Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Butein is a cAMP-specific PDE inhibitor, protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and SIRT1 activator. It sensitizes HeLa cells to Cisplatin by targeting FoxO3a via the AKT and ERK/p38 MAPK pathways.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $36 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $51 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $80 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $108 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $225 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $363 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $578 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $79 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Butein is a cAMP-specific PDE inhibitor, protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and SIRT1 activator. It sensitizes HeLa cells to Cisplatin by targeting FoxO3a via the AKT and ERK/p38 MAPK pathways. |
| Targets&IC50 | p60c-src:65 μM, EGF:65 μM, PDE4:10.4 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: HeLa cells were treated with Butein (2',3,4,4'-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) (10, 20, 40 μM) and cisplatin (10, 20, 30 μM), and the cells were evaluated by MTT method and interaction index Toxicity and detect cell apoptosis, and explore the effectiveness of combined treatment with Butein (2',3,4,4'-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) and cisplatin. RESULTS Treatment with Butein (2',3,4,4'-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) and cisplatin alone inhibited cell growth in a dose- and time-dependent manner; Butein (2',3,4,4'-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) at 20 μM Chalcone) and 20 μM cisplatin combined treatment for 48 h induced a significant synergistic cytotoxic effect; the combination of the two drugs could significantly enhance cell apoptosis. [3] METHODS: HeLa cells were treated with Butein (2’,3,4,4’-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) (20 μM) or cisplatin (20 μM), and Western blot analysis was performed to detect the phosphorylation levels of AKT, ERK and p38. RESULTS Butein (2',3,4,4'-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) significantly inhibited cisplatin-induced ERK and p38 phosphorylation, but had a significant effect on JNK expression; cisplatin or Butein (2',3, 4,4'-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) or combined use can inhibit AKT activation. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: Nude mice bearing Hela cell models were treated with Butein (2’,3,4,4’-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) (2 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected every two days) or Butein (2’,3,4,4’-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) (2 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected every two days) and cisplatin (2 mg/kg, intraperitoneally injected every 2 days) for 3 weeks, and the body weight and clinical symptoms of the mice were measured every other day; the effect of Butein (2’,3,4,4’-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) on the expression level of FoxO3a in tumor tissues was further evaluated by immunohistochemical staining. RESULTS The combined treatment (Butein (2’,3,4,4’-tetrahydroxy Chalcone) + cisplatin) had the most significant effect on tumor volume, while no significant difference was observed in body weight between control mice and mice treated with cisplatin alone or both drugs; the expression of FoxO3a was significantly increased in mice treated with Butein (2’,3,4,4’-tetrahydroxy Chalcone.[3] |
| Cell Research | The cells (5× 103/mL) are incubated in triplicate in a 96-well plate in the presence or absence of indicated concentration of Butein in a final volume of 0.2 mL for different time intervals at 37 ℃. Thereafter, 20 μL MTT solution (5 mg/mL in PBS) is added to each well. After a 2-hour incubation at 37 ℃, 0.1 mL lysis buffer (20% SDS, 50% dimethylformamide) is added, incubation is continued overnight at 37 ℃, and then the optical density at 570 nm is measured by plate reader. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | 2',3,4,4'-tetrahydroxy Chalcone |
| Molecular Weight | 272.25 |
| Formula | C15H12O5 |
| Cas No. | 487-52-5 |
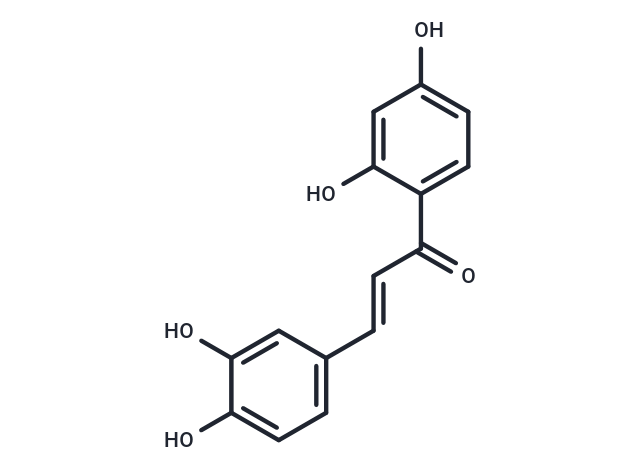
| Smiles | Oc1ccc(C(=O)\C=C\c2ccc(O)c(O)c2)c(O)c1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.483g/cm3 |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 237.5 mg/mL (872.36 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 51 mg/mL (187.33 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+90% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (9.18 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.