- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Shopping Cart
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester
Catalog No. T6429Cas No. 104594-70-9
Alias Phenylethyl Caffeate, CAPE
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (Phenylethyl Caffeate) (CAPE) inhibits the activation of nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B and may suppress p70S6K and Akt-driven signaling pathways, with antineoplastic, cytoprotective and immunomodulating activities. CAPE is the phenethyl alcohol ester of caffeic acid and a bioactive component of honeybee hive propolis. In addition, CAPE inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells through the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and subsequent induction of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1).
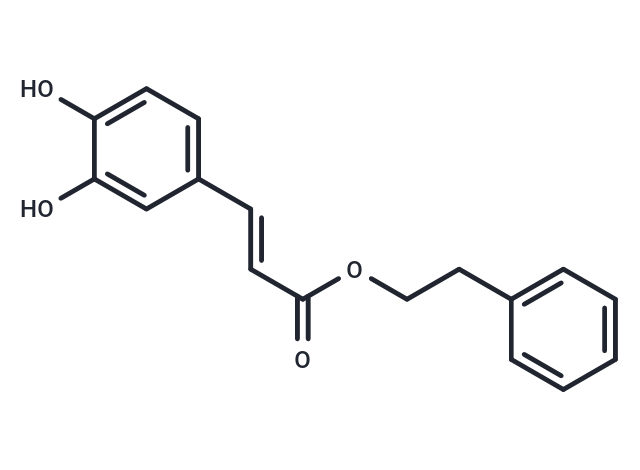
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester
Catalog No. T6429Alias Phenylethyl Caffeate, CAPECas No. 104594-70-9
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (Phenylethyl Caffeate) (CAPE) inhibits the activation of nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B and may suppress p70S6K and Akt-driven signaling pathways, with antineoplastic, cytoprotective and immunomodulating activities. CAPE is the phenethyl alcohol ester of caffeic acid and a bioactive component of honeybee hive propolis. In addition, CAPE inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells through the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and subsequent induction of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $33 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $50 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $61 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $74 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $106 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $173 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock |
Bulk & Custom
Add to Cart
Questions
View MoreSelect Batch
Purity:99.35%
Contact us for more batch information
All TargetMol products are for research purposes only and cannot be used for human consumption. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use TargetMol products for any other purpose.Product Introduction
Bioactivity
Chemical Properties
| Description | Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (Phenylethyl Caffeate) (CAPE) inhibits the activation of nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B and may suppress p70S6K and Akt-driven signaling pathways, with antineoplastic, cytoprotective and immunomodulating activities. CAPE is the phenethyl alcohol ester of caffeic acid and a bioactive component of honeybee hive propolis. In addition, CAPE inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells through the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and subsequent induction of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). |
| In vitro | Caffeic acid phenethyl ester blocks NF-κB activation induced by phorbol ester, ceramide, okadaic acid, and hydrogen peroxide by preventing the translocation of the p65 subunit of NF-κB to the nucleus. [1] In a series of tumor cell lines, Caffeic acid phenethyl ester shows promising antiproliferative activity with EC50 of 1.76, 3.16, 13.7, and 44.0 μM against murine colon 26-L5, murine B16-BL6 melanoma, human HT-1080 fibrosarcoma and human lung A549 adenocarcinoma cell lines, respectively. [2] Caffeic acid phenethyl ester, as a potent antioxidant, exerts its anti-apoptotic effect in cerebellar granule cells by blocking ROS formation and inhibiting caspase activity. [3] Moreover, Caffeic acid phenethyl ester attenuates the pro-inflammatory phenotype of LPS-stimulated HSCs, and LPS-induced sensitization of HSCs to fibrogenic cytokines by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. [4] |
| In vivo | In vivo, Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (10 mg/kg, i.p.) inhibits the growth and angiogenesis of primary tumors in C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice inoculated with Lewis lung carcinoma, colon carcinoma, and melanoma cells. [5] Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (5, 10, 20 mg/kg) also shows immunomodulatory effects in vivo by decreasing thymus weight and/or cellularity of thymus and spleen. [6] |
| Cell Research | Human HT-1080 fibrosarcoma, human lung A549 adenocarcinoma and murine B16-BL6 melanoma cell lines are maintained in EMEM medium supplemented with 10% FCS, 0.1% sodium bicarbonate and 2 mM glutamine. Murine colon 26-L5 carcinoma cell line, on the other hand, is maintained in RPMI medium containing the same supplements as in EMEM. These are all highly metastatic cell lines except for A-549 carcinoma. Cellular viability is determined using the standard MTT assay. In brief, exponentially growing cells are harvested and 100 μl of cell suspension containing 2000 cells is plated in 96-well microtiter plates. After 24 h of incubation to allow for cell attachment, the cells are treated with varying concentrations of test samples in medium (100 μl) and incubated for 72 h at 37°C under 5% CO2. Three hours after the addition of MTT, the amount of formazan formed is measured spectrophotometrically at 550 nm with a Perkin Elmer HTS-7000 plate reader. The test samples are first dissolved in DMSO and then diluted with medium; the final concentration of DMSO is less than 0.25%. Normal also had the same extent of DMSO. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) and doxorubicin HCl are used as positive controls, and EC50 values are calculated from the mean values of data from 4 wells. (Only for Reference) |
| Alias | Phenylethyl Caffeate, CAPE |
| Molecular Weight | 284.31 |
| Formula | C17H16O4 |
| Cas No. | 104594-70-9 |
| Smiles | Oc1ccc(\C=C\C(=O)OCCc2ccccc2)cc1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.266 g/cm3 |
Storage & Solubility Information
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 18.33 mg/mL (64.47 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 28.4 mg/mL (99.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/Ethanol
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sci Citations
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Please enter your animal experiment information in the following box and click Calculate to obtain the mother liquor preparation method and in vivo formula preparation method:
Mother liquor preparation method: 2 mg of drug dissolved in 50 μL DMSO (mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
(mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
Preparation method for in vivo formula: Take 50 μL DMSO main solution, add 300 μLPEG300
main solution, add 300 μLPEG300 mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O
mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O mix well and clarify
mix well and clarify
For Reference Only. Please develop an appropriate dissolution method based on your laboratory animals and route of administration.
Dose Conversion
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More Dose Conversion
Tech Support
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc
Keywords
Related Tags: buy Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester | purchase Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester | Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester cost | order Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester | Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester chemical structure | Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester in vivo | Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester in vitro | Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester formula | Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester molecular weight

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.



