Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

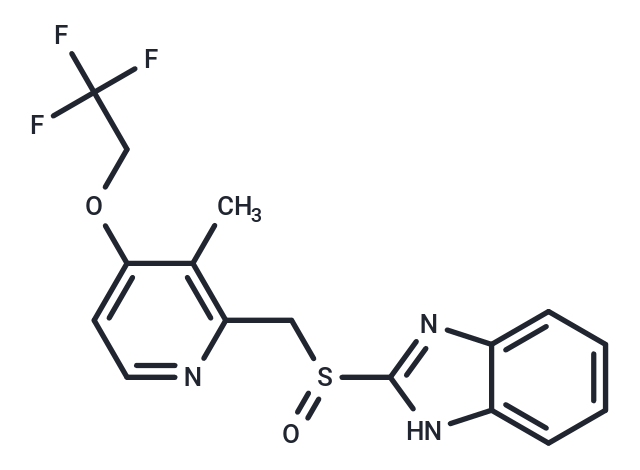
Lansoprazole (A-65006) is a 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethoxypyridyl derivative of timoprazole that is used in the therapy of STOMACH ULCERS and ZOLLINGER-ELLISON SYNDROME. The drug inhibits H(+)-K(+)-EXCHANGING ATPASE which is found in GASTRIC PARIETAL CELLS. Lansoprazole is a potent brain penetrant neutral sphingomyelinase (N-SMase) inhibitor (exosome inhibitor)
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $45 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $62 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Lansoprazole (A-65006) is a 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethoxypyridyl derivative of timoprazole that is used in the therapy of STOMACH ULCERS and ZOLLINGER-ELLISON SYNDROME. The drug inhibits H(+)-K(+)-EXCHANGING ATPASE which is found in GASTRIC PARIETAL CELLS. Lansoprazole is a potent brain penetrant neutral sphingomyelinase (N-SMase) inhibitor (exosome inhibitor) |
| In vitro | Lansoprazole significantly attenuates intestinal damage induced by ischemia-reperfusion or indomethacin. Exogenous administration of Lansoprazole can prevent injury to the small intestine caused by ischemia-reperfusion or indomethacin. Lansoprazole inhibits acute inflammatory responses and mucosal injury in rats subjected to ischemia-reperfusion or indomethacin-induced damage. |
| In vivo | Lansoprazole is a potent antisecretory agent that inhibits gastric acid secretion by blocking the stomach's hydrogen/potassium adenosine triphosphatase (H+, K+-ATPase). It suppresses the upregulation of adhesion molecules in blood vessels, neutrophil activation, and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines from activated endothelial cells. Furthermore, Lansoprazole induces the expression of various genes in gastric epithelial cells, including Phase II detoxifying enzymes (NADPH-quinone oxidoreductase, glutathione S-transferase) and antioxidative stress proteins (HO-1, thioredoxin reductase, and superoxide dismutase). In rat gastric epithelial cells, Lansoprazole upregulates HO-1 expression and exerts anti-inflammatory effects. |
| Alias | AG-1749, A-65006 |
| Molecular Weight | 369.36 |
| Formula | C16H14F3N3O2S |
| Cas No. | 103577-45-3 |
| Smiles | CC1=C(CS(=O)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3N2)N=CC=C1OCC(F)(F)F |
| Relative Density. | 1.5 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (135.37 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.