Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Article | 01 Feb 2024
WIKIMOLE—Ferrostatin & Deferoxamine mesylate
By TargetMol
Ferrostatin-1 T6500
Ferrostatin-1,also known as Ferrostatin 1 or Fer-1, is a selective ferroptosis inhibitor. It is a synthetically engineered antioxidant that prevents lipid membrane damage through a reduction mechanism, thereby inhibiting cell death.

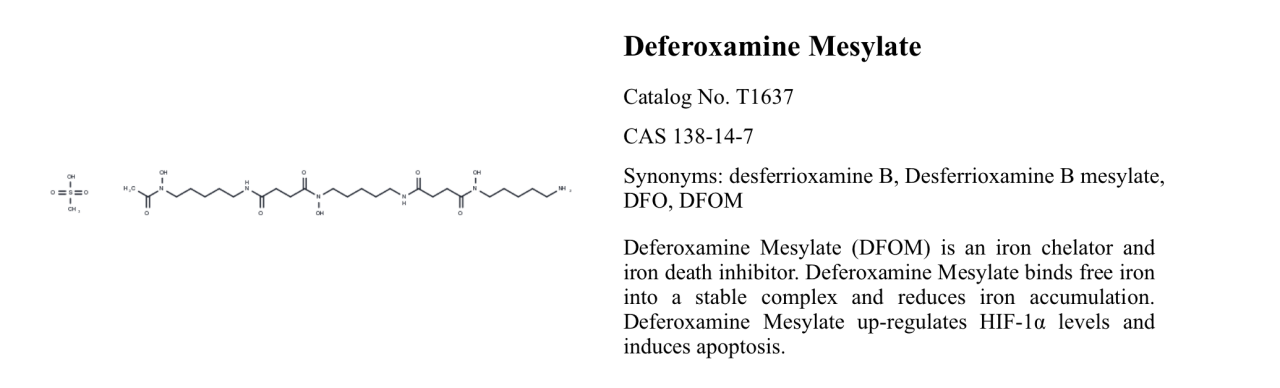
Deferoxamine mesylate T1637
Deferoxamine mesylate, also known as DFO, desferrioxamine, or desferoxamine mesylate, is an iron-chelating agent that binds to iron and several other metal cations. It is widely used to reduce the accumulation and deposition of iron in tissues, thereby suppressing cell death associated with iron overload.
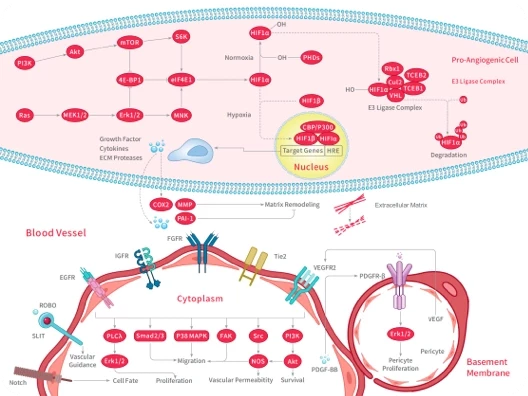
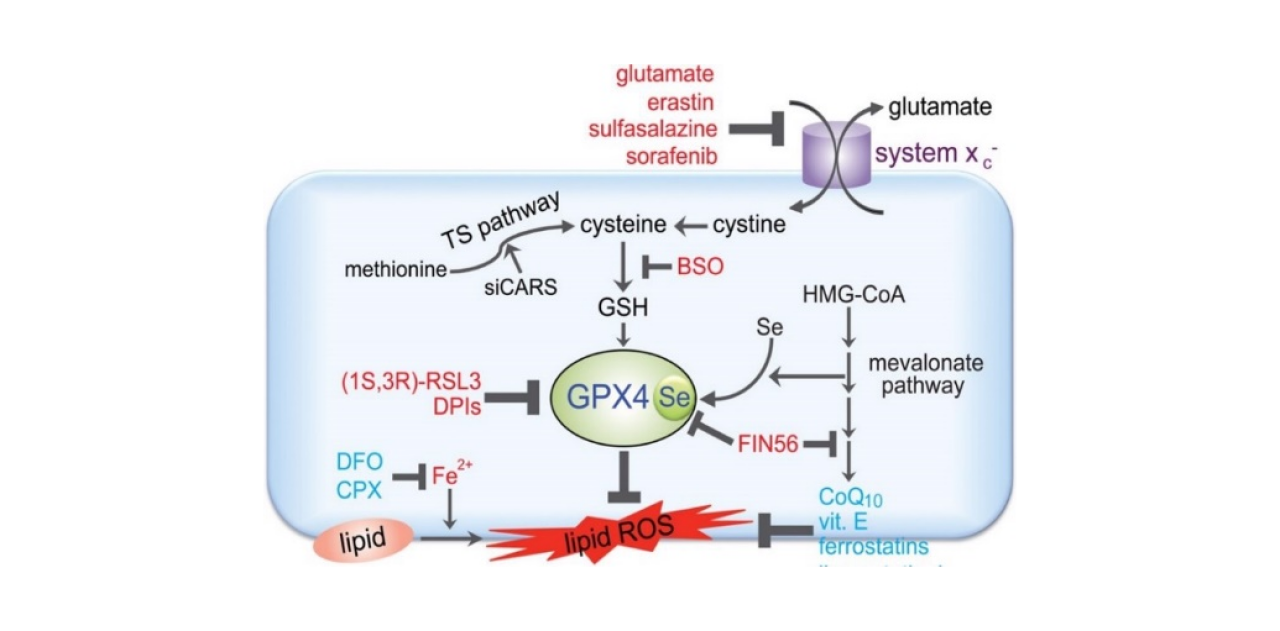
Mechanism of Action
Ferroptosis is a form of regulated cell death primarily caused by iron-dependent oxidative damage. Under physiological conditions, iron levels in cells are in dynamic equilibrium. Excessive iron ions can lead to cellular iron overload, characterized by the deposition of iron ions causing lipid peroxidation reactions and the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by iron metabolism. Ultimately, this results in cell death.
Ferroptosis can be inhibited by various small molecules, including Ferrostatin-1 and Deferoxamine mesylate. Ferrostatin-1, an antioxidant, inhibits cell ferroptosis by inducing the disappearance of lipid hydroperoxides through the generation of an anti-ferroptotic effect. Deferoxamine mesylate, on the other hand, is an iron-chelating agent that binds to iron ions, reducing the accumulation and deposition of iron in tissues and suppressing cell ferroptosis.
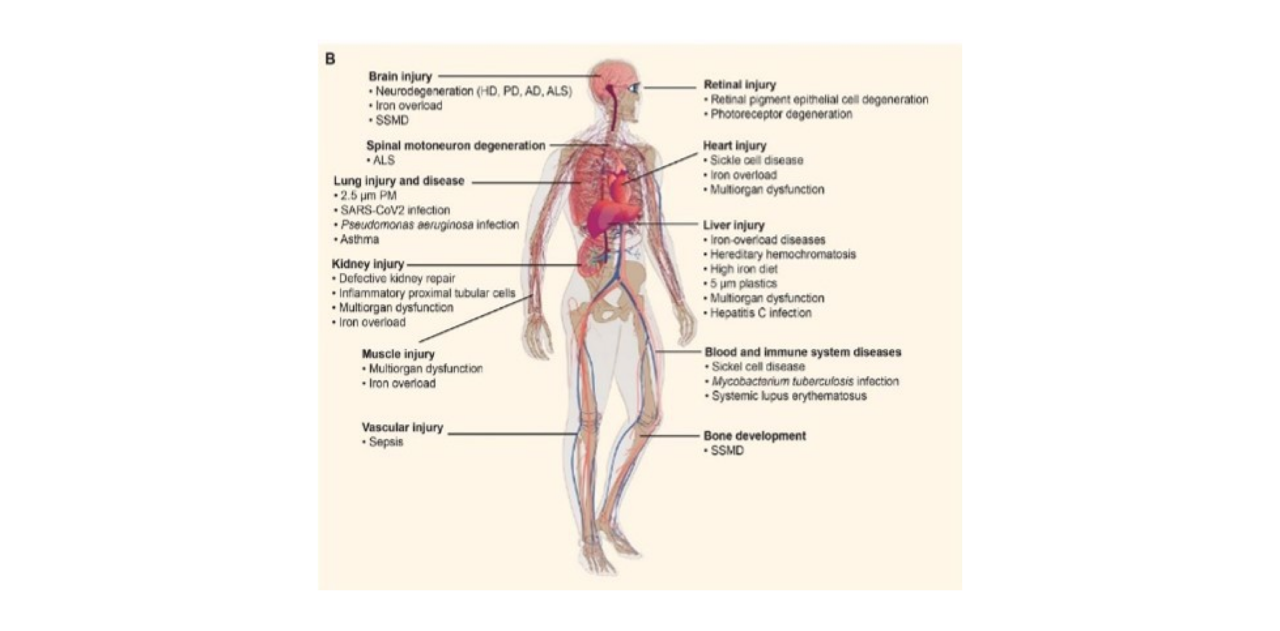
Biological Applications
Ferrostatin-1 and Deferoxamine mesylate, as inhibitors of ferroptosis, play crucial roles in regulating this iron-dependent form of cell death. Ferrostatin-1 regulates ferroptosis by influencing lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism, while Deferoxamine mesylate not only inhibits ferroptosis but also exhibits excellent antioxidant, anti-proliferative, and anti-tumor activities. Therefore, Deferoxamine mesylate is applicable to research in diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, as well as in anti-cancer and anti-COVID-19 studies. Abundant research indicates that modulating ferroptosis is pivotal in tumor suppression, immunity, neurodegenerative diseases, tissue and organ damage, as well as various inflammatory and infectious diseases.
Reference
[1] Miotto G, Rossetto M, Di Paolo ML, et al. Insight into the mechanism of ferroptosis inhibition by ferrostatin-1. Redox Biol. 2020;28:101328. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2019.101328
[2] Stockwell BR. Ferroptosis turns 10: Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell. 2022;185(14):2401-2421. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.003
[3] Xie J, Ye Z, Li L, et al. Ferrostatin?1 alleviates oxalate?induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury, fibrosis and calcium oxalate stone formation by inhibiting ferroptosis. Mol Med Rep. 2022;26(2):256. doi:10.3892/mmr.2022.12772
[4] Ni Z, Li Y, Song D, et al. Iron-overloaded follicular fluid increases the risk of endometriosis-related infertility by triggering granulosa cell ferroptosis and oocyte dysmaturity. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):579. Published 2022 Jul 4. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05037-8
[5] Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Other Articles


Subscription to TargetMol News
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.