High-Standard Entry Criteria
TargetMol’s Drug Repurposing Compound Library is built on rigorous inclusion standards to ensure that every compound in the library has a well-defined structure and high purity, verified by multiple analytical techniques such as NMR, HPLC, and LC-MS. Through a multi-step screening process, we eliminate compounds with undefined structures, including mixtures and polymers, as well as non-active agents such as sunscreens, contrast agents, and inorganic substances.
The library exclusively includes small-molecule drugs and drug candidates that are either FDA-approved or currently in clinical trials. Compounds that have not yet entered the clinical phase are excluded, ensuring the safety of the library and enhancing the efficiency of drug repurposing efforts. This approach helps shorten the drug development cycle. Additionally, accurate compound information and clear classification significantly improve screening efficiency and reduce unnecessary resource and time costs.
Significant Structural Diversity
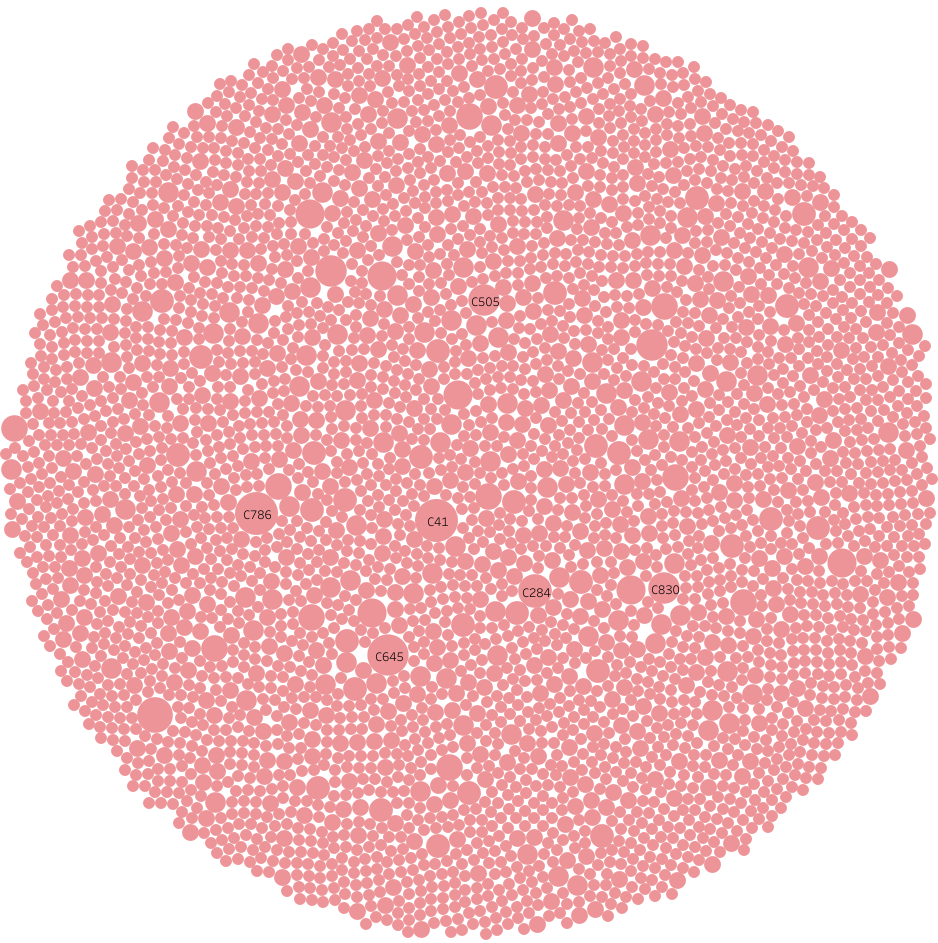
TargetMol’s Drug Repurposing Compound Library exhibits remarkable structural diversity, offering substantial advantages in drug discovery. Based on MACCS fingerprint analysis, the library can be categorized into 4,017 classes, effectively covering a broad chemical space. The library includes a wide variety of compounds, ranging from simple to highly complex chemical structures. This diversity provides a wealth of possibilities for identifying lead compounds with high affinity and specificity for target proteins, significantly advancing drug innovation.
Library Diversity Analysis
Diverse Compound Collection
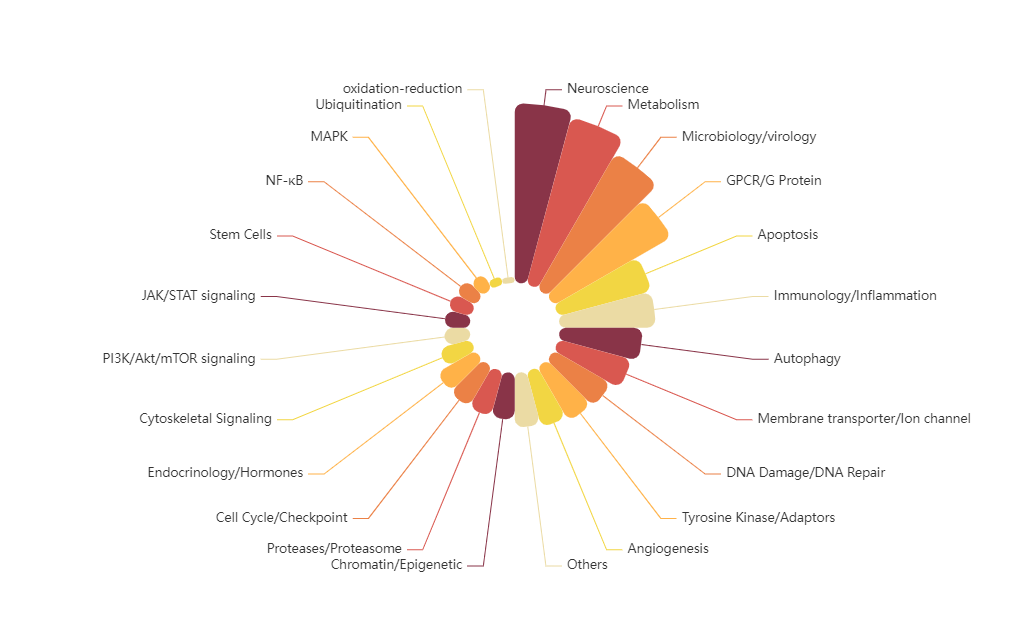
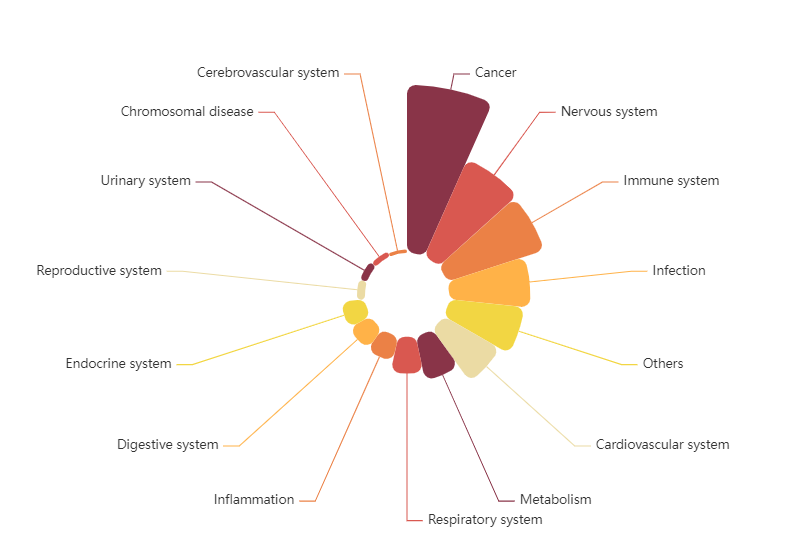
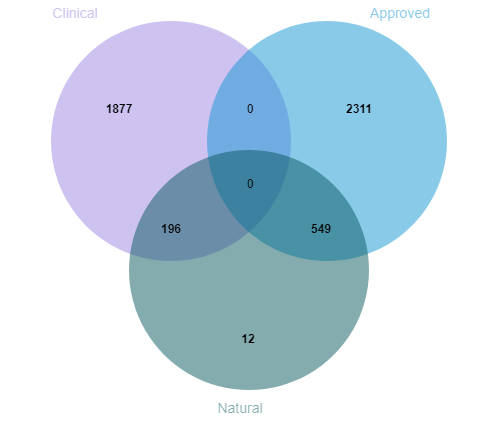
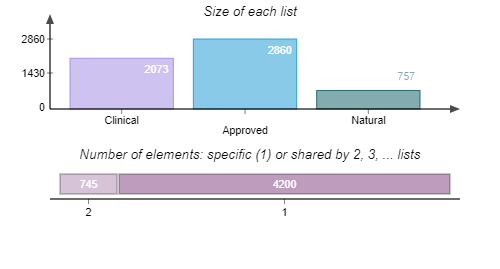
TargetMol’s Drug Repurposing Compound Library features not only a high degree of chemical diversity but also broad representation in terms of biological functions. The library includes compounds targeting key signaling pathways such as kinases, G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), ion channels, and epigenetic regulators. It comprehensively covers a wide range of disease areas including cancer, immune disorders, neurological diseases, metabolic diseases, and infectious diseases. The library contains 2,800+ approved drugs and 1,800+ clinical-stage drug candidates, including 190+ natural products that have entered clinical trials and 540+ natural products approved for market use. This library offers a rich and diverse chemical space, enabling researchers to explore new therapeutic strategies and accelerate the discovery of innovative drugs.
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty