Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

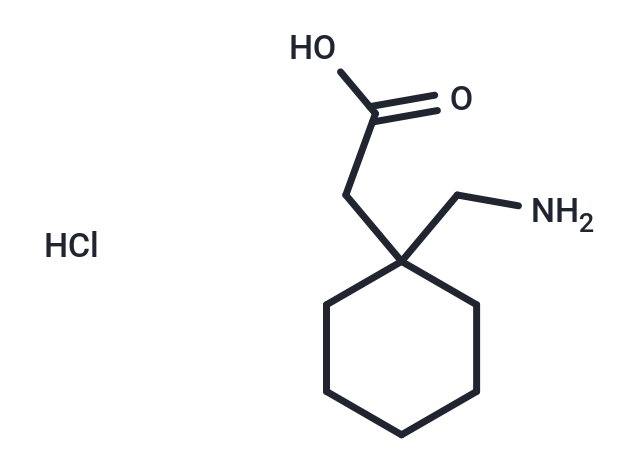
Gabapentin hydrochloride (Neurontin HCl) is a GABA analogue, used to treat seizures and neuropathic pain.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $34 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $51 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $72 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $105 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $176 | In Stock |
| Description | Gabapentin hydrochloride (Neurontin HCl) is a GABA analogue, used to treat seizures and neuropathic pain. |
| Targets&IC50 | α2δ Ca2+ channel:140 nM |
| In vitro | Gabapentin suppresses ectopic afferent discharge activity generated from injured peripheral nerves. Gabapentin, in a range of 30 to 90 mg/kg, significantly attenuates allodynia in nerve-injured rats. Gabapentin dose-dependently inhibits the ectopic discharge activity of 15 injured sciatic afferent nerve fibers through an action on impulse generation. [1] Gabapentin inhibits KCl (30 mM)-evoked voltage-dependent Ca(2+) influx. Gabapentin potently inhibits the peak whole-cell Ca(2+) channel current (I(Ba)) in a dose-dependent manner with an estimated IC(50) value of 167 nM. Gabapentin inhibition is voltage-dependent, producing an approximately 7 mV hyperpolarizing shift in current voltage properties and reducing a non-inactivating component of whole-cell current activated at relatively depolarized potentials. [2] Gabapentin selectively activates heterodimeric GABAB1a-B2 receptors, but not GABAB1b-B2 or GABAB1c-B2 receptors. Gabapentin selectively activates presynaptic GABAB heteroreceptors on glutamatergic terminals, but not GABAB autoreceptors on GABAergic terminals. Gabapentin is found to inhibit both the excitatory synaptic transmission in vitro and the neuronal response to noxious electrical and mechanical stimulation in vivo mediated by α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA), but not those mediated by N-methyl-D-asparate (NMDA) receptors. Gabapentin acts as an AMPA-receptor antagonist in the rat spinal cord to exert its spinal antinociceptive effect. Gabapentin depresses, but NMDA enhanced, the presynaptic fiber volley in the CA1 region of rat hippocampal slices. [3] |
| Alias | Neurontin HCl, Gabapentin HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 207.7 |
| Formula | C9H17NO2·HCl |
| Cas No. | 60142-95-2 |
| Smiles | Cl.NCC1(CC(O)=O)CCCCC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.329 kg/m3. Temperature:20 °C. |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: Insoluble H2O: 10 mM, Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.