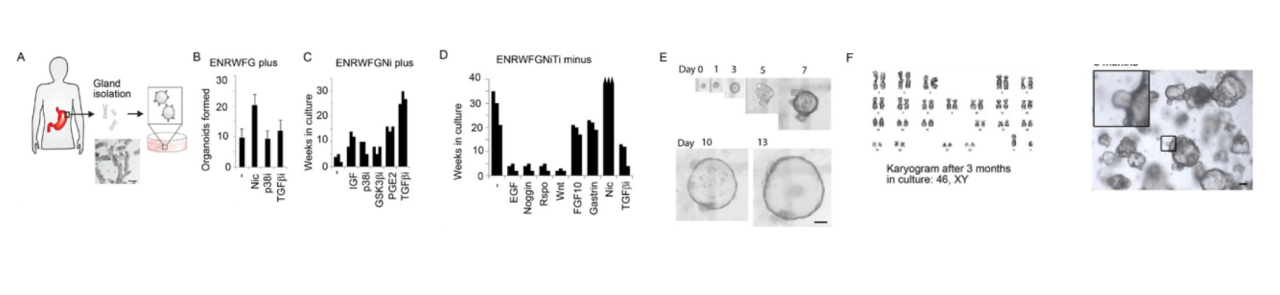
In the culture process of gastrointestinal organs, gastrin I can promote gastric acid secretion, proliferation, and repair of gastric mucosal cells. It also simulates the physiological environment in the body, helping to maintain the normal development and function of gastric organs. Therefore, in the culture process of gastrointestinal organs, gastrin I is often added as an auxiliary factor to the culture medium.
Reference
[1] Gastrin. J Pak Med Assoc. 1978;28(2):13-14.
[2] Bartfeld S, Bayram T, van de Wetering M, Huch M, Begthel H, Kujala P, Vries R, Peters PJ, Clevers H. In vitro expansion of human gastric epithelial stem cells and their responses to bacterial infection. Gastroenterology. 2015 Jan;148(1):126-136.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.09.042. Epub 2014 Oct 13. PMID: 25307862; PMCID: PMC4274199.
[3] Mahe MM, Aihara E, Schumacher MA, Zavros Y, Montrose MH, Helmrath MA, Sato T, Shroyer NF. Establishment of Gastrointestinal Epithelial Organoids. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2013 Dec 19;3(4):217-40. doi: 10.1002/9780470942390.mo130179. PMID: 25105065; PMCID: PMC4120977.
Reference
[1] Gastrin. J Pak Med Assoc. 1978;28(2):13-14.
[2] Bartfeld S, Bayram T, van de Wetering M, Huch M, Begthel H, Kujala P, Vries R, Peters PJ, Clevers H. In vitro expansion of human gastric epithelial stem cells and their responses to bacterial infection. Gastroenterology. 2015 Jan;148(1):126-136.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.09.042. Epub 2014 Oct 13. PMID: 25307862; PMCID: PMC4274199.
[3] Mahe MM, Aihara E, Schumacher MA, Zavros Y, Montrose MH, Helmrath MA, Sato T, Shroyer NF. Establishment of Gastrointestinal Epithelial Organoids. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2013 Dec 19;3(4):217-40. doi: 10.1002/9780470942390.mo130179. PMID: 25105065; PMCID: PMC4120977.
Other Articles


Subscription to TargetMol News
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.