Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Sulfacetamide sodium monohydrate, a sulfonamide antibiotic, has been investigated for the treatment of rosacea and pityriasis versicolor.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $29 | Backorder |
| Description | Sulfacetamide sodium monohydrate, a sulfonamide antibiotic, has been investigated for the treatment of rosacea and pityriasis versicolor. |
| Targets&IC50 | DHPS:9.5 μM |
| In vitro | Sulfacetamide inhibits Arabidopsis DHPS with IC50 of 9.5 μM, pKa=5.4[1]. Sulfacetamide induces anti-proliferative effects on T-47D cells and it is independent of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Sulfacetamide treatment lowers expression of p53/DRAM pathway in parallel with upregulation of Akt/mTOR pathway promoting cytoprotective autophagy. The LD50 of sulfacetamide in T-47D cells after 48 h is 41 mM. Sulfacetamide does not cause DNA fragmentation. In cells treated with sulfacetamide, the ATG5 expression level increases suggesting an increase in autophagosome formation in the autophagy pathway. Autophagy induction in the sulfathiazole and sulfacetamide treatments is not accompanied by apoptosis and occurred without any distinctive arrest in a phase of the cell cycle. It triggers autophagy in T-47D cells via a DAPK independent pathway[2]. Sodium sulfacetamide or sulfacetamide is a bacteriostatic agent that is active against sulfonamide-sensitive Gramnegative and Gram-positive bacteria, including Streptococci, Staphylococci, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas pyocyanea, Salmonella spp., Proteus vulgaris, and Nocardia, which are usually isolated in secondary infections of the skin. Sulfacetamide inhibits mannose-6-phosphate isomerase (also known as phosphomannose isomerase (PMI)), which is considered the key enzyme in kinetoplastid energy metabolism[3]. |
| In vivo | The LD50 of sulfacetamide for mice is 16,500 mg/kg by the oral route. In humans, the side effects include erythema, moderate swelling, nausea, vomiting, and headache. In addition to these side effects, the occurrence of StevensJohnson syndrome is reported in HIV-positive patients who received sulfacetamide drops for eye infections. All of these side effects, however, are associated with oral administration or high drug absorption through the skin, mucous membranes, and the conjunctiva, whereas topical use is not associated with strong side effects. |
| Cell Research | Cells are cultured in RPMI medium 1640, supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin/streptomycin, in a humidified atmosphere of 5% carbon dioxide in air at 37°C. According to MTT assay, the LC50 of sulfathiazole and sulfacetamide after 48 h is determined as 6.5 mM and 41 mM, respectively. Doxorubicin and sodium salt of sulfadrugs are dissolved in culture medium to the final desired concentration based on the determined LC50 and filtered. Cells (at 80% confluency) are incubated with freshly prepared drugs for 48h in a humidified incubator before being trypsinized and washed with phosphate-buffer saline 3 times and stored at ?70°C. For cell viability assay, cells are seeded in at least triplicate wells for each concentration of drug per time at 1 × 104 cells/well in a 96-well plate. After 24h of seeding, the cells has grown to ~80% confluency. The medium is changed to that containing drugs at concentrations ranging from 0.0-50 mM. The concentration range for doxorubicin is 0-6 μM. After 24, 48 and 72 h, each well is filled with 25 μl MTT stock solution (4 mg/ml or 100 μg/well) and incubated for 3 h at 37°C. Formazan crystals are dissolved in 100 μl of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and quantified using a microplate reader at 570 nm. The MTT assays are performed at least 3 times for each drug and the percentage of surviving cells relative to control (untreated sample) is calculated.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | Sulfacetamide sodium salt hydrate |
| Molecular Weight | 254.2 |
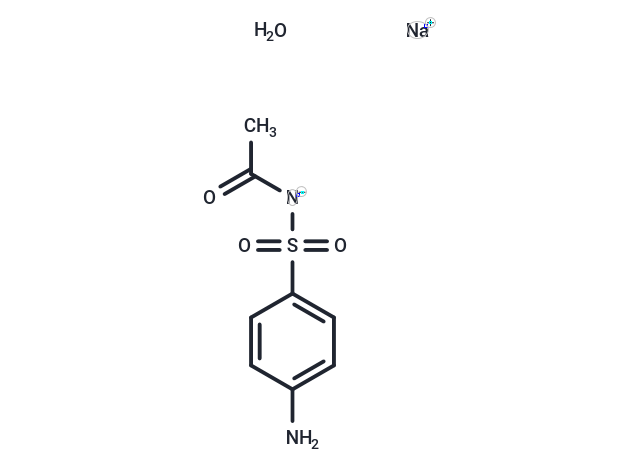
| Formula | C8H9N2NaO3S·H2O |
| Cas No. | 6209-17-2 |
| Smiles | O.[Na+].CC(=O)[N-]S(=O)(=O)c1ccc(N)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 16.67 mg/mL (65.57 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 196.7 mM, Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.