Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Article | 26 Jan 2024
WIKIMOLE—Forkskolin
By TargetMol
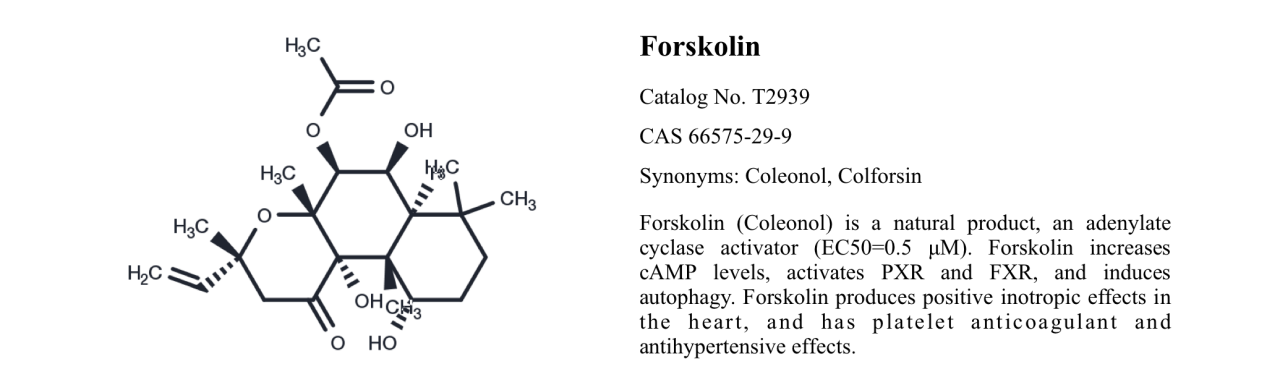
Forskolin, also known as Coleonol or Colforsin, is a diterpene natural product extracted from the roots of the Coleus forskohlii plant. It serves as an activator of adenylate cyclase, leading to an increase in the levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP).
Mechanism of Action
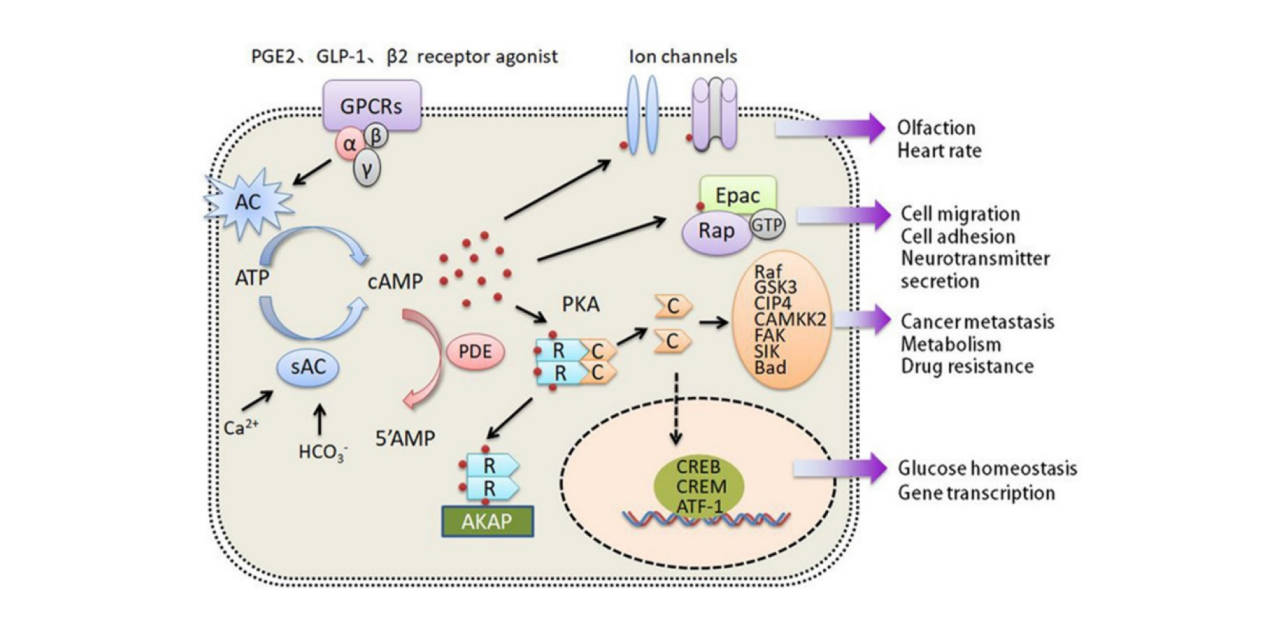
Forskolin, as a direct, rapid, and reversible activator of adenylate cyclase, increases cellular cAMP levels. Intracellular cAMP serves as a secondary messenger involved in various physiological processes such as cell differentiation, proliferation, metabolic regulation, and inflammatory responses. The known signaling pathways of cAMP primarily transmit signals through the activation of protein kinase A (PKA). cAMP molecules can bind to two cAMP-binding domains in the subunits of PKA, releasing its two subunits, activating PKA, and phosphorylating downstream target proteins. Additionally, the cAMP signaling pathway includes membrane receptors (ion channels), Epac, and others. The cAMP signaling pathway plays a crucial role in maintaining normal physiological functions, growth and development processes, metabolic regulation, and inflammatory responses.
Biological Applications
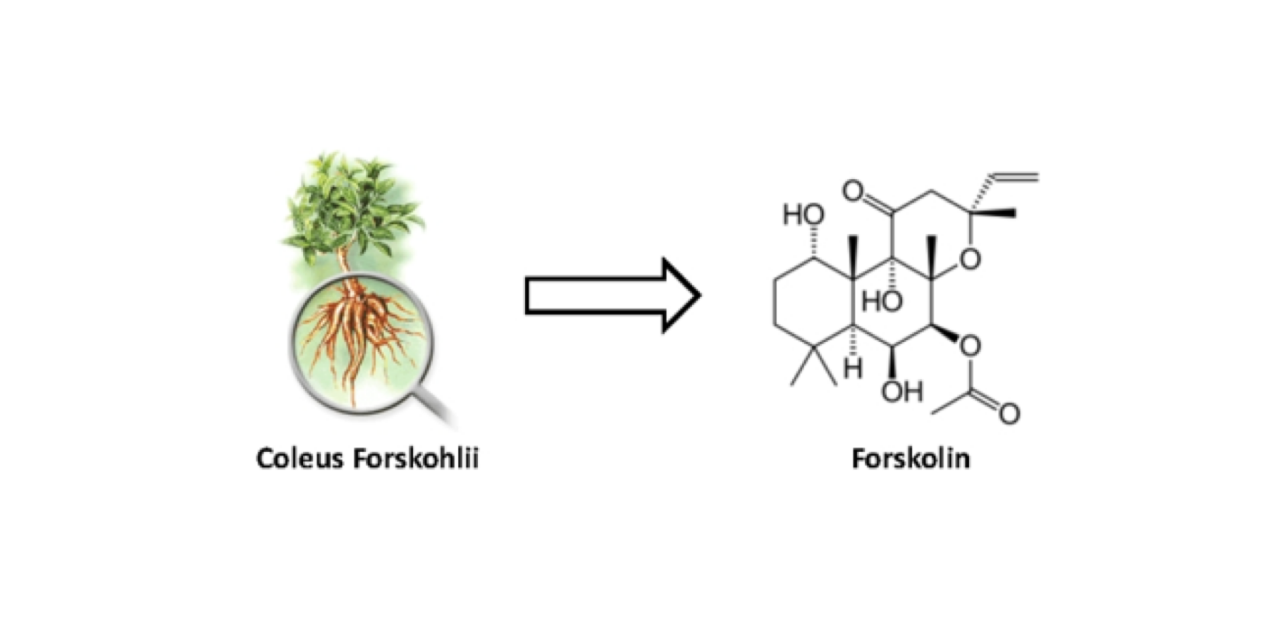
Natural forskolin is primarily extracted from the root tissues of the plant Coleus forskohlii and holds significant medicinal value. It is known to exhibit favorable pharmacological activities in areas such as anti-cancer, anti-viral, anti-asthmatic, anti-hypertensive, and cardiac strengthening. As a cAMP activator, it has been used as a valuable tool to reveal the significance of cAMP in various cellular events across different organs, potentially providing more therapeutic targets for treating diseases.
In the cardiovascular system, the cAMP signaling pathway plays a role in regulating processes such as heart contraction and relaxation. In the nervous system, the activation of the cAMP signaling pathway can promote synaptic transmission in neurons and enhance memory formation. In metabolic-related diseases like diabetes and obesity, the regulatory effects of the cAMP signaling pathway are associated with insulin secretion and energy metabolism.
The cAMP signaling pathway also plays a crucial role in regulating the immune system. In T cells, the activation of the cAMP signaling pathway inhibits cell activation, contributing to immune tolerance. In macrophages, the activation of the cAMP signaling pathway suppresses the production of nitric oxide, serving as an anti-inflammatory effect.
Reference
[1] Zhao B, Du F, Xu P, Shu C, Sankaran B, Bell SL, Liu M, Lei Y, Gao X, Fu X, Zhu F, Liu Y, Laganowsky A, Zheng X, Ji JY, West AP, Watson RO, Li P. A conserved PLPLRT/SD motif of STING mediates the recruitment and activation of TBK1. Nature. 2019 May;569(7758):718-722. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1228-x. Epub 2019 May 22. PMID: 31118511; PMCID: PMC6596994.
[2] Zhang Z, Zhou H, Ouyang X, et al. Multifaceted functions of STING in human health and disease: from molecular mechanism to targeted strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):394. Published 2022 Dec 23. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01252-z
[3] Xie W, Patel DJ. Structure-based mechanisms of 2'3'-cGAMP intercellular transport in the cGAS-STING immune pathway. Trends Immunol. 2023;44(6):450-467. doi:10.1016/j.it.2023.04.006
[4] Xie W, Lama L, Yang X, et al. Arabinose- and xylose-modified analogs of 2',3'-cGAMP act as STING agonists. Cell Chem Biol. 2023;30(11):1366-1376.e7. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.07.002
[5] Zhu Q, Hu H, Liu H, Shen H, Yan Z, Gao L. A synthetic STING agonist inhibits the replication of human parainfluenza virus 3 and rhinovirus 16 through distinct mechanisms. Antiviral Res. 2020;183:104933. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104933
[6] Carozza JA, B?hnert V, Nguyen KC, et al. Extracellular cGAMP is a cancer cell-produced immunotransmitter involved in radiation-induced anti-cancer immunity. Nat Cancer. 2020;1(2):184-196. doi:10.1038/s43018-020-0028-4
Other Articles


Subscription to TargetMol News
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.