 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Angiotensin II is a major biologically active vasoconstrictor peptide that regulates blood pressure by binding to AT1R and AT2R receptors. It stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, promotes aldosterone synthesis, and enhances renal function. Additionally, it induces vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and increases collagen synthesis, leading to vascular and myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis. It also promotes apoptosis and endothelial capillary formation. Angiotensin II is commonly used to induce hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy animal models.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $37 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $59 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $123 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $225 | In Stock | - | |
| 100 mg | $321 | In Stock | - | |
| 500 mg | $779 | Inquiry | Inquiry |
| Description | Angiotensin II is a major biologically active vasoconstrictor peptide that regulates blood pressure by binding to AT1R and AT2R receptors. It stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, promotes aldosterone synthesis, and enhances renal function. Additionally, it induces vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and increases collagen synthesis, leading to vascular and myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis. It also promotes apoptosis and endothelial capillary formation. Angiotensin II is commonly used to induce hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy animal models. |
| Targets&IC50 | CHO cells viability:0.52 nM (EC50), CHO cells viability:1.5 nM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HCC) HepG-2, SMMC-7721, and MHCC97-H were treated with Angiotensin II (1-1000 nM) for 24-72 h. The cell viability was determined using MTT. RESULTS: Angiotensin II induced HCC cell lines to show higher growth in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. [1] METHODS: Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were treated with Angiotensin II (1 μmol/L) for 5 min-48 h. HMGB1 and IL-6 expression levels were measured by ELISA and RT-qPCR. RESULTS: Angiotensin II enhanced the expression levels of HMGB1 and IL-6 in cardiomyocytes. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To determine insulin action in a human hypertensive mouse model, Angiotensin II (1.1 mg/kg in 0.9% saline) was administered to C57Bl/6J mice using an osmotic minipump for two to four weeks. RESULTS: Blood pressure increased after Angiotensin II treatment. The increase in serum insulin was greater in Angiotensin II-treated mice after glucose administration. Long-term Angiotensin II treatment for four weeks enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in mice. [3] METHODS: To analyze genotoxic effects in vivo, Angiotensin II (60 ng/kg/min-1 μg/kg/min) was administered using an osmotic minipump to C57Bl/6J mice for four weeks. RESULTS: Angiotensin II increased SBP up to 38 mmHg over control and adversely affected renal function in mice. In the heart, a significant increase in reactive oxygen species formation and double-strand breaks were detected at the highest administered dose. In the kidney, a dose-dependent increase in superoxide formation, double-strand breaks and DNA base modification mutations were observed. [4] |
| Disease Modeling Protocol | Hypertension model
*Precautions: |
| Animal Research | (129×C57BL/6) F1 mice, which lack AT1A receptors Angiotensin II used, are fed 10 gm/day gelled 0.25% NaCl diet that contains all nutrients and water. After 28 days of Angiotensin II infusion, hearts are harvested, weighed fixed in formalin, sectioned, and stained with Masson trichrome. |
| Synonyms | Hypertensin II, DRVYIHPF, Angiotensin II, Ang II |
| Molecular Weight | 1046.18 |
| Formula | C50H71N13O12 |
| Cas No. | 4474-91-3 |
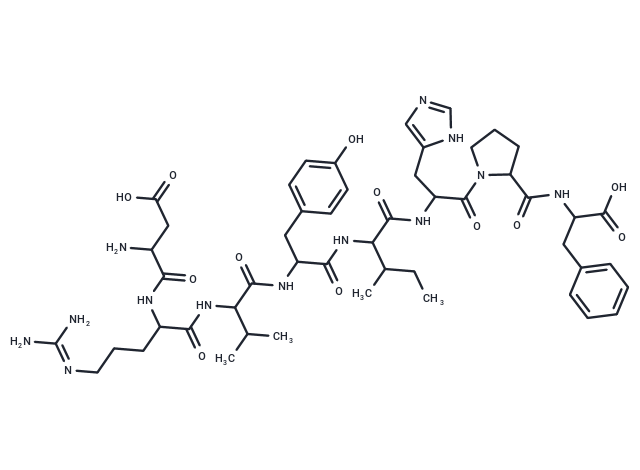
| Smiles | CCC(C)C(NC(=O)C(Cc1ccc(O)cc1)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N)NC(=O)C(N)CC(O)=O)C(C)C)C(=O)NC(Cc1cnc[nH]1)C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)NC(Cc1ccccc1)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.43g/cm3 |
| Sequence | Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-Phe |
| Sequence Short | DRVYIHPF |
| Storage | keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 10.52 mg/mL (10.06 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.