Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
NEWS | 2 August 2024
WIKIMOLE—Oxaliplatin
By TargetMol
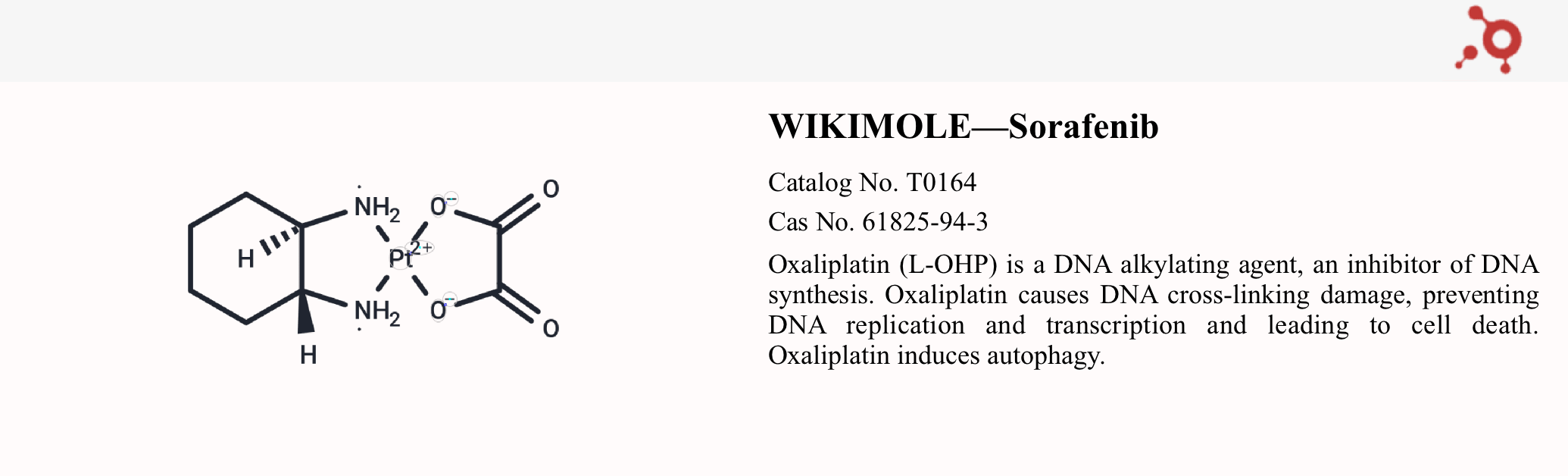
Oxaliplatin is a chemical drug widely used in cancer treatment. As a platinum-based anticancer drug, oxaliplatin has achieved significant success in treating various types of cancer, particularly colorectal cancer. Its primary mechanism of action is through forming cross-links with DNA, thereby inhibiting DNA replication and transcription, ultimately leading to cancer cell death. Due to its unique molecular structure, oxaliplatin has relatively low nephrotoxicity, but its neurotoxicity is more pronounced.
Mechanism of Action
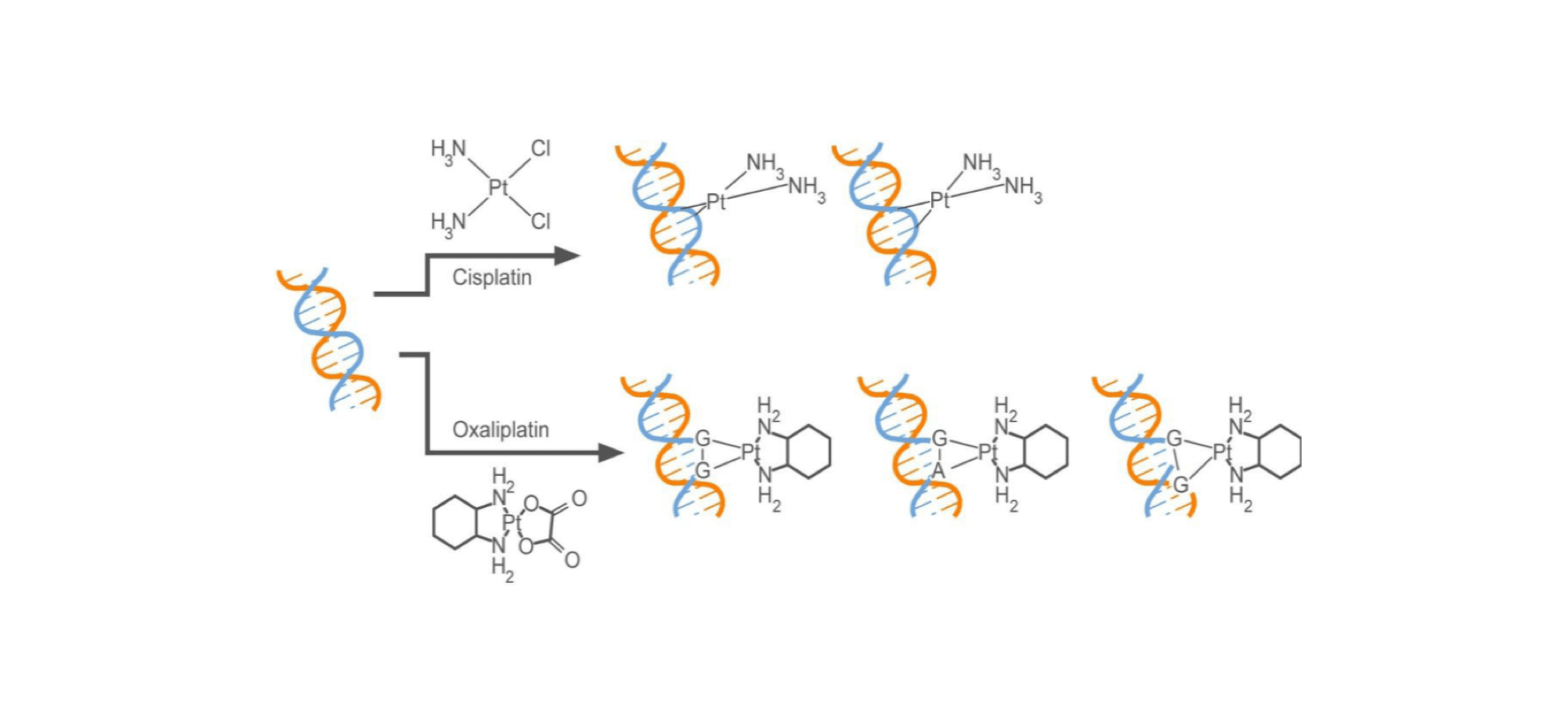
Oxaliplatin and cisplatin both belong to the class of platinum-based anticancer drugs and are widely used to treat various forms of cancer. Their primary mechanism of action is to form cross-links with DNA, thereby hindering DNA replication and transcription, ultimately inducing cell apoptosis. Unlike cisplatin and carboplatin, the DNA adducts formed by oxaliplatin are larger and more hydrophobic, making it more effective in inhibiting DNA synthesis. Additionally, the DACH ligand in oxaliplatin increases the size and hydrophobicity of the adducts, rendering them more stable and difficult to repair[1].
Application
In 2002, oxaliplatin passed clinical trials and received FDA approval as an anticancer drug for the treatment of colorectal cancer. As a new generation platinum compound, oxaliplatin, in combination with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and leucovorin, has significantly improved the survival rate of colorectal cancer patients. Additionally, oxaliplatin has shown efficacy against other types of cancer, including gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and breast cancer.
References
[1] Raymond E, Chaney SG, Taamma A, Cvitkovic E. Oxaliplatin: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. Ann Oncol. 1998 Oct;9(10):1053-71. doi: 10.1023/a:1008213732429. PMID: 9834817.
[2] Kline CL, El-Deiry WS. Personalizing colon cancer therapeutics: targeting old and new mechanisms of action. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2013 Aug 21;6(8):988-1038. doi: 10.3390/ph6080988. PMID: 24276379.
[3] Kelland L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007 Aug;7(8):573-84. doi: 10.1038/nrc2167. Epub 2007 Jul 12. PMID: 17625587.
Other Articles


Subscription to TargetMol News
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.