- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Suramin Sodium Salt
Suramin Sodium Salt (BAY-205) is a sodium salt form of suramin, a polysulphonated naphthylurea with potential antineoplastic activity. Suramin blocks the binding of various growth factors, including insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), epidermal growth factor (EGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and tumor growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), to their receptors, thereby inhibiting endothelial cell proliferation and migration. This agent also inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)- and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)-induced angiogenesis; retroviral reverse transcriptase; uncoupling of G-proteins from receptors; topoisomerases; cellular folate transport; and steroidogenesis.
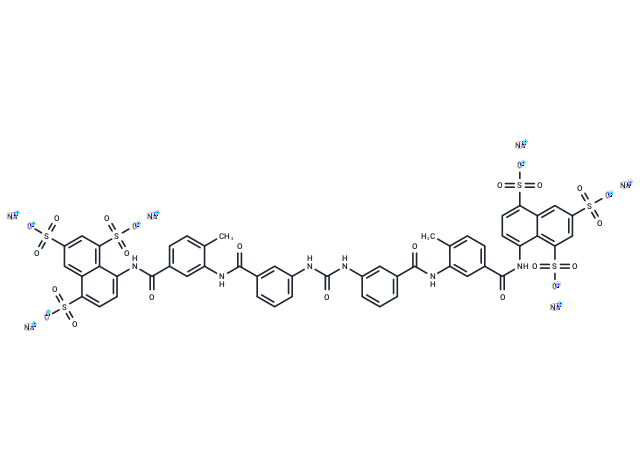
Suramin Sodium Salt
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $145 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $247 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $369 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $554 | In Stock |
Product Introduction
| Description | Suramin Sodium Salt (BAY-205) is a sodium salt form of suramin, a polysulphonated naphthylurea with potential antineoplastic activity. Suramin blocks the binding of various growth factors, including insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), epidermal growth factor (EGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and tumor growth factor-beta (TGF-beta), to their receptors, thereby inhibiting endothelial cell proliferation and migration. This agent also inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)- and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF)-induced angiogenesis; retroviral reverse transcriptase; uncoupling of G-proteins from receptors; topoisomerases; cellular folate transport; and steroidogenesis. |
| Targets&IC50 | DNA topo II:5 μM |
| In vitro | Suramin inhibits cell proliferation and DNA synthesis in cultured HeLa cells. The replication of SV40 DNA is completely abolished by 40 μM suramin. DNA polymerase α is sensitive to lower concentrations of suramin (IC50=8 μM) than is DNA polymerase δ (IC50=36 μM), whereas DNA polymerase β is relatively insensitive to the drug (IC50 of 90 μM)[1]. Suramin is a potent inhibitor of DNA strand exchange and ATPase activities of bacterial RecA proteins. Suramin inhibits RecA-catalysed proteolytic cleavage of the LexA repressor. The mechanism underlying such inhibitory actions of suramin involves its ability to disassemble RecA–single-stranded DNA filaments[2]. Suramin is a potent inhibitor of the nuclear enzyme DNA topoisomerase II. Suramin inhibits purified yeast topoisomerase II with an IC50 of about 5 μM[3]. |
| In vivo | Treatment with suramin shows lower values for pulmonary artery pressure, right ventricular hypertrophy, and distal vessel muscularization on day 21 compared to control rats. Suramin treatment suppresses PA-SMC proliferation and attenuates both the inflammatory response and the deposition of collagen[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | The ATPase assay is performed in a 10 μL reaction mixture containing 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 1 mM DTT, 8 mM MgCl2, 5 μM M13 circular ssDNA, 2.5 μM RecA from the specified bacterial species and increasing concentrations of suramin. The reaction is initiated by the addition of 2 mM [α-32P]ATP, incubated for 30 min at 37°C and stopped by the addition of 25 mM EDTA[2]. |
| Alias | Suramin hexasodium salt, NF-060, BAY-205 |
| Molecular Weight | 1429.15 |
| Formula | C51H34N6Na6O23S6 |
| Cas No. | 129-46-4 |
| Smiles | [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].Cc1ccc(cc1NC(=O)c1cccc(NC(=O)Nc2cccc(c2)C(=O)Nc2cc(ccc2C)C(=O)Nc2ccc(c3cc(cc(c23)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)c1)C(=O)Nc1ccc(c2cc(cc(c12)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (34.99 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sci Citations
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Dose Conversion
Tech Support
Keywords

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.



