Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Ruxolitinib (INCB018424) is a JAK1/2 inhibitor (IC50=3.3/2.8 nM) that is potent and selective. Rixolitinib exhibits antitumor activity and induces autophagy and apoptosis.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $53 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $68 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $93 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $118 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $157 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $257 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $436 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $59 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Ruxolitinib (INCB018424) is a JAK1/2 inhibitor (IC50=3.3/2.8 nM) that is potent and selective. Rixolitinib exhibits antitumor activity and induces autophagy and apoptosis. |
| Targets&IC50 | TYK2:19 nM (cell free), JAK1:3.3 nM (cell free), JAK2:2.8 nM (cell free), JAK3:428 nM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Ba/F3-EpoR-JAK2V617F cells were treated with Ruxolitinib (0-10 μM) for 48 h. Cell viability was measured using Cell-Titer Glo. RESULTS: Ruxolitinib dose-dependently decreased cell viability with an IC50 of 126 nM.[1] METHODS: Hodgkin's lymphoma cells HDLM-2 were treated with Ruxolitinib (10-100 nM) for 24 h, and the expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Ruxolitinib significantly inhibited the downstream activities of p-STAT3 and p-STAT5 in a dose-dependent manner, while total STAT3 and STAT5 levels remained unchanged. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, Ruxolitinib (3-30 mg/kg, 5% dimethyl acetamide, 0.5% methocellulose) was administered by gavage to BALB/c mice harboring the tumor Ba/F3-JAK2V617F twice daily for three weeks. RESULTS: Ruxolitinib significantly reduced splenomegaly and circulating levels of inflammatory cytokines and preferentially eliminated tumor cells, resulting in significantly prolonged survival without myelosuppressive or immunosuppressive effects. [1] METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, Ruxolitinib (150 mg/kg) was orally administered to BALB/c nude mice bearing the human colorectal tumor LS411N every two days for two weeks. RESULTS: Oral administration of Ruxolitinib significantly inhibited the growth of human colorectal tumors in vivo without causing hepatotoxicity. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | The kinase domains of human JAK1 (837-1142), JAK2 (828-1132), JAK3 (781-1124), and Tyk2 (873-1187) were cloned by PCR with N-terminal epitope tags. Recombinant proteins were expressed using Sf21 cells and baculovirus vectors and purified with affinity chromatography. JAK kinase assays used a homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence assay with the peptide substrate (-EQEDEPEGDYFEWLE). Each enzyme reaction was carried out with test compound or control, JAK enzyme, 500nM peptide, adenosine triphosphate (ATP; 1mM), and 2.0% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for 1 hour. The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) was calculated as the compound concentration required for inhibition of 50% of the fluorescent signal. Biochemical assays for CHK2 and c-MET enzymes were performed using standard conditions (Michaelis constant [Km] ATP) with recombinantly expressed catalytic domains from each protein and synthetic peptide substrates. An additional panel of kinase assays (Abl, Akt1, AurA, AurB, CDC2, CDK2, CDK4, CHK2, c-kit, c-Met, EGFR, EphB4, ERK1, ERK2, FLT-1, HER2, IGF1R, IKKα, IKKβ, JAK2, JAK3, JNK1, Lck, MEK1, p38α, p70S6K, PKA, PKCα, Src, and ZAP70) was performed using standard conditions using 200nM INCB018424. Significant inhibition was defined as more than or equal to 30% (average of duplicate assays) compared with control values [1]. |
| Cell Research | Cells were seeded at 2000/well of white bottom 96-well plates, treated with compounds from DMSO stocks (0.2% final DMSO concentration), and incubated for 48 hours at 37°C with 5% CO2. Viability was measured by cellular ATP determination using the Cell-Titer Glo luciferase reagent or viable cell counting. Values were transformed to percent inhibition relative to vehicle control, and IC50 curves were fitted according to nonlinear regression analysis of the data using PRISM GraphPad [1]. |
| Animal Research | All of the procedures were conducted in accordance with the US Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Mice were fed standard rodent chow and provided with water ad libitum. Ba/F3-JAK2V617F cells (10^5 per mouse) were inoculated intravenously into 6- to 8-week-old female BALB/c mice. Survival was monitored daily, and moribund mice were humanely killed and considered deceased at time of death. Treatment with vehicle (5% dimethylacetamide, 0.5% methocellulose) or INCB018424 began within 24 hours of cell inoculation, twice daily by oral gavage. Hematologic parameters were measured using a Bayer Advia120 analyzed, and statistical significance was determined using Dunnett testing [1]. |
| Synonyms | INCB018424, (R)-Ruxolitinib |
| Molecular Weight | 306.36 |
| Formula | C17H18N6 |
| Cas No. | 941678-49-5 |
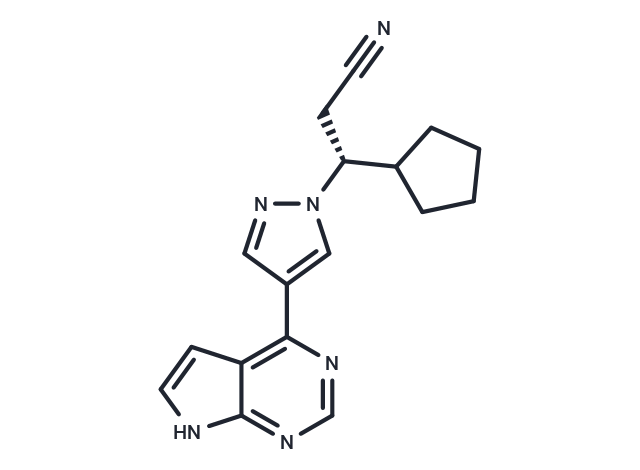
| Smiles | N#CC[C@H](C1CCCC1)n1cc(cn1)-c1ncnc2[nH]ccc12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.40g/cm3 |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 242 mg/mL (789.92 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 5.7 mg/mL (18.61 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.