 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Y-27632 dihydrochloride (Y-27632 2HCl) is an orally potent, ATP-competitive inhibitor of ROCK-I and ROCK-II. Y-27632 dihydrochloride also inhibits isolation-induced apoptosis in mouse prostate stem or progenitor cells.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $31 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $44 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $82 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $140 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $233 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $35 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Y-27632 dihydrochloride (Y-27632 2HCl) is an orally potent, ATP-competitive inhibitor of ROCK-I and ROCK-II. Y-27632 dihydrochloride also inhibits isolation-induced apoptosis in mouse prostate stem or progenitor cells. |
| Targets&IC50 | PKA:25 μM (Ki), ROCK1:220 nM (Ki), CITK:5.3 μM (Ki), PKCα:73 μM (Ki), PKN:3.1 μM (Ki), Citron kinase:5.3 μM (Ki), ROCK1 (p160ROCK):140 nM (Ki, cell free), ROCK2:300 nM (Ki, cell free) |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human induced pluripotent stem cells, marmoset iPSC, were treated with Y-27632 (5-20 μM) for 7 days and clone formation was detected by AKP. RESULTS: Y-27632 significantly improved the cloning efficiency of marmoset iPSC. [1] METHODS: Adult adipose tissue-derived stem cells ADSCs were treated with Y-27632 (5 μmol/L) for 1 h. The morphological changes of ADSCs were detected. RESULTS: Y-27632 dose-dependently induced neuronal differentiation in ADSCs. the percentage of neuron-like cells in ADSCs treated with 5 μmol/L Y-27632 for 1 h was (93.5±4.7)%. [2] METHODS: Crab monkey embryonic stem cells cyES were routinely passaged or treated with Y-27632 (1-10 μM) for 24 h. Live-dead staining was performed using the Flow Cytometry method, and BrdU was detected using a kit. RESULTS: Y-27632 promoted the increase of cyES surviving cells. Y-27632 did not promote cell proliferation, but protected the cells from cell death after single-cell digestion. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To investigate the therapeutic potential of Y-27632 in motor neuron disease, Y-27632 (2 or 30 mg/kg in drinking water) was administered orally to SOD1G93A mice in the ALS model for 137 days. RESULTS: Y-27632 2 mg/kg treatment was ineffective, Y-27632 30 mg/kg treatment improved motor function in male mice, and female mice showed only limited improvement. [4] METHODS: To investigate the effect of Y-27632 on liver fibrosis, Y-27632 (30 mg/kg) was administered orally to rats with dimethylnitrosamine (DMN)-induced liver fibrosis once a day for four weeks. RESULTS: Y-27632 treatment significantly reduced the incidence of DMN-induced hepatic fibrosis and lowered the levels of collagen and hydroxyproline as well as the expression of α-SMA in the liver. [5] |
| Kinase Assay | Recombinant ROCK1/2, PKN, or citron kinase is expressed in HeLa cells as Myc-tagged proteins by transfection using Lipofectamine and is precipitated from the cell lysates by the use of 9E10 monoclonal anti-Myc antibody coupled to G protein-Sepharose. Recovered immunocomplexes are incubated with various concentrations of [32P]ATP and 10 mg of histone type 2 as substrates in the absence or presence of various concentrations of either Y-27632 or Y-30141 at 30°C for 30 min in a total volume of 30 μL of the kinase buffer containing 50 mM HEPES-NaOH, pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl2, 5 mM MnCl2, 0.02% Briji 35, and 2 mM dithiothreitol. PKCa is incubated with 5 μM [32P]ATP and 200 μg/mL histone type 2 as substrates in the absence or presence of various concentrations of either Y-27632 or Y-30141 at 30°C for 10 min in a kinase buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 0.5 mM CaCl2, 5 mM magnesium acetate, 25 μg/mL phosphatidylserine, 50 ng/mL 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and 0.001% leupeptin in a total volume of 30 μL. Incubation is terminated by the addition of 10 μL of 43 Laemmli sample buffer. After boiling for 5 min, the mixture is subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on a 16% gel. The gel is stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue and then dried. The bands corresponding to histone type 2 are excised, and the radioactivity is measured [1]. |
| Cell Research | HeLa cells are plated at a density of 3×10^4 cells per 3.5-cm dish. The cells are cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS in the presence of 10 mM Thymidine for 16 h. After the cells are washed with DMEM containing 10% FBS, they are cultured for an additional 8 h, and then 40 ng/mL of Nocodazole is added. After 11.5 h of the Nocodazole treatment, various concentrations of Y-27632 (0-300 μM) or vehicle is added and the cells are incubated for another 30 min [1]. |
| Animal Research | A group of animals was injected with a single dose of pentylenetetrazole (PTZ, 65?mg/kg) to investigate if the two Rho-kinase inhibitors, fasudil, and Y-27632, changed the onset of PTZ seizures. Fasudil, Y-27632 or saline was given intraperitoneally 30?min before the PTZ injection. Each mouse was then observed for a 15-min period to measure the onset of the first myoclonic jerk, the onset of the first clonic convulsion and the occurrence of tonic hindlimb extension. Some of the animals died after tonic hindlimb extension, which is an expected outcome of acute PTZ injection. After the observation period, all animals were killed by halothane anesthesia [5]. Seven-week-old male Wistar rats were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital. A silver clip (0.2 mm in diameter) was placed on the left renal artery in the preparation of the renal hypertensive rats. In the preparation of the DOCA-salt hypertensive rats, the left kidney was removed and a DOCA pellet (50 mg) was implanted subcutaneously. The DOCA rats were then fed an 8% salt diet. Rats from both groups were used after 8 weeks in the experiments, together with a male, 17–22-week old spontaneously hypertensive rats. The average systolic pressure in these groups of hypertensive rats ranged from 209 to 237 mm Hg, and no significant difference was found between groups. Eight-week-old male Wistar rats were used as controls. Their average systolic pressure was 139 mm Hg. Y-27632was administered orally. The systolic blood pressure was measured by the tail cuff method at 1, 3, 5, 7 and 24 h. The rats were prewarmed to 40 8C for 10 min before each measurement. No toxicity was found in rats treated with 30 mg kg?1 of Y-27632 administered per os once per day for 10 days [4]. |
| Synonyms | Y-27632 2HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 320.26 |
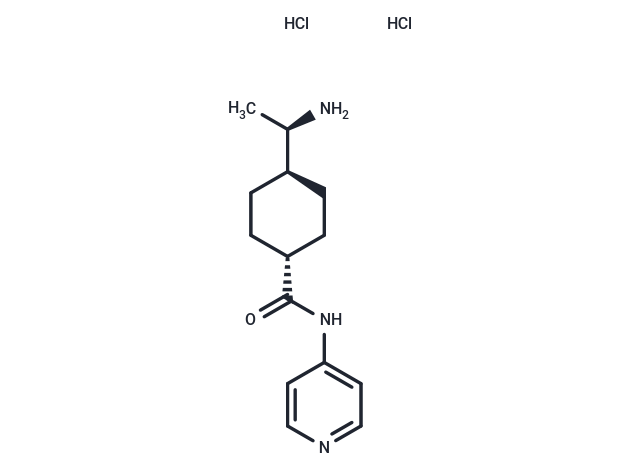
| Formula | C14H21N3O·2HCl |
| Cas No. | 129830-38-2 |
| Smiles | Cl.Cl.C[C@@H](N)[C@H]1CC[C@@H](CC1)C(=O)Nc1ccncc1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from moisture,keep away from direct sunlight,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 255 mg/mL (796.23 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 32.03 mg/mL (100.01 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 5 mg/mL (15.61 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.