Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Sirtinol is a selective SIRT1/2 inhibitor (IC50: 131/38 μM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $36 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $53 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $85 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $188 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $360 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $535 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,180 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $53 | In Stock |
| Description | Sirtinol is a selective SIRT1/2 inhibitor (IC50: 131/38 μM). |
| Targets&IC50 | SIRT1:131 μM, ySir2:48 μM, SIRT2:38 μM |
| In vitro | In male SD rats, Sirtinol (1 mg/kg) can mitigate the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and protect against post-traumatic hemorrhage. |
| In vivo | In both MCF-7 and H1299 cells, treatment with Sirtinol (100 μM) for 24 hours led to sustained growth inhibition lasting until the 9th day after Sirtinol withdrawal. Sirtinol induced an increase in SA-β-gal activity and PAI-1 expression in MCF-7 and H1299 cells, outperforming Splitomicin. In these cell types, Sirtinol (>33 μM) more effectively inhibited colony formation compared to Splitomicin. Sirtinol (100 μM) significantly reduced the phosphorylation levels of ERK, JNK/SAPK, and p38 MAPK in MCF-7 and H1299 cells, both under basal conditions and following EGF or IGF-I induction. It also blocked the basal and EGF-induced Ras activity. Consistent with this, Sirtinol treatment reduced the phosphorylation of MEK, Raf-1, MKK7, and SEK1/MKK4 induced by the basal level and by IGF-I or EGF. It effectively inhibited the enzymatic activity of recombinant yeast Sir2p in vitro (IC50: 68 μM), without inhibiting human HDAC1, suggesting that Sirtinol may be a specific inhibitor for the sirtuin family. Unlike TSA, Sirtinol did not alter the overall acetylation levels of histones and tubulin in human primary fibroblasts or change the morphology of HeLa tumor cell lines. Sirtinol inhibited Sirt1 activity, thereby increasing UV and H2O2-induced p53 acetylation, which accelerated apoptosis in skin keratinocytes. The blockade of Sirt1 enzymatic activity by Sirtinol significantly inhibited the growth and viability of human-derived PCa cells without affecting normal prostatic epithelial cells. |
| Kinase Assay | Inhibition in vitro of human Sirt2 activity: 1.5 μg of recombinant human GST-Sirt2 (amino acids 18-340) are incubated at 30°C for 2 hours in 50 μL of assay buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.8, 4 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM dithiothreitol with different concentrations of Sirtinol, 50 μM NAD, and tritiated acetylated HeLa histones (1000 cpm), purified by acid extraction. HDAC activity is determined by scintillation counting of the ethyl acetate-soluble [3H]acetic acid. |
| Cell Research | Cells are grown to 60% confluence and then treated with 30 μM or 120 μM sirtinol for 24 or 48 hours. Cells are trypsinized and collected. The cells are pelleted by centrifugation and resuspended in PBS (120 μL). Trypan blue (0.4% in PBS; 10 μL) is added to a smaller aliquot (10 μL) of cell suspension, and the number of cells (viable unstained and nonviable blue) are counted. (Only for Reference) |
| Molecular Weight | 394.47 |
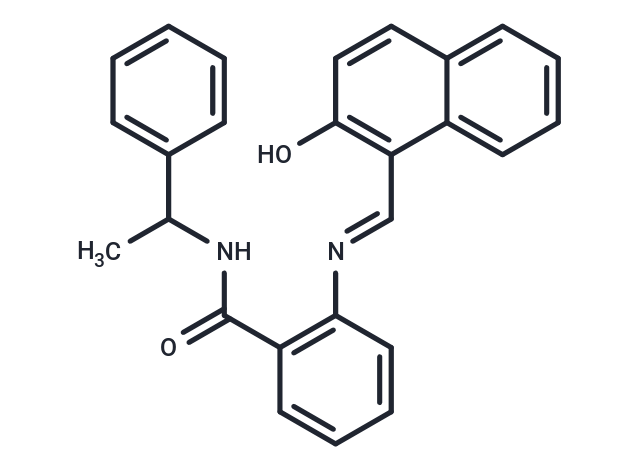
| Formula | C26H22N2O2 |
| Cas No. | 410536-97-9 |
| Smiles | CC(NC(=O)C1=C(C=CC=C1)\N=C\C1=C(O)C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)C1=CC=CC=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.276g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 6.25 mg/mL (15.84 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.