Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

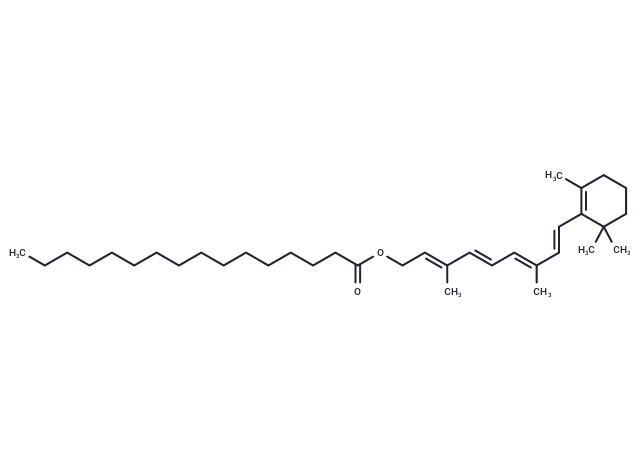
Retinyl palmitate (Vitamin A palmitate) is a naturally-occurring phenyl analogue of retinol, with potential antineoplastic and chemopreventive activities.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $42 | In Stock |
| Description | Retinyl palmitate (Vitamin A palmitate) is a naturally-occurring phenyl analogue of retinol, with potential antineoplastic and chemopreventive activities. |
| In vitro | The microencapsulation of vitamin A palmitate by gelatin-acacia complex is a promising method for converting an oily vitamin to solid powders for an aid to handling and ease of incorporation in preparations. [1] |
| In vivo | Vitamin A Palmitate (80 mg/kg daily p.o.) or (800 mg/kg once a week p.o.) dose-dependently decreases the size of papillomas in mice, the daily administration induces a somewhat higher extent of regression than the weekly application if the total doses are compared. Water miscible solutions of Vitamin A Palmitate as well as of Vitamin A acid given by the oral route elicit the same effect on papillomas. [2] Vitamin A Palmitate (A single simultaneous injection of 150 g) enhances cell-mediated immunity to sheep red blood cells(SRBC) as early as 3 days following immunization, and the enhancement persists for at least 3 weeks. [3] |
| Alias | Vitamin A palmitate, Retinyl (Vitamin A) Palmitate, Retinol palmitate |
| Molecular Weight | 524.86 |
| Formula | C36H60O2 |
| Cas No. | 79-81-2 |
| Smiles | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC\C=C(/C)\C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C |
| Relative Density. | 0.92 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (95.26 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.