Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

R406 free base (R406 (free base)) is a potent Syk inhibitor.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $64 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $98 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $197 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $355 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $563 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,180 | In Stock |
| Description | R406 free base (R406 (free base)) is a potent Syk inhibitor. |
| Targets&IC50 | Syk:41 nM |
| In vitro | Oral administration of R406 to mice with immune complex-induced inflammatory responses significantly inhibited the cutaneous reverse passive Arthus reaction, with treatments at 1 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg yielding suppression rates of 72% and 86% respectively, compared to the control group. Furthermore, treatment with 10 mg/kg R406 in mice pre-treated with collagen antibodies markedly reduced inflammation and swelling, diminished progressive arthritis to a lower level, and delayed the onset in the K/BxN serum transfer mouse model, reducing clinical arthritis severity by 50%. |
| In vivo | Treatment with R406 at concentrations of 1 μM or 4 μM induces caspase 9 and 3 activation in DLBCL cell lines, leading to significant cell apoptosis without activating caspase 8. R406 selectively inhibits the Syk-dependent signaling pathways in various cells, demonstrating superior efficacy with EC50 values ranging from 33 nM to 171 nM compared to its effect on Syk-independent pathways. It effectively inhibits cell proliferation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cell lines, with EC50 values between 0.8 μM to 8.1 μM. Pre-treatment with R406 completely blocks phosphorylation of SYK525/526 and SYK-dependent phosphorylation of BLNK post B-cell receptor (BCR) cross-linking in R406-sensitive DLBCL. Additionally, after 24 and 48 hours of R406 treatment, MMP-9 mRNA levels significantly reduced by 2.8 and 4.3 times, respectively, compared to control groups, thereby decreasing the invasiveness of RL cells. |
| Kinase Assay | In-vitro Fluorescence Polarization Kinase Assays: R406 is serially diluted in DMSO and then diluted to 1% DMSO in kinase buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0.1 mg/mL acetylated BGG). ATP and substrate in kinase buffer are added at room temperature, resulting in a final DMSO concentration on 0.2%. The kinase reactions are performed in a final volume of 20 μL containing 5 μM HS1 peptide substrate and 4 μM ATP and started by addition of 0.125 ng of Syk in kinase buffer. The reaction is allowed to proceed for 40 minutes at room temperature. The reaction is stopped by the addition of 20 μL of PTK quench mix containing EDTA/anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (1X final)/fluorescent phosphopeptide tracer (0.5X final) diluted in FP Dilution Buffer. The plate is incubated for 30 minutes in the dark at room temperature and then read on a Polarion fluorescence polarization plate reader. Data are converted to amount of phosphopeptide present using a calibration curve generated by competition with the phosphopeptide competitor provided in the Tyrosine Kinase Assay Kit. For IC50 determination, R406 is tested at eleven concentrations in duplicate and curve-fitting is performed by non-linear regression analysis using Prism GraphPad Software. |
| Cell Research | DLBCL cell lines are treated with serial dilutions of R406 (0.3, 0.6, 1.25, 2.5, or 5 μM) for 72 or 96 hours. Thereafter, cellular proliferation is determined by MTT assay, and cell apoptosis is assessed by using annexin V–FITC/propidium iodide (PI) staining. For the determination of caspase 9, 8, and 3, cells are lysed, size-fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), and immunoblotted. (Only for Reference) |
| Alias | R406 (free base) |
| Molecular Weight | 470.45 |
| Formula | C22H23FN6O5 |
| Cas No. | 841290-80-0 |
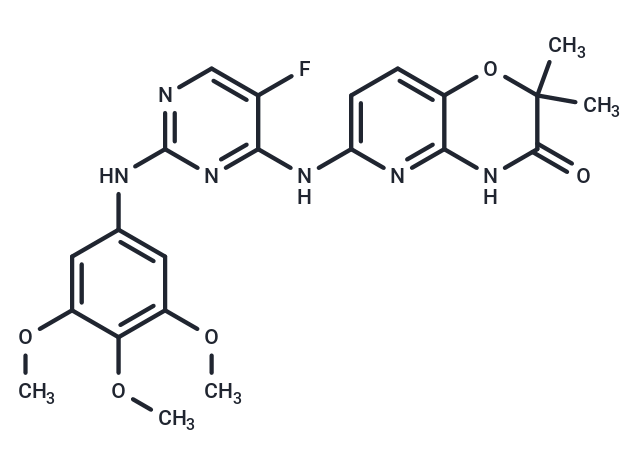
| Smiles | COc1cc(Nc2ncc(F)c(Nc3ccc4OC(C)(C)C(=O)Nc4n3)n2)cc(OC)c1OC |
| Relative Density. | 1.358 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 4.71 mg/mL (10 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.