Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Article | 01 Mar 2024
WIKIMOLE—Durlobactam
By TargetMol
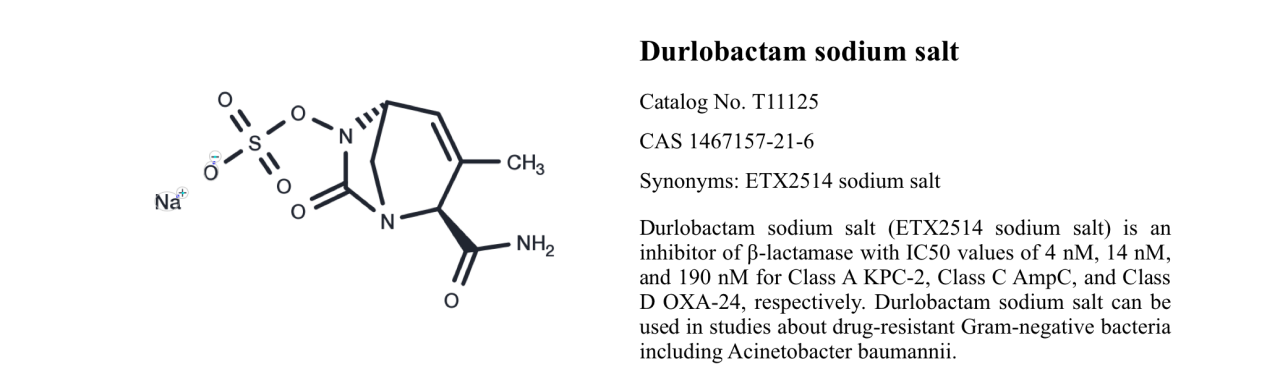
Durlobactam sodium salt, catalog number T11125, is the sodium salt form of Durlobactam, also known as ETX2514, Duobatan sodium, and Durobatan sodium. It is a beta-lactamase inhibitor with varying degrees of inhibition against beta-lactamases of classes A, C, and D. Durlobactam sodium salt can be used for research on multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, including Acinetobacter baumannii.
About β-lactamases
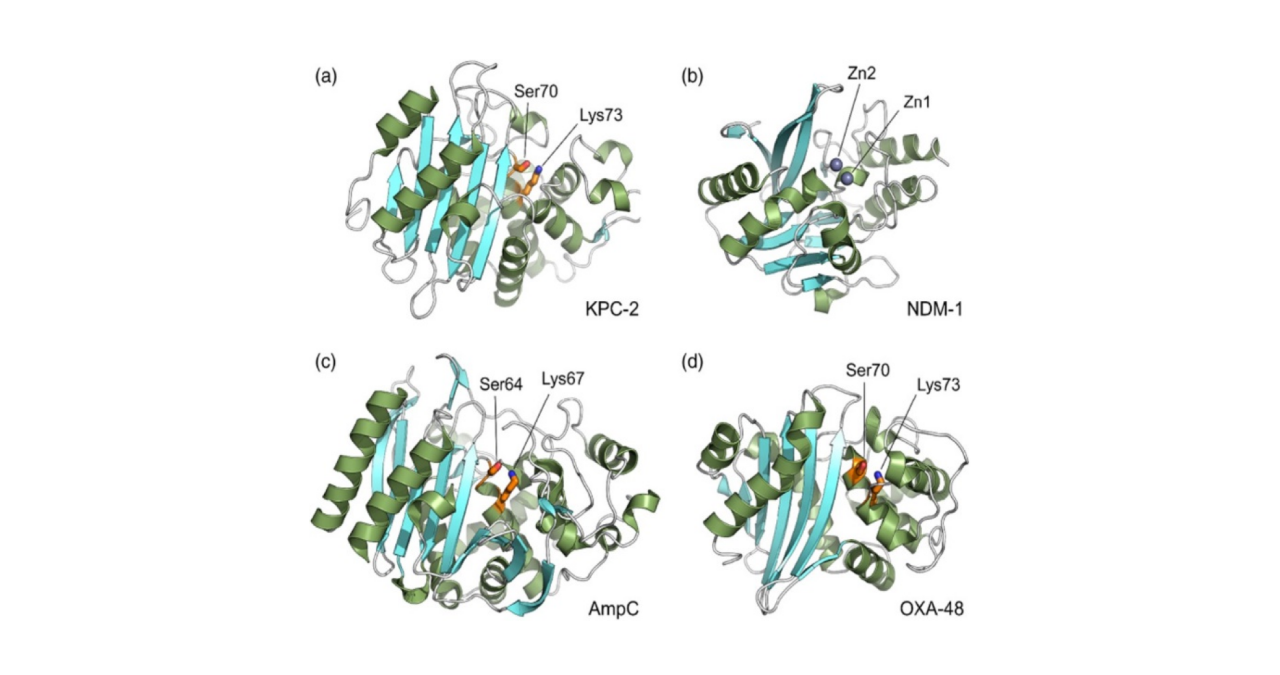
Beta-lactamases are enzymes produced by certain bacteria, categorized into four classes (A, B, C, and D). These enzymes contribute to bacterial multidrug resistance by inactivating beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, and carbapenems. Beta-lactam antibiotics constitute a widely used class of antibiotics characterized by a common four-membered core structure known as a beta-lactam ring. Beta-lactamases hydrolyze the beta-lactam ring, rendering the antibiotics ineffective and leading to bacterial resistance.
Gram-negative bacteria commonly produce beta-lactamases, and clinically relevant organisms include members of the Acinetobacter–Calcoaceticus–Baumannii (ACB) complex. The rapid acquisition of multidrug resistance, encompassing fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, and carbapenems, by the ACB complex limits therapeutic options, posing a significant global public health threat. The development of drugs targeting such bacteria is of crucial clinical importance.
Clinical research
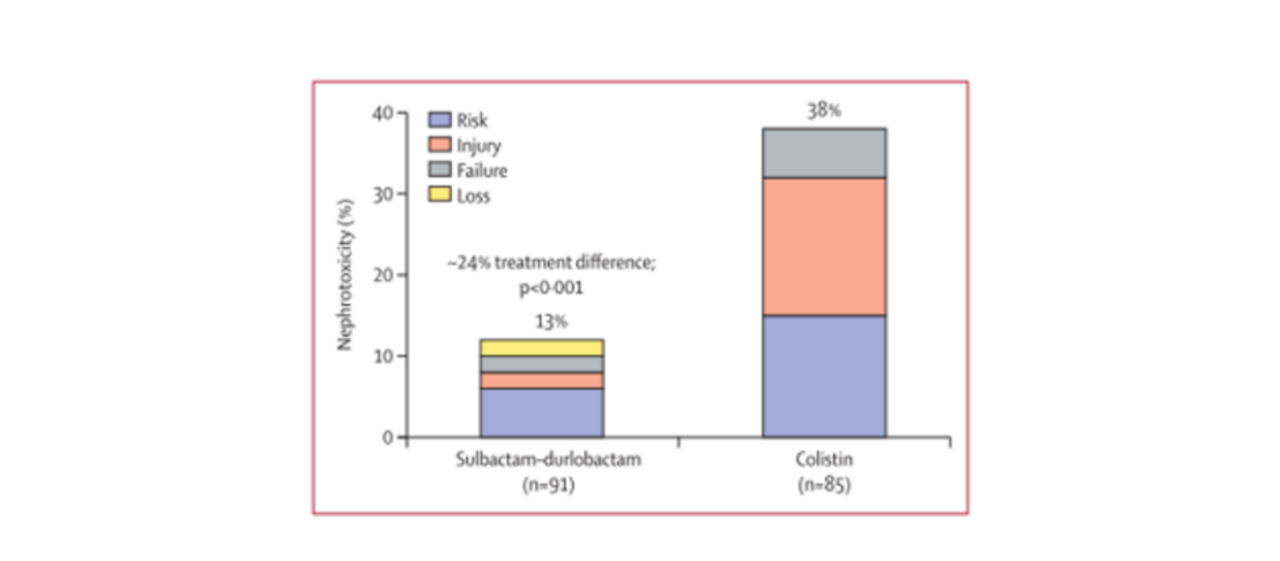
In the Phase 3 clinical trials of Sulbactam/Durlobactam, the effectiveness and safety of Sulbactam/Durlobactam in comparison to the combination of Imipenem-Cilastatin-Relebactam (ICR) with Colistin were evaluated for the treatment of severe infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (ABC).
The study randomized 181 patients, with 125 patients confirmed to have carbapenem-resistant ABC strains included in the primary efficacy analysis. In the Sulbactam/Durlobactam group of 63 patients, the 28-day all-cause mortality rate was 12 cases (19%), while in the Colistin group of 62 patients, it was 20 cases (32%). The incidence of renal toxicity was significantly lower in the Sulbactam/Durlobactam group compared to Colistin (as shown in the figure below), and the incidence of severe adverse events was also lower in the Sulbactam/Durlobactam group than the Colistin group.
Reference
[1] Tooke CL, Hinchliffe P, Bragginton EC, et al. β-Lactamases and β-Lactamase Inhibitors in the 21st Century. J Mol Biol. 2019;431(18):3472-3500. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2019.04.002
[2] Keam SJ. Sulbactam/Durlobactam: First Approval. Drugs. 2023;83(13):1245-1252. doi:10.1007/s40265-023-01920-6
[3] Kaye KS, Shorr AF, Wunderink RG, et al. Efficacy and safety of sulbactam-durlobactam versus colistin for the treatment of patients with serious infections caused by Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex: a multicentre, randomised, active-controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority clinical trial (ATTACK). Lancet Infect Dis. 2023;23(9):1072-1084. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00184-6
Other Articles


Subscription to TargetMol News
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.