Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Vidarabine (Adenine Arabinoside) is a nucleoside antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces antibioticus. It has some antineoplastic properties and has broad spectrum activity against DNA viruses in cell cultures and significant antiviral activity against infections caused by a variety of viruses such as the herpes viruses, the VACCINIA VIRUS and varicella zoster virus.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $38 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $81 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock |
| Description | Vidarabine (Adenine Arabinoside) is a nucleoside antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces antibioticus. It has some antineoplastic properties and has broad spectrum activity against DNA viruses in cell cultures and significant antiviral activity against infections caused by a variety of viruses such as the herpes viruses, the VACCINIA VIRUS and varicella zoster virus. |
| Targets&IC50 | HSV2:11.3 μg/mL (IC50), HSV1:9.3 μg/mL (IC50) |
| In vitro | Vidarabine and Acyclovir have a synergistic effect on wild type . Vidarabine is capable of inhibiting acyclovir-resistant/TK-deficient mutants of HSV and VZV, because it is phosphorylated to its active vidarabine–triphosphate form by cellular kinases and is not dependent for its activation on the viral TK. [1] Vidarabine and acyclovir (ACV) alone show a concentration-dependent inhibition of plaque formation of HSV-1 in Vero cells. Vidarabine combined with acidic protein bound polysaccharide (APBP) show synergistic effects on the plaque formation of HSV-1 in Vero cells. [2] Vidarabine acts directly on the DNA polymerase of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and double-strand DNA viruses, including human adenoviruses. Vidarabine specifically inhibits adenovirus type 11 replication without obvious cytotoxicity in vitro. Vidarabine acts less on the synthesis of early proteins but rather on those after DNA replication. [3] Vidarabine is an antiviral drug with activity against herpes viruses, poxviruses, and certain rhabdoviruses, hepadnarviruses, and RNA tumor viruses. Vidarabine also is active against vaccinia virus both in vitro and in vivo. [4] |
| In vivo | Vidarabine is rapidly deaminated to 9-β-D-arabinofuranosyl hypoxanthine (Ara-Hx) as the principal metabolite. [3] |
| Alias | Vira-A, Arabinosyladenine, Ara-A, Adenine Arabinoside, 9-β-D-Arabinofuranosyladenine |
| Molecular Weight | 267.24 |
| Formula | C10H13N5O4 |
| Cas No. | 5536-17-4 |
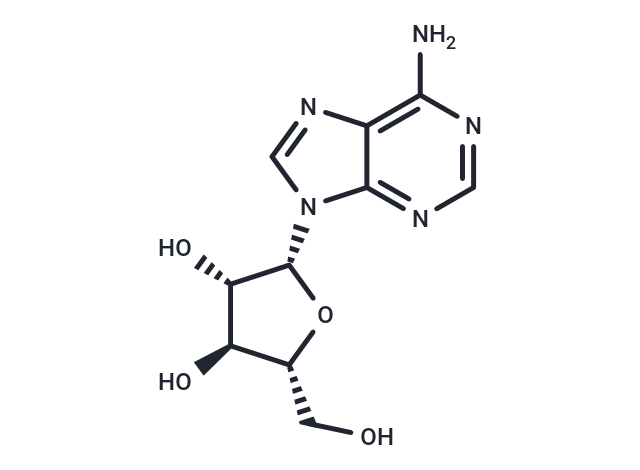
| Smiles | O[C@@H]1[C@H](N2C=3C(N=C2)=C(N)N=CN3)O[C@H](CO)[C@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 2.08g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice./Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 3 mg/mL (11.23 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 75 mg/mL (280.65 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.