Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Flufenamic acid (Arlef) is an anthranilic acid derivative with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. It is used in musculoskeletal and joint disorders and administered by mouth and topically.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $33 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $60 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $95 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Flufenamic acid (Arlef) is an anthranilic acid derivative with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. It is used in musculoskeletal and joint disorders and administered by mouth and topically. |
| In vivo | Under peak amyloid fibril formation conditions (pH 4.4), Flufenamic acid binds to wild-type transthyretin (KD1=30 nM, KD2=255 nM), V30M transthyretin (KD1=41 nM, KD2=320 nM), and L55P transthyretin (KD1=74 nM, KD2=682 nM) with high affinity and negative cooperativity (pH value 7.6), fully inhibiting fibril formation at a concentration of 10.8 μM. In Xenopus oocytes, Flufenamic acid reversibly suppresses ICl(Ca) in a dose-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 28 mM, without affecting the shape of the current-voltage curve in response to depolarizing voltage. Flufenamic acid inhibits the calcium-activated non-selective cation channels in the basolateral membrane of rat pancreatic exocrine cells activated by an inward-outward patch with an IC50 of 10 μM. The compound also inhibits currents activated by intracellular ADP-ribose in recombinant human TRPM2 (hTRPM2) channels and the CRI-G1 rat insulinoma cell line. Additionally, it reversibly inhibits (IC50=13.8 μM) DAP and phase discharge in rat suprachiasmatic neurons with similar kinetics, without significantly affecting membrane potential, spike threshold, or input resistance (P > 0.05), nor does it significantly affect the frequency and amplitude of spontaneous synaptic potentials. |
| Synonyms | Nichisedan, Arlef, Achless |
| Molecular Weight | 281.23 |
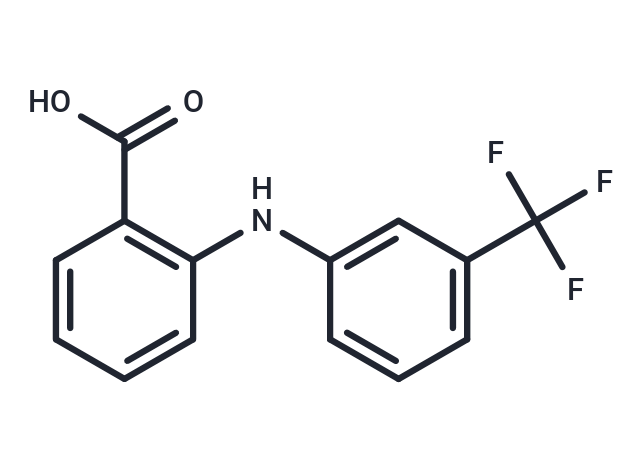
| Formula | C14H10F3NO2 |
| Cas No. | 530-78-9 |
| Smiles | OC(=O)C1=C(NC2=CC(=CC=C2)C(F)(F)F)C=CC=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.395g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 28.1 mg/mL (99.92 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 55 mg/mL (195.57 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.