- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Physalin B
Physalin B is one of the major active compounds from the Solanaceae family of plants and has a wide range of biological activities for the treatment of inflammatory eczema and herpes, among other diseases.Physalin B ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response due to acute lung injury by inhibiting NF-κB and NLRP3 through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway.Physalin B inhibits PDGF-BB-induced VSMC proliferation and migration and phenotypic transformation through activation of the Nrf2 pathway. Physalin B inhibits PDGF-BB-induced VSMC proliferation, migration and phenotypic transformation through activation of the Nrf2 pathway.Physalin B exerts antitumor activity by inhibiting LAP2α-HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of glioma-associated oncogene 1 and hepatic stellate cell activation.
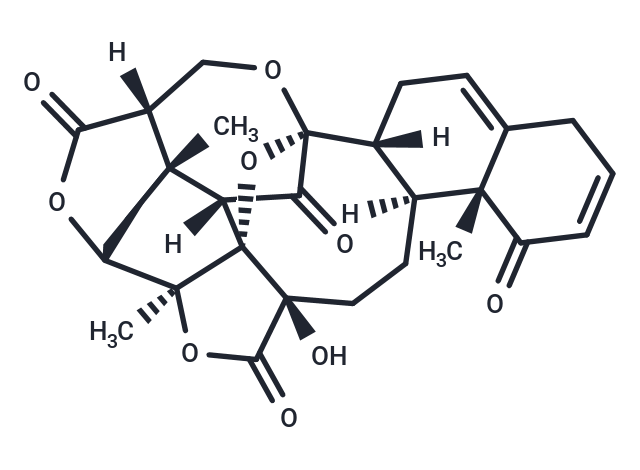
Physalin B
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $362 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $870 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $1,180 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $1,770 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $2,390 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $1,320 | In Stock |
Product Introduction
| Description | Physalin B is one of the major active compounds from the Solanaceae family of plants and has a wide range of biological activities for the treatment of inflammatory eczema and herpes, among other diseases.Physalin B ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response due to acute lung injury by inhibiting NF-κB and NLRP3 through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway.Physalin B inhibits PDGF-BB-induced VSMC proliferation and migration and phenotypic transformation through activation of the Nrf2 pathway. Physalin B inhibits PDGF-BB-induced VSMC proliferation, migration and phenotypic transformation through activation of the Nrf2 pathway.Physalin B exerts antitumor activity by inhibiting LAP2α-HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of glioma-associated oncogene 1 and hepatic stellate cell activation. |
| In vitro | Physalin B inhibited the viability of HCT116 cells with an IC50 value of 1.35 μmol/L. Treatment of the cells with physalin B (2.5-10 μmol/L) induced apoptosis and the cleavage of PARP and caspase-3. Meanwhile, physalin B treatment induced autophagosome formation, and accumulation of LC3-II and p62, but decreased Beclin 1 protein level. Marked changes of microtubules and F-actin microfilaments were observed in physalin B-treated cells, which led to the blockage of co-localization of autophagosomes and lysosomes. Physalin B treatment dose-dependently increased the phosphorylation of p38, ERK, and JNK in the cells, whereas the p38 inhibitor SB202190, ERK inhibitor U0126, or JNK inhibitor SP600125 could partially reduce physalin B-induced PARP cleavage and p62 accumulation. Moreover, physalin B treatment dose-dependently increased mito-ROS production in the cells, whereas the ROS scavenger NAC could reverse physalin B-induced effects, including incomplete autophagic response, accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins, changes of microtubules and F-actin, activation of p38, ERK and JNK, as well as cell death and apoptosis. Physalin B induces mito-ROS, which not only inhibits the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway but also induces an incomplete autophagic response in HCT116 cells in vitro.[2] |
| Alias | NSC-287088 |
| Molecular Weight | 510.53 |
| Formula | C28H30O9 |
| Cas No. | 23133-56-4 |
| Smiles | [H][C@@]12C(=O)[C@]34O[C@]11[C@@](C)(OC(=O)[C@@]1(O)CC[C@@]1([H])[C@@]3([H])CC=C3CC=CC(=O)[C@]13C)[C@H]1C[C@]2(C)[C@@]([H])(CO4)C(=O)O1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.51 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |
Sci Citations
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Dose Conversion
Tech Support
Keywords

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.



