Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


HDAC-IN-7 (HBI-8000) (Chidamide impurity) is an impurity of Chidamide. Chidamide is a potent and orally bioavailable inhibitor of HDAC enzymes class I (HDAC1/2/3) and class IIb (HDAC10).
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 56.00 | |
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 79.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 139.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 239.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 477.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 698.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 993.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 119.00 |





| Description | HDAC-IN-7 (HBI-8000) (Chidamide impurity) is an impurity of Chidamide. Chidamide is a potent and orally bioavailable inhibitor of HDAC enzymes class I (HDAC1/2/3) and class IIb (HDAC10). |
| Targets&IC50 | HDAC8:733nM, HDAC1:95nM, HDAC10:78 nM, HDAC11:432 nM, HDAC3:67nM, HDAC2:160nM |
| In vitro | Chidamide (CS055) at low concentrations dramatically inhibits cell proliferation in each cell line. After Chidamide treatment, cells arrest at the G0/G1 phase in a dose-dependent manner. Western blot analysis indicats that cyclin E1 and E2 protein expression is down-regulated after Chidamide treatment, which is consistent with the cell-cycle analysis. As the changes in cyclin E1 are much more significant than cyclin E2, cyclin E1 is up-regulated in HL60 and K562 cells by lentiviral transduction. The effect on leukaemia proliferation by Chidamide inhibition are largely weakened when cyclin E1 is overexpressed. It is therefore likely that cyclin E1 levels are decreased by Chidamide which induces cell-cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase[2]. Chidamide causes a significant concentration-dependent inhibitory effect on cell proliferation in comparison to the vehicle-treated cells (P<0.05). The maximal inhibitory effect is reached at 5 μM[3]. |
| In vivo | Inhibition of tumor growth by Chidamide (CS055) treatment is observed in a dose-dependent manner, demonstrating the anti-tumor activity of Chidamide. Control tumors grow to an average volume of 14.51 cm3 after 20 days, and Chidamide-treated tumors grow to 11.68, 11.05 and 8.45 cm3, corresponding to 19.54%, 23.83% and 41.80% growth inhibition respectively. The average tumor mass in animals treated with vehicle is 9.4±2.7 g and is 8.4±2.4 g for animals treated with low-dose Chidamide. In animals treated with a moderate dose of Chidamide, tumor mass is 7.6±1.6 g and those receiving high-dose Chidamide has a tumor mass of 5.4±1.5 g (P<0.01). Additionally, Chidamide treatment prolongs the survival of nude mice bearing HL60 xenografts. Moreover, the level of lipid peroxidation product (MDA), which is a presumptive measure of ROS-mediated injury, is increased in tumor tissue accompanied by treatment of Chidamide, suggesting that Chidamide-induced ROS generation might play a role[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | HDAC activity is detected as described in the Colorimetric HDAC Activity Assay kit. Each reaction (100 μL) contains nuclear protein (50 μg) extract from leukaemia cells and HDAC substrate. To test the effect of HDACis, Chidamide (CS055) and MS-275 are added to the mixtures and incubated at 37°C for 1 h. The HDAC activities are measured by a microplate readers at 405 nm. The positive control (only nuclear extract and vehicle) is set as 100% and double-distilled water containing 10 μM Trichostatin A, a known strong HDACi, is used as a negative control and set as 0%[2]. |
| Cell Research | Chidamide (CS055) is dissolved in DMSO and stored, and then diluted with appropriate medium before use[2]. Proliferation of the PaTu8988 cells is evaluated using CCK-8 assay. PaTu8988 cells are randomly into 4 groups and incubated in the absence or presence of concentrations of 0, 1.25, 2.5 and 5 μM) of Chidamide for 48 h. Subsequently, 10 μL CCK-8 is added in each well and incubated for 2 h. The optical density of each well is then measured with a microplate reader at 450 nm. The cell survival rate is calculated using the formula: Cell survival rate (%)=1-(ODctrl-ODsample)/ODctrl×100%[2]. |
| Synonyms | HBI-8000, CS055, Chidamide impurity |
| Molecular Weight | 390.41 |
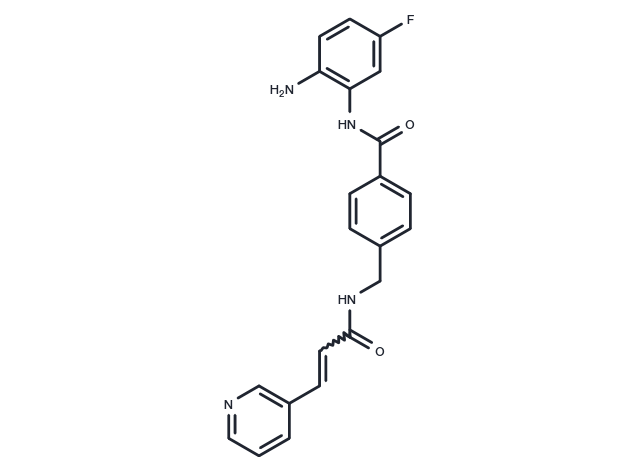
| Formula | C22H19FN4O2 |
| CAS No. | 743420-02-2 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 41 mg/mL
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
HDAC-IN-7 743420-02-2 Chromatin/Epigenetic DNA Damage/DNA Repair HDAC HBI-8000 CS-055 HDAC IN 7 HBI 8000 CS 055 HBI8000 CS055 Chidamide impurity HDACIN7 inhibitor inhibit
