High-Standard Entry Criteria
TargetMol's Bioactive Compounds Library Max is established upon rigorous entry standards to ensure that every compound included is structurally well-defined and of exceptional purity, verified through multiple analytical techniques such as NMR, HPLC, and LC-MS. Our multi-layered screening mechanism effectively eliminates compounds with ambiguous structures, such as mixtures and polymers. Moreover, we specifically exclude substances like sunscreens, contrast agents, dyes, fragrances, plastic additives, and intermediates—compounds typically lacking biological activity due to their specificity and stability, which generally prevent interactions with biological systems. This meticulous curation reduces time and resource waste caused by ineffective screenings.
To further enhance hit rates in activity screening, we have introduced TargetMol’s exclusive novel compounds (Part B), all of which have well-defined targets and have undergone activity testing at both cellular and protein levels.
Significant Structural Diversity
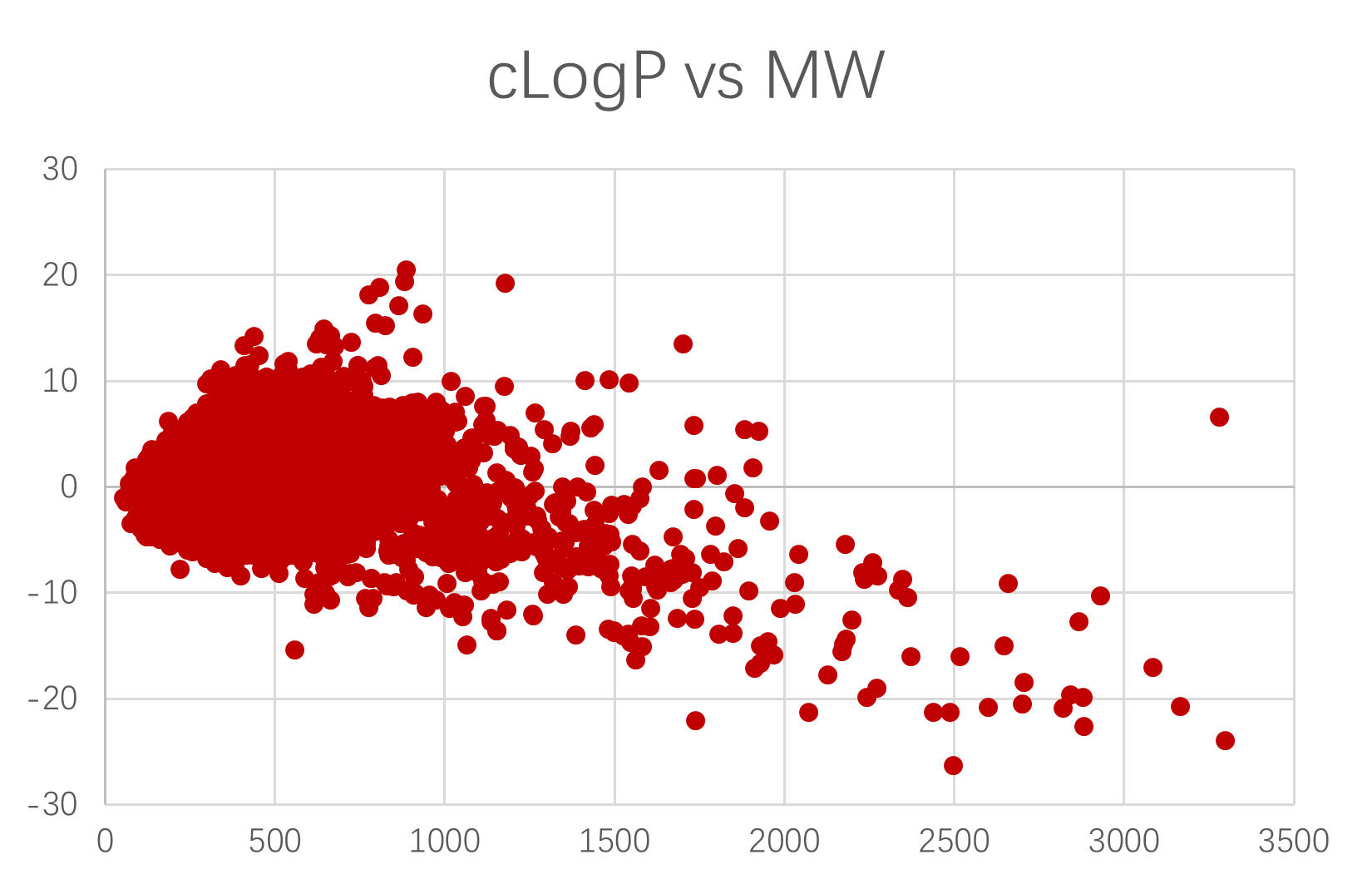
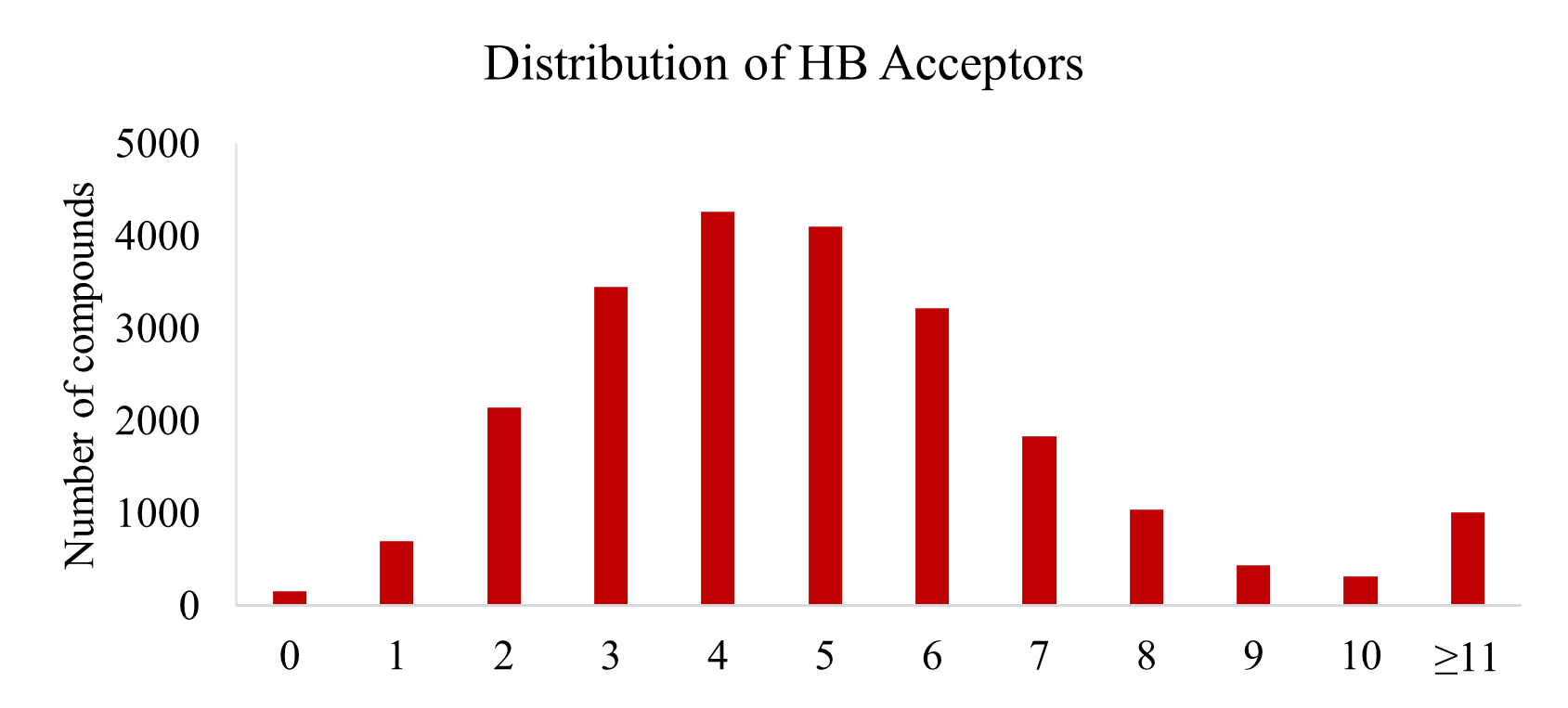
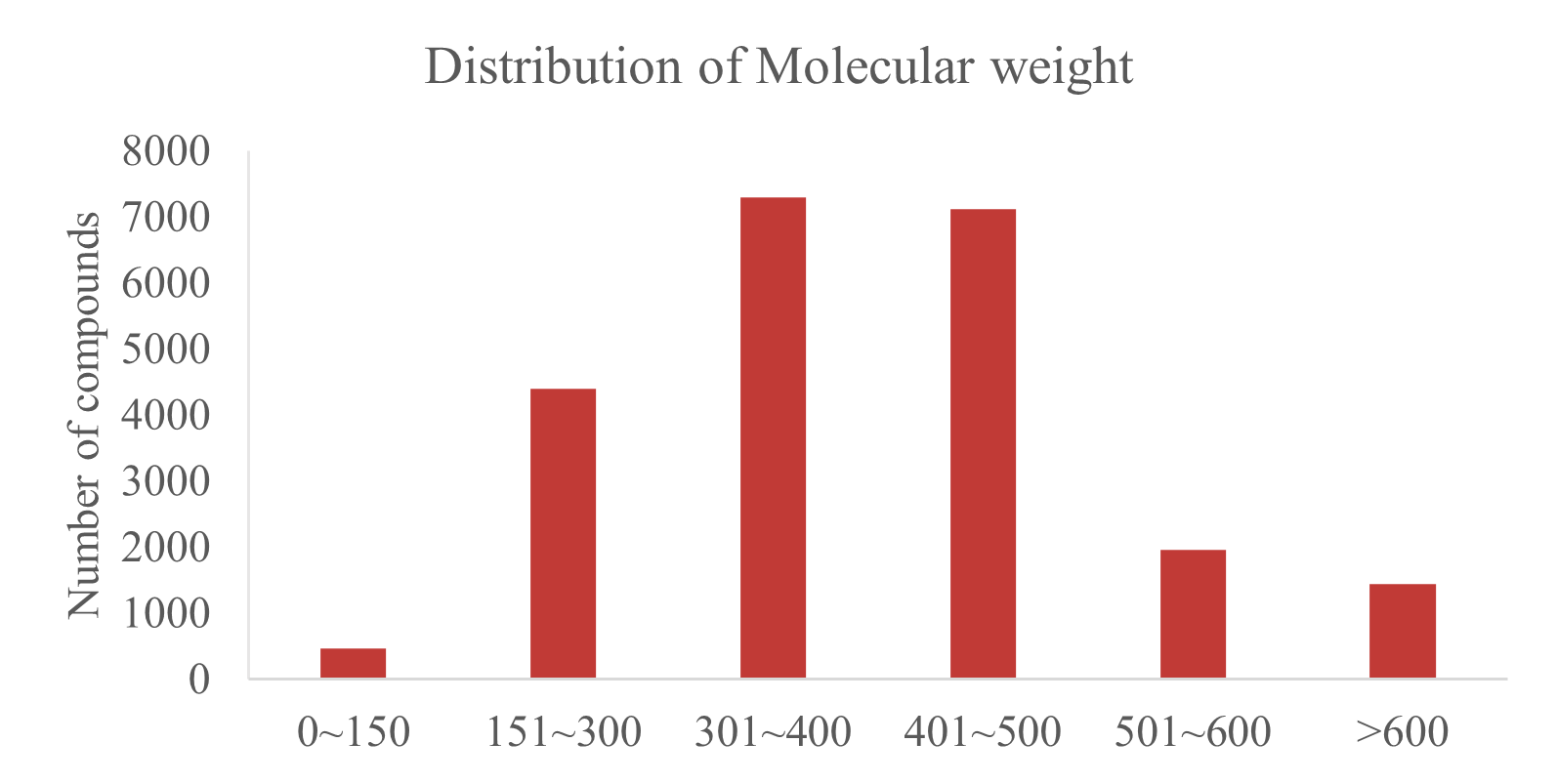
TargetMol’s Bioactive Compounds Library Max features extensive scaffold diversity and structural complexity, offering a substantial advantage in drug discovery. Based on the Bemis-Murcko scaffold classification, our library is categorized into 15,111 unique classes, each representing a distinct molecular scaffold, thereby extensively covering a broad chemical space. The compounds range from simple to highly complex structures, providing a diverse foundation for identifying lead compounds with strong affinity and specificity toward target proteins. This structural richness significantly advances pharmaceutical innovation. Whether targeting traditional drug targets or emerging, more challenging ones, our Bioactive Compounds Library Max offers a wealth of candidate molecules to accelerate the drug development process.
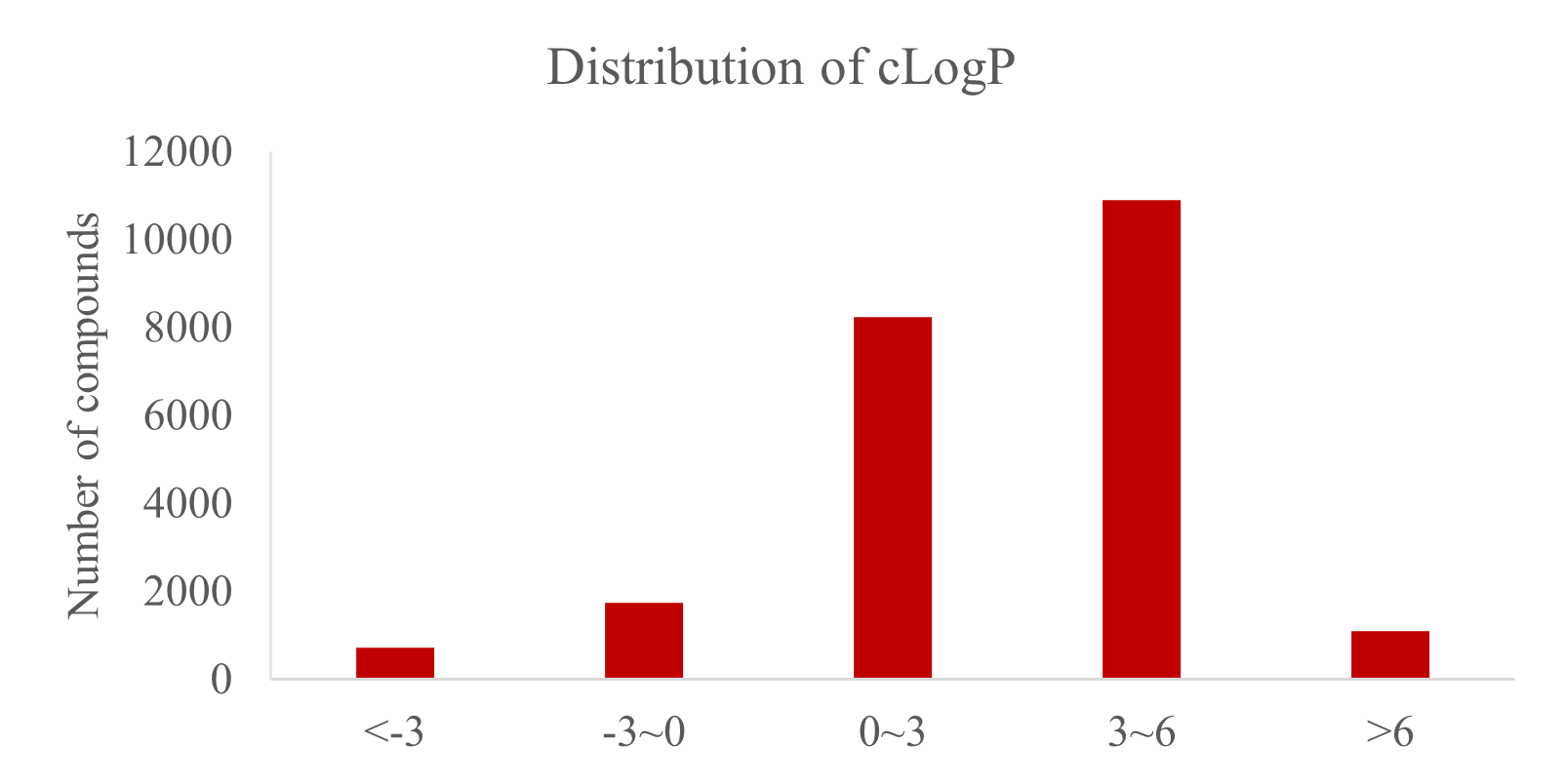
Library Diversity Analysis
Superior Drug-Like Properties
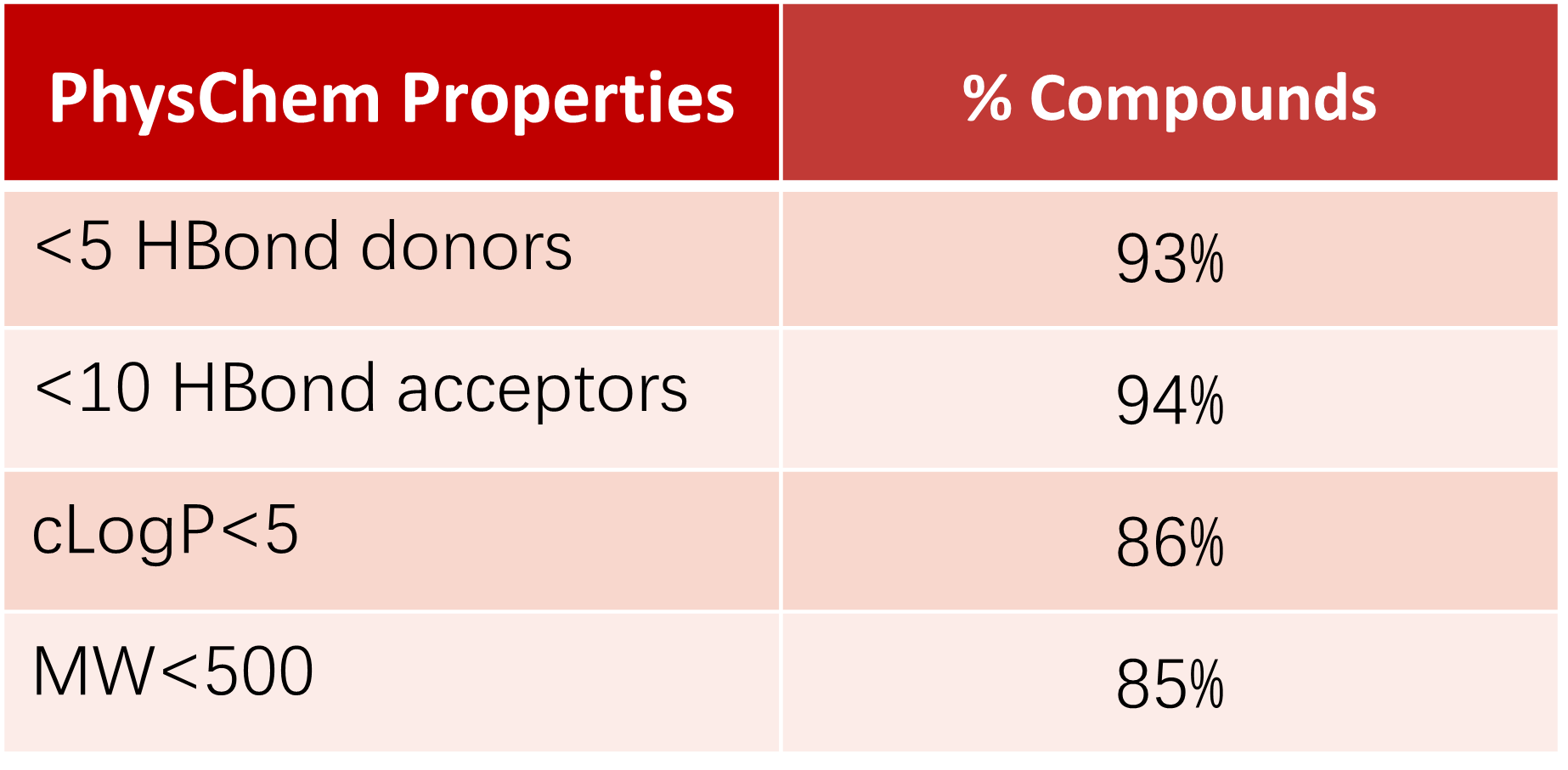
73% of the compounds in TargetMol's Bioactive Compounds Library Max comply with Lipinski’s "Rule of Five" (Ro5), indicating excellent bioavailability and permeability.
Multidimensional Pharmacokinetic Analysis
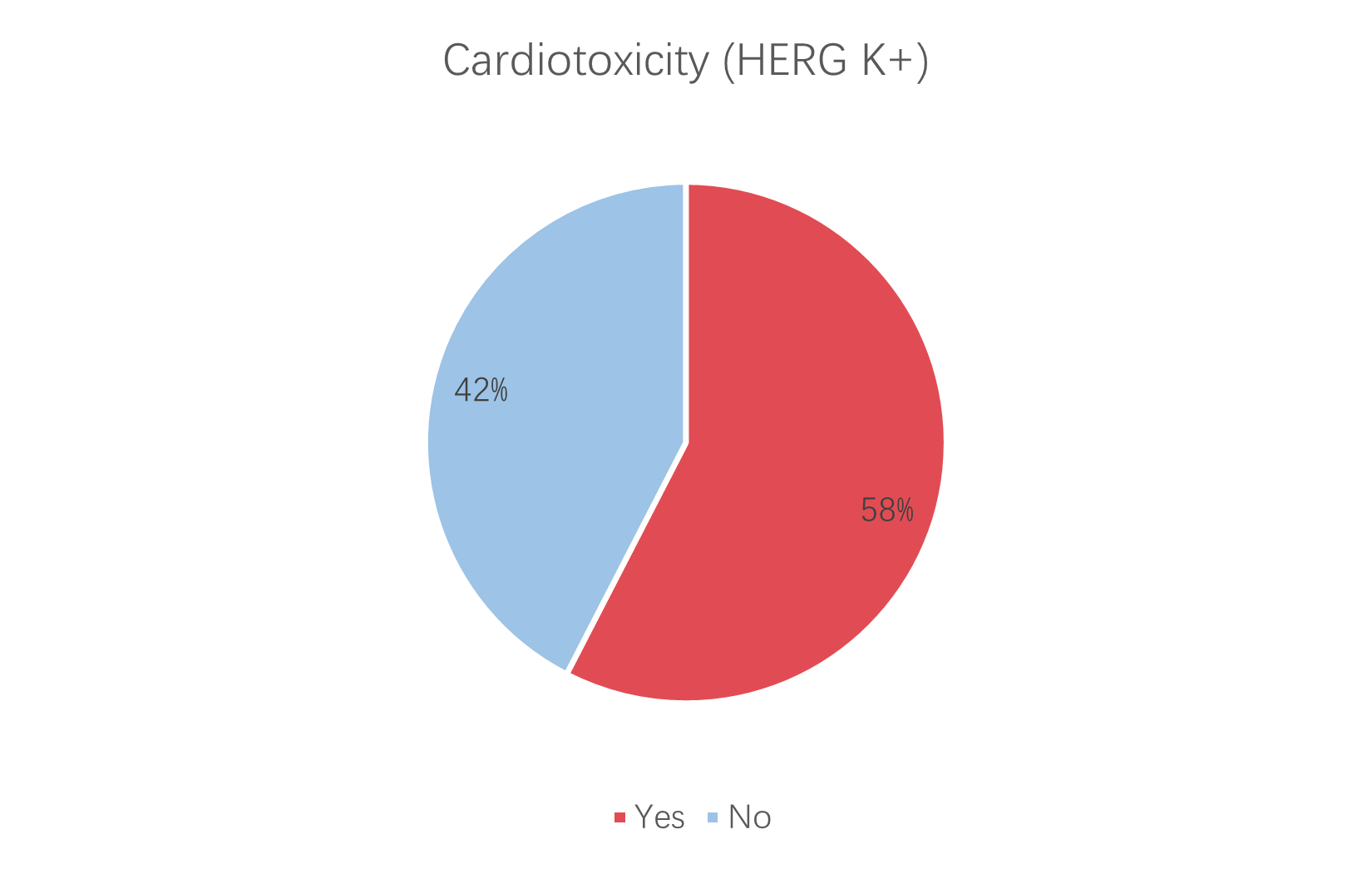
A multidimensional evaluation is conducted on TargetMol’s Bioactive Compounds Library Max, which systematically analyzes three key pharmacological parameters: blood-brain barrier permeability, cardiotoxicity (HERG K+ channel inhibition), and oral absorption performance.
15% of the compounds can cross the blood-brain barrier, while 85% cannot.
58% of the compounds exhibit cardiotoxicity, while 42% do not.
60% of the compounds are highly orally absorbable, 28% are orally absorbable, and 12% are poorly orally absorbable.
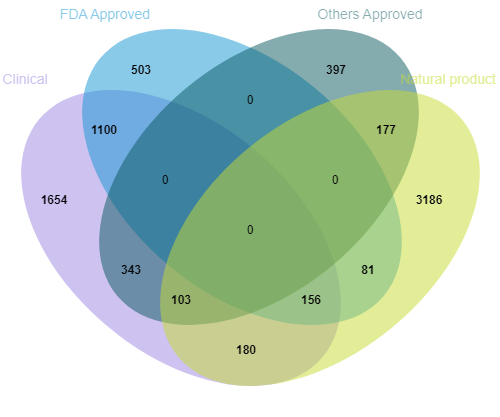
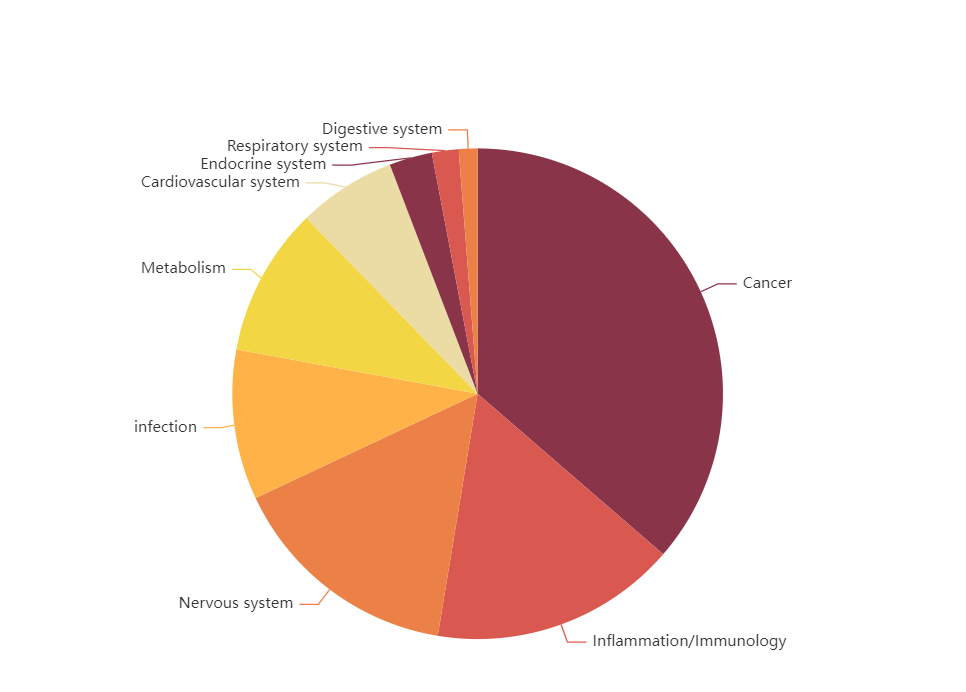
Diverse Compound Collection
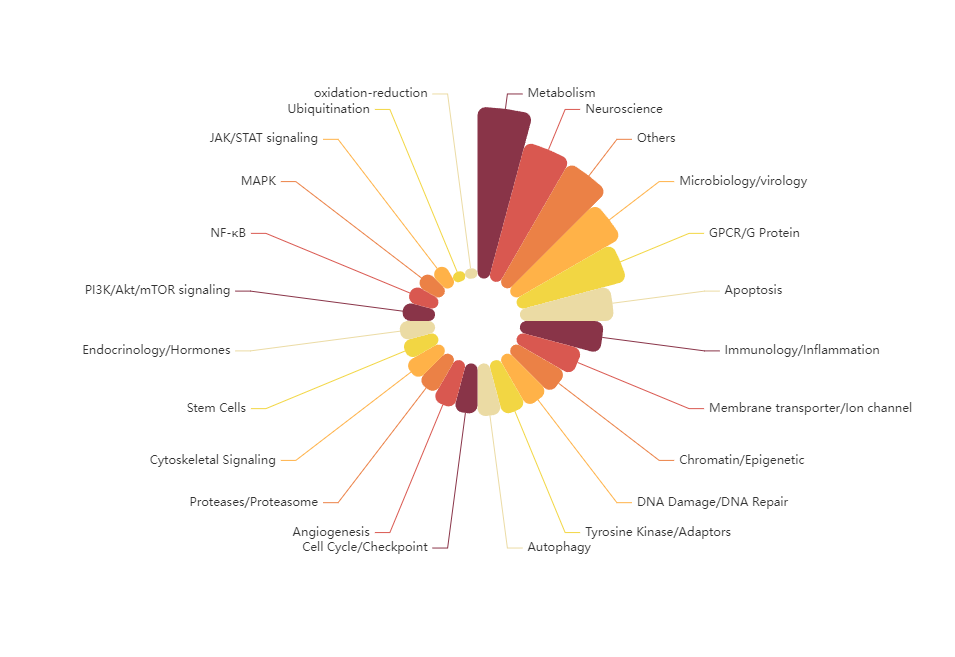
TargetMol’s Bioactive Compounds Library Max encompasses a wide range of molecule types with diverse biological activities. This includes approved drugs, clinical trial candidates, literature-reported bioactive compounds, and molecules capable of eliciting responses at the cellular, tissue, or even whole-organism level. The library covers not only major signaling pathways and targets but also many emerging therapeutic targets. The Bioactive Compounds Library Max (L4010) is established upon the classic L4000 library by adding approximately 300 new targets, bringing the total to nearly 900 targets across about 4,000 receptors. This significantly enhances the likelihood of successful screening hits. The library spans a broad spectrum of therapeutic areas, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders.
Regular Updates to Compound Libraries
We ensure our compound libraries remain at the forefront of scientific research by regularly updating our database with compounds mentioned in cutting-edge literature and newly custom-synthesized compounds.
Flexible Packaging Options
We offer a variety of standard packaging sizes (e.g., 30 μL, 50 μL, 100 μL, 250 μL, 1 mg), and we can customize packaging solutions to meet specific needs.
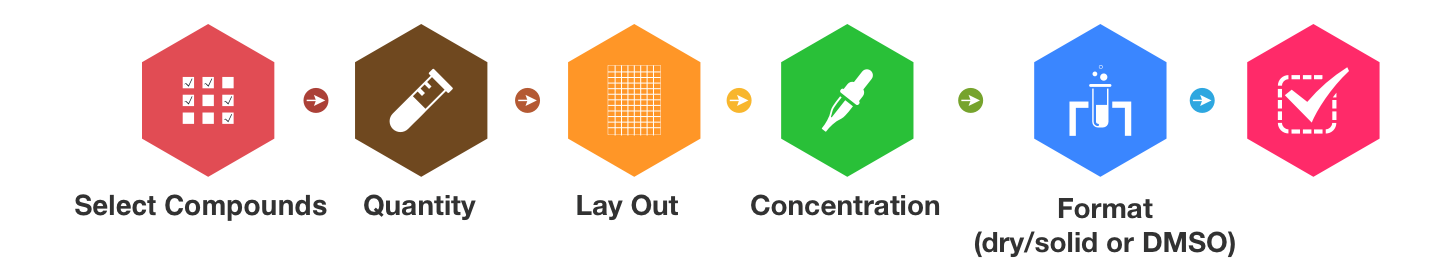
Customized Services
To support specific needs, we offer tailored screening services, including the design and synthesis of customized compound libraries and the execution of personalized screening projects. Our highly flexible service model is designed to efficiently meet unique needs of scientists and accelerate breakthrough discoveries.
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty