 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) is an analog of glucose, an inhibitor of glycolysis. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose has antiviral activity, as well as inhibitory cell proliferation and apoptosis-inducing activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $33 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $45 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $113 | - | In Stock | |
| 10 g | $163 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) is an analog of glucose, an inhibitor of glycolysis. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose has antiviral activity, as well as inhibitory cell proliferation and apoptosis-inducing activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | Kasumi-1 cells viability:0.92 mM, NB4 cells viability:5.75 mM, THP-1 cells viability:16.14 mM, EtHK enzyme:5.66 mM (Km), B-CPAP cells viability:1.154 mM, HL-60 cells viability:15.55 mM, Caenorhabditis elegans growth:19.5 mM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Pancreatic cancer cells MIA PaCa2, BxPC-3, ASPC-1 and ovarian cancer cells OVCAR-3, HEY, SK-OV-3 were treated with 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (0.01-100 mM) for 48 h. Cell proliferation was detected using MTT. RESULTS: 2-Deoxy-D-glucose showed significant antiproliferative activity against tumor cells with IC50 values ranging from 1.45-13.34 mM. [1] METHODS: Triple-negative breast cancer cells Hs578T were treated with 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (15 mM) for 24 days, and cell motility was detected by Migration assay and Invasion assay. RESULTS: 2-Deoxy-D-glucose inhibited the migration and invasion of Hs578T cells. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the effects on leukocyte subpopulation distribution and function, 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (500-1500 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally into BDF1 mice once or thrice. RESULTS: Blood glucose concentrations increased in a dose-dependent manner in mice injected with up to 1500 mg/kg of 2-Deoxy-D-glucose. Corticosterone levels, leukocyte counts in the spleen, and CD3+ cells in the thymus increased after one or three injections of 2-Deoxy-D-glucose up to 1500 mg/kg. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose administration induced dose-dependent changes in thymic and splenic cell distribution and function. [3] METHODS: To test the antitumor activity in vivo, 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (1000 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to C57BL/6 mice bearing melanoma B16 once daily for eight days. RESULTS: 2-Deoxy-D-glucose significantly inhibited tumor growth, and TAMs showed a significant decrease in Arg, Fizz, CD206 and Vegf expression after 2-Deoxy-D-glucose treatment. [4] |
| Cell Research | 2×103 H460 or H157 cells are seeded in 96-well cell culture plates. Cells are treated with 5 mM 2-DG only, 5 or 10 μM IGF1R inhibitor II only, or a combination of 2-DG and IGF1R inhibitor II. Cell growth inhibition is determined after 48 h by the CellTiter 96® AQueous nonradioactive cell proliferation assay. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | NSC 15193, D-Arabino-2-deoxyhexose, Ba 2758, 2-DG, 2-deoxyglucose, 2-Deoxy-D-arabino-hexose |
| Molecular Weight | 164.16 |
| Formula | C6H12O5 |
| Cas No. | 154-17-6 |
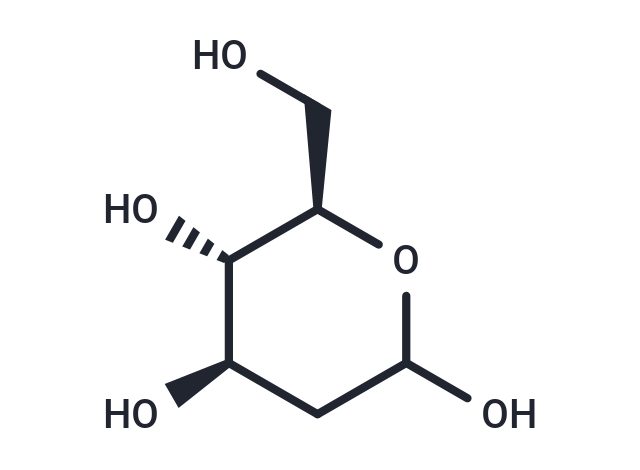
| Smiles | OC[C@H]1OC(O)C[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.533 g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature,store under nitrogen,keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 100 mg/mL (609.16 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 60 mg/mL (365.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.