Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
NEWS | 30 August 2024
WIKIMOLE—Bortezomib
By TargetMol
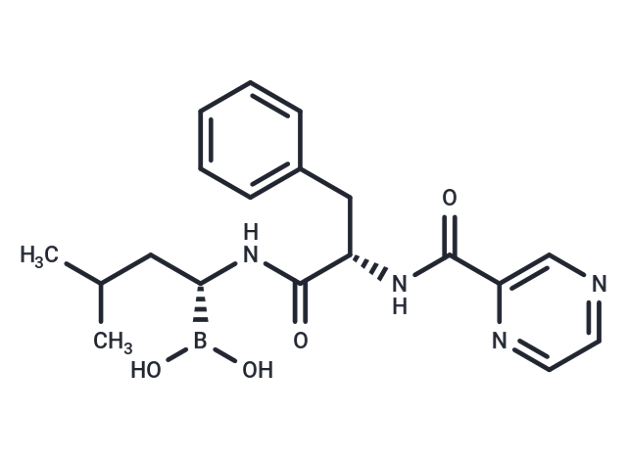
Bortezomibis a 20S proteasome inhibitor (Ki = 0.6 nM) with antitumor activity, capable of inhibiting NF-κB, disrupting the cell cycle, and inducing apoptosis[1].
It has been approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma and mantle cell lymphoma in patients who have undergone at least one prior therapy[2].
Mechanism of Action
-Proteasome Inhibition:
Bortezomib primarily functions by inhibiting the activity of the 26S proteasome. The 26S proteasome is responsible for degrading many intracellular proteins, especially those that are ubiquitinated, such as abnormal or unnecessary proteins. By inhibiting the proteasome, Bortezomib disrupts the normal degradation process of these proteins, leading to their accumulation within the cell.
-Impact on NF-κB Signaling Pathway:
The proteasome is crucial for the degradation of IκB in the NF-κB signaling pathway. Inhibiting the proteasome prevents the degradation of IκB, thereby inhibiting the activation and translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus, ultimately reducing the expression of genes it regulates, including those that promote cell survival and proliferation.
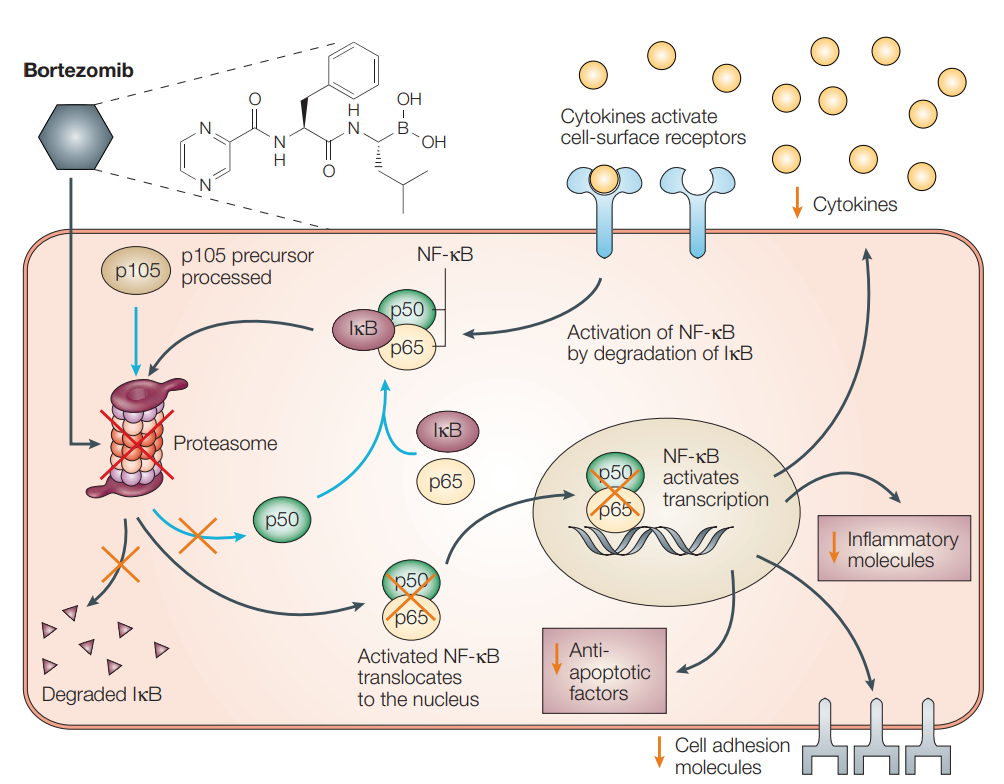
Bortezomib 和 NF-κB[5]
-Induction of Apoptosis:
Bortezomib can trigger apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells through various pathways, including the modulation of cell cycle regulatory proteins, apoptosis-related proteins, and oxidative stress levels.
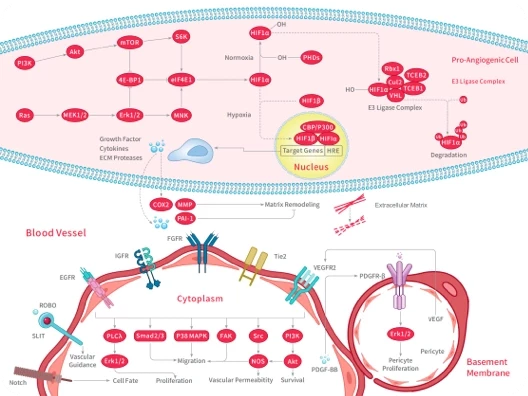
-Anti-Angiogenic Effects:
By inhibiting the production of specific growth factors, such as VEGF, Bortezomib can reduce the formation of new blood vessels around tumors, thereby limiting tumor growth and development.
-Immunomodulation:
Bortezomib can also indirectly combat tumor cells by affecting the function of the immune system, such as by enhancing the activity of natural killer (NK) cells and T cells.
Application
-Anti-Tumor Research
Cancer Therapy Target Validation: Used to validate the effectiveness of the proteasome as a potential target for cancer therapy.
Drug Screening and Optimization: By assessing the combined effects of Bortezomib with other compounds, new anti-cancer drugs can be screened or existing drug combinations optimized.
Drug Resistance Research: Investigate the mechanisms of tumor cell resistance to Bortezomib, providing strategies to overcome resistance.
Drug Development and Screening: Through modification and optimization of Bortezomib's structure and activity, new proteasome inhibitors with higher activity and lower side effects can be developed.
Drug Interaction Studies: Evaluate the potential of Bortezomib in combination therapy by studying its interactions with other drugs.
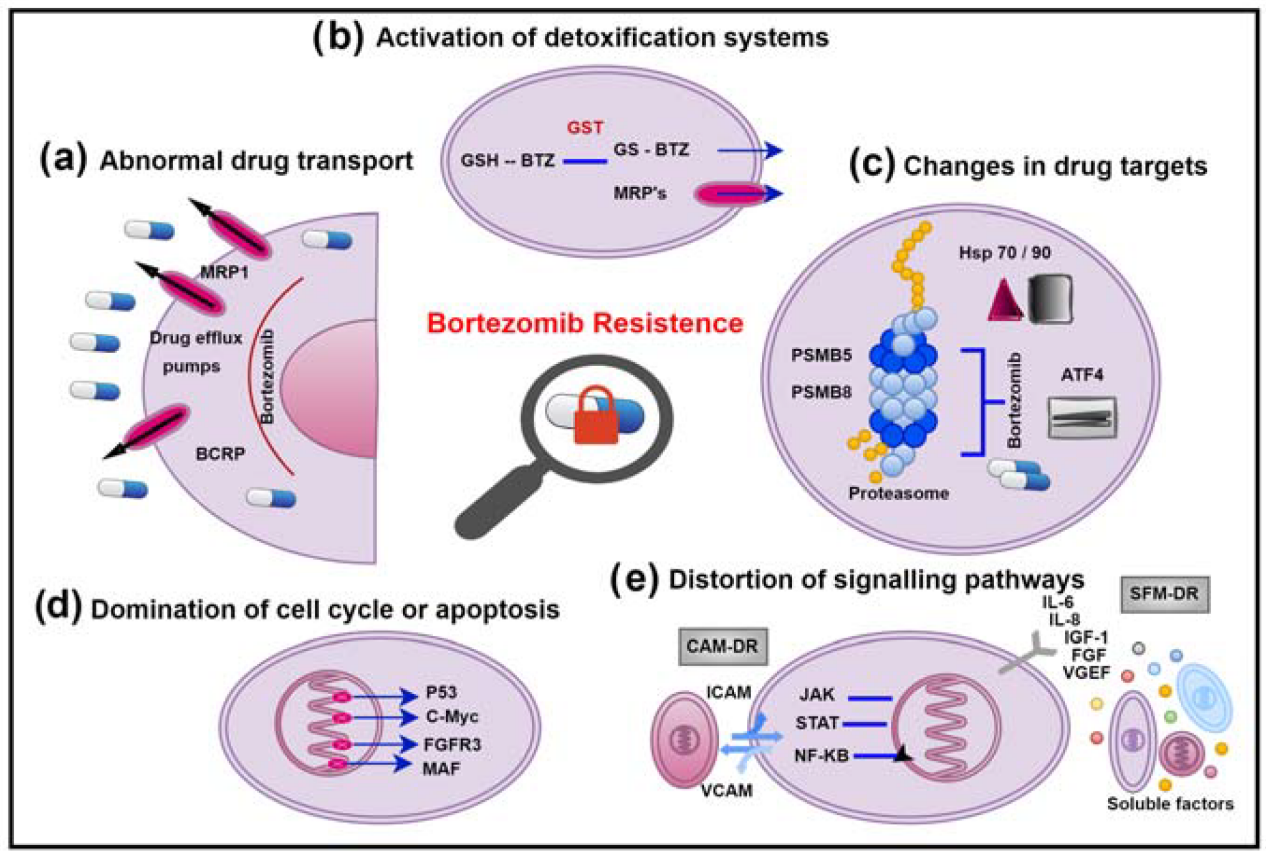
Bortezomib resistance mechanisms in MM.[6]
-Mechanism Research
Signaling Pathway Research: Bortezomib can inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is significant for studying inflammation, immune responses, and tumor development.
Gene Expression Regulation: By affecting the stability of transcription factors, Bortezomib can help scientists understand the mechanisms of gene expression regulation.
Protein Degradation Regulation: As a proteasome inhibitor, Bortezomib can block the degradation of proteins within cells, leading to the accumulation of proteins that regulate the cell cycle and apoptosis, such as p53, Bid, Bax, p21, and p27, thereby affecting tumor cell growth and survival.
-Disease Model Construction
In Vitro Models: Used to construct in vitro models of hematologic malignancies such as multiple myeloma and lymphoma.
In Vivo Models: Construct animal models to study the development of diseases and the effects of treatments.
-Immunology Research
Immunomodulatory Effects: Since Bortezomib can affect the function of immune cells, it can be used to study immunoregulatory mechanisms.
References
[1]Bonvini P, et al. Bortezomib-mediated 26S proteasome inhibition causes cell-cycle arrest and induces apoptosis in CD-30+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Leukemia. 2007 Apr;21(4):838-42.
[2]Scott K, et al. Bortezomib for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 20;4(4):CD010816.
[3]Cvek B, Dvorak Z. The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) and the mechanism of action of Bortezomib. Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(15):1483-99.
[4]Piperdi B, Ling YH, Liebes L, Muggia F, Perez-Soler R. Bortezomib: understanding the mechanism of action. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Nov;10(11):2029-30.
[5]Paramore, A., Frantz, S. Bortezomib. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2, 611–612 (2003).
[6]Kozalak G, et al. Review on Bortezomib Resistance in Multiple Myeloma and Potential Role of Emerging Technologies. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;16(1):111.
Other Articles


Subscription to TargetMol News
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.