Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


TCS7010 (Aurora A Inhibitor I) is a novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of Aurora A with IC50 of 3.4 nM in a cell-free assay. It is 1000-fold more selective for Aurora A than Aurora B.
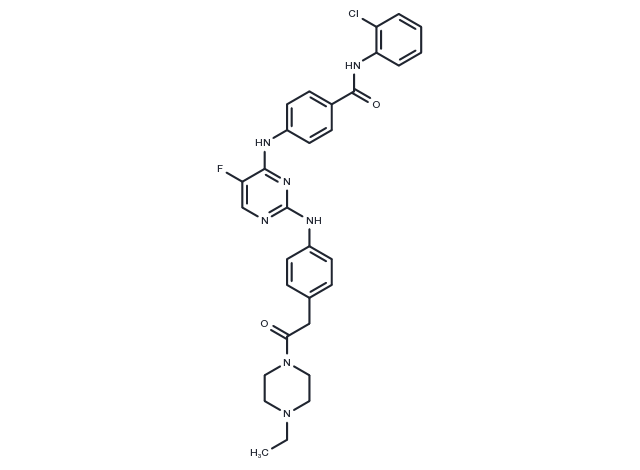
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | In stock | $ 32.00 | |
| 2 mg | In stock | $ 45.00 | |
| 5 mg | In stock | $ 72.00 | |
| 10 mg | In stock | $ 127.00 | |
| 25 mg | In stock | $ 230.00 | |
| 50 mg | In stock | $ 398.00 | |
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 592.00 | |
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 1,280.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 94.00 |



| Description | TCS7010 (Aurora A Inhibitor I) is a novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of Aurora A with IC50 of 3.4 nM in a cell-free assay. It is 1000-fold more selective for Aurora A than Aurora B. |
| Targets&IC50 | Aurora A:3.4 nM |
| In vitro | Aurora A Inhibitor I is a 2,4-dianilinopyrimidine that selectively and potently inhibits Aurora A. Aurora A Inhibitor I effectively inhibits the proliferation of HCT116 and HT29 cells, with IC50 of 190 nM and 2.9 μM, respectively. The Aurora A selectivity of Aurora A Inhibitor I against Aurora B depends on a single amino acid (Thr217) of Aurora A. [1] In KCL-22 cells, Aurora A Inhibitor I (1-5 μM) increases G2/M cell fraction, induces histone H3 serine 10 phosphorylation, and suppresses mitotic Aurora A autophosphorylation on Thr288. Aurora A Inhibitor I (0.5-5 μM) also suppresses cell proliferation in KCL-22 cells, as well as BCR-ABL-negative leukemia cell lines KG-1 and HL-60. Aurora A Inhibitor I effectively induces apoptosis in KCL-22 cells at 5 μM. [2] In a recent study, Aurora A Inhibitor I is also found to inhibit cell growth of HCT116, HT29, and HeLa cells, with IC50 of 377.6 nM, 5.6 μM, and 416 nM. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | Auroras A and B Inhibition Assays: Both Auroras A and B are assayed in ELISA format using a GST fusion (pGEX-4T) of the N-terminus of Histone H3 (aa 1?18) as substrate. Plates are coated with 2 μg/mL substrate in PBS then blocked with 1 mg/mL I-block in PBS. Kinase reactions are run for 40 min with 5 ng/mL (0.16 nM) Aurora A or 45 ng/mL (1.1 nM) Aurora B at 30 μM ATP (~ Km) in kinase buffer. Final DMSO concentration is 4%. Product is detected by incubation with antiphosphohistone H3 (Ser10) 6 g3 mouse monoclonal antibody and sheep-anti-mouse HRP conjugate, followed by washing and addition of TMB substrate. After quenching with 1 M phosphoric acid, plates are read at 450 nM. |
| Cell Research | Cells are seeded in 384-well plates on day 0 in 50 μL of complete medium and incubated overnight in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37 °C. On day 1, 10 μL of Aurora A Inhibitor I is added. On day 4, plates are allowed to reach room temperature, and 30 μL Cell Titer-Glo reagent is added to each well to measure total ATP levels. Plates are read after shaking 15 min at room temperature.(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | Aurora A Inhibitor I |
| Molecular Weight | 588.07 |
| Formula | C31H31ClFN7O2 |
| CAS No. | 1158838-45-9 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: 58.8 mg/mL (100 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
TCS7010 1158838-45-9 Apoptosis Cell Cycle/Checkpoint Chromatin/Epigenetic Aurora Kinase TCS 7010 inhibit Aurora A Inhibitor I Inhibitor TCS-7010 inhibitor
