Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

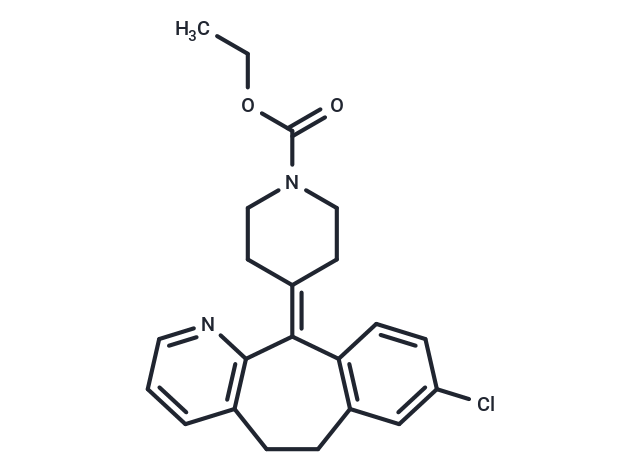
Loratadine (SCH 29851) is a second-generation histamine H1 receptor antagonist used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis and urticaria. Unlike most classical antihistamines (HISTAMINE H1 ANTAGONISTS) it lacks central nervous system depressing effects such as drowsiness.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $56 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $129 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | Loratadine (SCH 29851) is a second-generation histamine H1 receptor antagonist used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis and urticaria. Unlike most classical antihistamines (HISTAMINE H1 ANTAGONISTS) it lacks central nervous system depressing effects such as drowsiness. |
| Targets&IC50 | B(0)AT2:4 μM |
| In vivo | Loratadine blocks Kv1.5 channels in a concentration-, voltage-, time-, and use-dependent manner when expressed in human Ltk-cells transfected with the hKv1.5 channel gene at concentrations exceeding therapeutic plasma levels. It also inhibits rhinovirus-induced upregulation of ICAM-1 in main bronchial or transformed respiratory epithelial cells. Identified as a selective inhibitor of B(0)AT 2 with an IC50 of 4 μM, loratadine exhibits low or no activity against several other members of the SLC6 family. Pre-incubation with loratadine concentration-dependently suppresses the release of histamine and LTC4 in human FcεRI+ cells upon challenge with Der p1 antigen or anti-FcεRI. In human umbilical vein endothelial cells, loratadine significantly inhibits histamine-induced secretion of IL-6 and IL-8, with its active metabolites showing even stronger effects. Additionally, loratadine in a dose-dependent manner inhibits the mRNA of ICAM-1 induced by rhinovirus infection and completely suppresses the activation of the rhinovirus-induced ICAM-1 promoter. |
| Alias | SCH 29851, Loratidine |
| Molecular Weight | 382.88 |
| Formula | C22H23ClN2O2 |
| Cas No. | 79794-75-5 |
| Smiles | CCOC(=O)N1CC\C(CC1)=C1/C2=C(CCC3=C1N=CC=C3)C=C(Cl)C=C2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.261 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 77 mg/mL (201.11 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (130.59 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/Ethanol
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.