Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Orantinib (NSC 702827) , a excellent effective against PDGFR autophosphorylation with Ki of 8 nM, also highly inhibits Flk-1 and FGFR1 trans-phosphorylation. It shows little effect against IGF-1R, Met, Src, Lck, Zap70, Abl and CDK2 and does not suppresses EGFR.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $47 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $72 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $153 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $293 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $515 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $51 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Orantinib (NSC 702827) , a excellent effective against PDGFR autophosphorylation with Ki of 8 nM, also highly inhibits Flk-1 and FGFR1 trans-phosphorylation. It shows little effect against IGF-1R, Met, Src, Lck, Zap70, Abl and CDK2 and does not suppresses EGFR. |
| Targets&IC50 | FLT1:2.1 μM (Ki), PDGFRβ:8 nM(Ki), FGFR1:1.2 μM (Ki) |
| In vitro | In the HT29 human colorectal cancer tumor model, TSU-68 (200 mg/kg) reduced the average vascular permeability at the tumor margin and the average plasma volume fraction at the tumor center. In athymic mice bearing various xenografts, including A375, Colo205, H460, Calu-6, C6, SF763T, and SKOV3TP5 cells, TSU-68 (75-200 mg/kg) inhibited cell growth. In the rabbit VX2 liver tumor model, TSU-68 (200 mg/kg) enhanced the efficacy of injected chemotherapy. Additionally, in C6 glioma xenografts, TSU-68 (75 mg/kg) also blocked tumor angiogenesis. |
| In vivo | TSU-68 is an ATP-competitive inhibitor that acts on Flk-1/KDR, FGFR1, and PDGFRβ kinase phosphorylation with respective Ki values of 2.1 μM, 1.2 μM, and 8 nM. In human megakaryoblastic leukemia MO7E cells, TSU-68 (IC50=0.1-1 μM) inhibits the tyrosine autophosphorylation of the c-kit receptor for hepatocyte growth factor and the phosphorylation of ERK1/2. It also suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in MO7E cells stimulated by SCF, with an IC50 of 0.29 μM. In NIH-3T3 cells overexpressing PDGFRβ, TSU-68 (0.03-0.1 μM) inhibits the PDGFRβ tyrosine phosphorylation stimulated by PDGF. Additionally, in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) stimulated by vascular endothelial growth factor, TSU-68 (0.03-10 μM) prevents KDR tyrosine phosphorylation. However, in NIH-3T3 cells overexpressing EGFR, TSU-68 (100 μM) does not inhibit the tyrosine phosphorylation of EGFR stimulated by EGF. Furthermore, TSU-68 inhibits the proliferation of HUVECs driven by vascular endothelial growth factor and FGF, with average IC50 values of 0.34 and 9.6 μM, respectively. |
| Kinase Assay | trans-Phosphorylation Reactions: Tyrosine kinase assays to quantitate the trans-phosphorylation activity of Flk-1 and FGFR1 are performed in 96-well microtiter plates precoated (20 μg/well in PBS; incubated overnight at 4 °C) with the peptide substrate poly-Glu,Tyr (4:1). Excess protein binding sites are blocked with 1-5% (w/v) BSA in PBS. Purified GST-FGFR1 (kinase domain) or GST-Flk-1 (cytoplasmic domain) fusion proteins are then added to the microtiter wells in 2 × concentration kinase dilution buffer consisting of 100 mM HEPES, 50 mM NaCl, 40 μM NaVO4, and 0.02% (w/v) BSA. The final enzyme concentration for GST-Flk-1 and GST-FGFR1 is 50 ng/mL. SU6668 is dissolved in DMSO at 100× the final required concentration and diluted 1:25 in Water. Twenty-five μL of diluted SU6668 are subsequently added to each reaction well. The kinase reaction is initiated by the addition of different concentrations of ATP in a solution of MnCl2 so that the final ATP concentrations spanned the Km for the enzyme, and the final concentration of MnCl2 is 10 mM. The plates are incubated for 5-15 min at room temperature before stopping the reaction with the addition of EDTA. The plates are then washed three times with TBST. Rabbit polyclonal antiphosphotyrosine antisera are added to the wells at a 1: 10000 dilution in TBST containing 0.5% (w/v) BSA, 0.025% (w/v) nonfat dry milk, and 100 μM NaVO4 and incubated for 1 hour at 37 °C. The plates are then washed three times with TBST, followed by the addition of goat anti-rabbit antisera conjugated with HRP. The plates are incubated for 1 hour at 37 °C and then washed three times with TBST. The amount of phosphotyrosine in each well is quantitated after the addition of 2,2 |
| Cell Research | Cells are seeded (3 × 105 cells/35-mm well) in DMEM containing 10% (v/v) FBS and grow to confluence and then quiesced in DMEM containing 0.1% serum for 2 hours before drug treatment. HUVECs (seeded at 2 × 106 cells/10-cm plate) are grown to confluence in endothelial cell growth media and then quiesced in endothelial cell basal media containing 0.5% FBS for 24 hours before drug treatment. All cell lines are incubated with SU6668 for 1 hour before ligand stimulation (100 ng/mL) for 10 min. Western blotting is perfor (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | TSU-68, SU6668, NSC 702827 |
| Molecular Weight | 310.35 |
| Formula | C18H18N2O3 |
| Cas No. | 252916-29-3 |
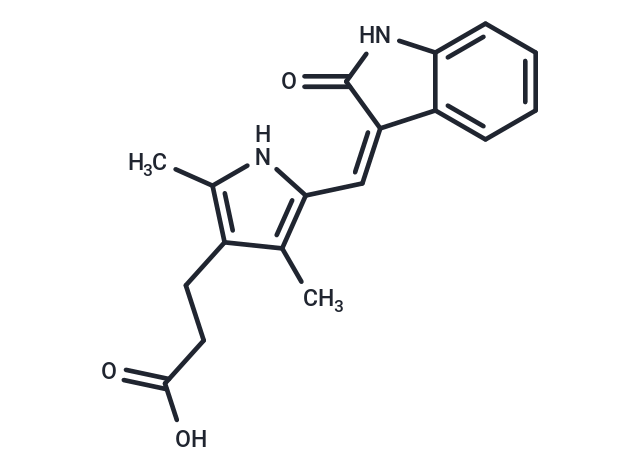
| Smiles | Cc1[nH]c(\C=C2/C(=O)Nc3ccccc23)c(C)c1CCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.328g/cm3 |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | 1eq. NaOH: 31 mg/mL (99.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 40 mg/mL (128.89 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 10 mg/mL (32.22 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1eq. NaOH/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.