 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

R406 (R-406 besylate) is an effective Syk inhibitor (IC50: 41 nM) and shows no effects on Lyn.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $40 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $55 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $86 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $153 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $333 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $495 | In Stock | - | |
| 100 mg | $719 | In Stock | - | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $129 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | R406 (R-406 besylate) is an effective Syk inhibitor (IC50: 41 nM) and shows no effects on Lyn. |
| Targets&IC50 | Syk:30 nM (Ki, cell free), Syk:41 nM (Ki, cell free) |
| In vitro | R406 dose-dependently inhibited anti-IgE-mediated CHMC degranulation measured as tryptase release (EC50: 0.056 μM) but showed no activity on ionomycin-triggered tryptase release. R406 also inhibited the anti-IgE induced production and release of LTC4 and cytokines and chemokines, including TNF, IL-8, and GM-CSF. R406 potently inhibited Syk kinase activity in vitro with an IC50 of 41 nM. Subsequent enzyme kinetic studies showed R406 to be a competitive inhibitor for ATP binding with a Ki of 30 nM [1]. R406 induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest while decreasing downstream phosphatidylinositol-3'-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling in EBV+ B cell lymphoma PTLD lines in vitro [2]. The prosurvival effects promoted by anti-IgM stimulation and nurselike cells were abrogated by R406. BCR triggering up-regulated adhesion molecules and increased CLL cell migration toward the chemokines CXCL12 and CXCL13. BCR activation also enhanced CLL cell migration beneath marrow stromal cells. These responses were blocked by R406, which furthermore abrogated BCR-dependent secretion of T-cell chemokines (CCL3 and CCL4) by CLL cells [3]. |
| In vivo | Prophylactic treatment of mice with R406 administered 1 h before immune complex challenge reduced the cutaneous reverse passive Arthus reaction by approximately 72 and 86% at 1 and 5 mg/kg, respectively, compared with the vehicle control. The net optical density reading of extravasated dye extracted after treatment with R406 at 1 or 5 mg/kg R406 was reduced from 0.14 (vehicle) to 0.04 or 0.02, respectively. Treatment of injected C57BL/6 mice with 10 mg/kg R406 bid delayed the onset and reduced the severity of clinical arthritis. Paw thickening and clinical arthritis were reduced by approximately 50% [1]. R406 did not inhibit or delay the in vivo growth of solid tumors established from EBV-infected B cell lines. Instead, tumor growth in adjacent inguinal lymph nodes was observed exclusively in fostamatinib (R406 prodrug)-treated animals [2]. |
| Kinase Assay | The fluorescence polarization reactions were performed as described elsewhere. For Ki determination, duplicate 200-μl reactions were set up at eight different ATP concentrations from 200 μM (2-fold serial dilutions) in the presence of either DMSO or R406 at 125, 62.5, 31.25, 15.5, or 7.8 nM. At different time points, 20 μl of each reaction was removed and quenched to stop the reaction. For each concentration of R406, the rate of reaction at each concentration of ATP was determined and plotted against the ATP concentration to determine the apparent Km and Vmax (maximal rate). Finally, the apparent Km (or apparent Km/Vmax) was plotted against the inhibitor concentration to determine the Ki. All data analysis was performed using Prism and Prism enzyme kinetics programs [1]. |
| Cell Research | Human primary macrophages were derived from CD14 peripheral blood mononuclear cell according to the protocol specified in the monocyte isolation kit and by subsequently expanding the monocytes in 100 ng/ml human GM-CSF for 5 days to drive differentiation to macrophages. THP-1 cells were primed with 10 ng/ml IFN-γ for 6 days before stimulation. Monocyte-derived macrophages were stimulated by immobilized (plate-bound) human IgG. R406 and 15,000 cells were added to the IgG-coated wells and incubated for 16 to 20 h at 37°C. LPS was used at a final concentration of 10 ng/ml in uncoated wells. TNF concentration in the supernatants was measured by Luminex assay [1]. |
| Animal Research | Mice were challenged intravenously with 1% ovalbumin (OVA) in saline (10 mg/kg) containing 1% Evans blue dye. Ten minutes later, mice were anesthetized with isofluorane and shaved dorsolaterally. The rabbit anti-OVA IgG (50 μg/25 μl) was injected intradermally on the left side of the back at three adjacent locations. Three injections of rabbit polyclonal IgG (50 μg/25 μl) on the opposite side of the same animal served as controls. R406 or vehicle (67% PEG 400) was administered to animals 60 min before antibody/antigen challenge. Four hours after challenge, the animals were euthanized, and skin tissue was assessed for edema and inflammation by measuring dye extravasation into the surrounding tissue. Punch biopsy of the injection sites (8 mm) were incubated in 2 ml of formamide at 80°C overnight. The concentration of the extravasated Evans blue dye was measured spectrophotometrically at OD610 [1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 628.63 |
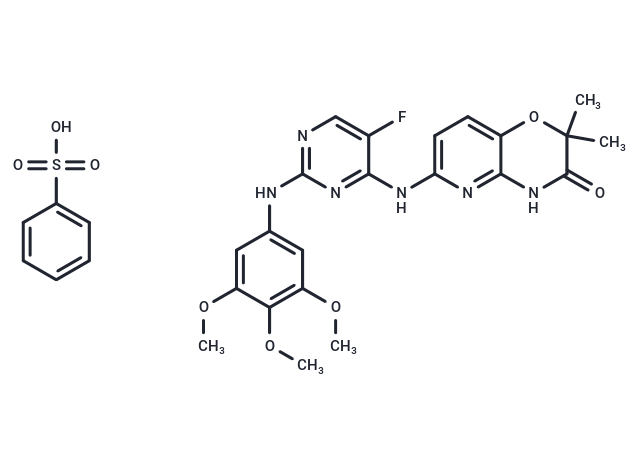
| Formula | C22H23FN6O5·C6H6O3S |
| Cas No. | 841290-81-1 |
| Smiles | OS(=O)(=O)c1ccccc1.COc1cc(Nc2ncc(F)c(Nc3ccc4OC(C)(C)C(=O)Nc4n3)n2)cc(OC)c1OC |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 8 mg/mL (12.73 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 100 mg/mL (159.08 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 4 mg/mL (6.36 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.