 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

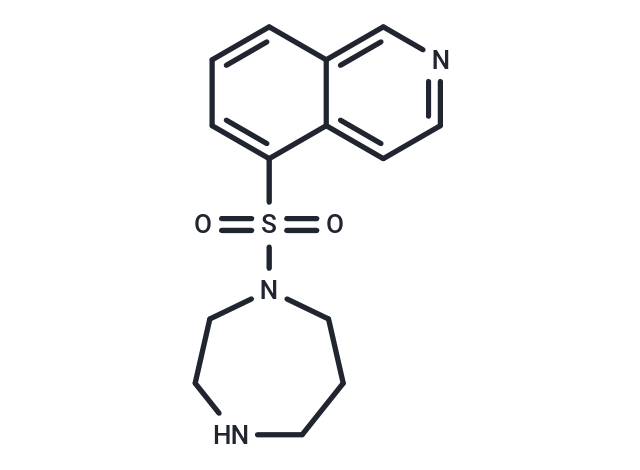
Fasudil (HA-1077) is a potent inhibitor of ROCK1, PKA, PKC, and MLCK.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $33 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $45 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $62 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $107 | - | In Stock |
| Description | Fasudil (HA-1077) is a potent inhibitor of ROCK1, PKA, PKC, and MLCK. |
| Targets&IC50 | MLCK:55 μM(Ki), ROCK1:0.33 μM(Ki), PKC:9.3 μM(Ki), PKA:1.0 μM(Ki), PKG:1.65 μM, ROCK2:0.158 μM |
| In vitro | Fasudil (Hydrochloride) has vasodilatory action and occupies the adenine pocket of the ATP-binding site of the enzyme[1]. Fasudil is a class of calcium antagonists. Fasudil produces a competitive inhibition of the Ca2+-induced contraction of the depolarized rabbit aorta. Fasudil is able to inhibit contractile responses to KCl, phenylephnne (PHE) and prostaglandin (PG) F2a[2]. Fasudil also exhibits vasodilator actions by inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline, histamine, angiotensin, and dopamine induced spiral strips contraction[3]. Fasudil induces disorganization of actin stress fiber and cell migration inhibition[4]. Fasudil inhibits hepatic stellate cells spreading, the formation of stress fibers, and expression of α-SMA with concomitant suppression of cell growth, but does not induce apoptosis. Fasudil suppresses the LPA-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK and p38 MAPK[5]. |
| In vivo | Fasudil (30 μg) produces an approximate 50% increase in CBF via intra-coronary injection to dogs. Fasudil (0.01, 0.03, 0.1 and 0.3 mg/kg, bolus, i.v.) dose-dependently decreases MBP and increases HR, VBF, CBF, RBF, and FBF. A total dose of 1.0 ng/mL Fasudil increases cardiac output. The infusion of Fasudil i.v. produces a significant fall in MBP, left ventricular systolic pressure and total peripheral resistance with an increase in HR and cardiac output, but without significant changes in right atrial pressure, dP/dt or left ventricular minute work in dogs[3]. Fasudil administration displays protectable effects on cardiovascular disease and reduces the activation of JNK and attenuates mitochondrial-nuclear translocation of AIF under ischemic injury[6]. The oral administration of Fasudil (a dosage of 100 mg/kg/day) significantly reduces incidence and mean maximum clinical score of EAE in SJL/J mice immunized with PLP p139-151. Treatment of mice with Fasudil suppresses the proliferative response of splenocytes to the antigen. Oral administration of Fasudil decreases inflammation, demyelination, axonal loss and APP positivein spinal cord of Fasudil-treated mice[7]. |
| Kinase Assay | Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity is assayed in a reaction mixture containing, in a final volume of 0.2 mL, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0), 10 mM magnesium acetate, 2 mM EGTA, 1 μM cyclic AMP or absence of cyclic AMP, 3.3 to 20 μM [r-32P] ATP (4×105 c.p.m.), 0.5 μg of the enzyme, 100 μg of histone H2B and compound. The mixture is incubated at 30°C for 5 min. The reaction is terminated by adding 1mL of ice-cold 20% trichloroacetic acid after adding 500 μg of bovine serum albumin as a carrier protein. The sample is centrifuged at 3000 r.p.m. for 15min, the pellet is resuspended in ice-cold 10% trichloro-acetic acid solution and the centrifugation-resuspension cycle is repeated three times. The final pellet is dissolved in 1 mL of 1 N NaOH and radioactivity is measured with a liquid scintillation counter[1]. |
| Synonyms | HA-1077, AT877 |
| Molecular Weight | 291.37 |
| Formula | C14H17N3O2S |
| Cas No. | 103745-39-7 |
| Smiles | O=S(=O)(N1CCCNCC1)c1cccc2cnccc12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.31g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 61.875 mg/mL (212.36 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.