Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
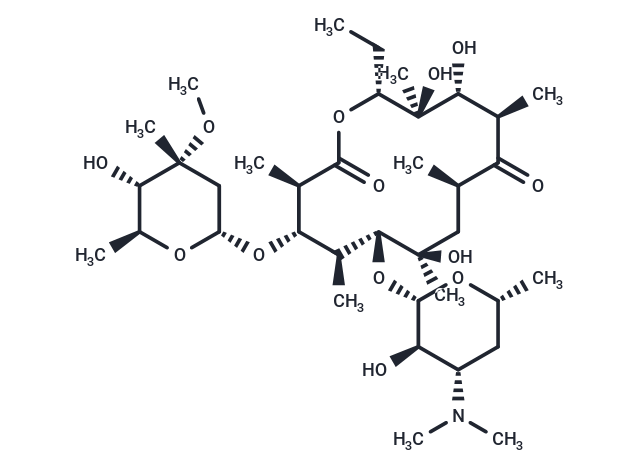
Erythromycin (E-Mycin) is a Macrolide and Macrolide Antimicrobial. The physiologic effect of erythromycin is by means of Decreased Sebaceous Gland Activity.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $44 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $53 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $97 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $48 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Erythromycin (E-Mycin) is a Macrolide and Macrolide Antimicrobial. The physiologic effect of erythromycin is by means of Decreased Sebaceous Gland Activity. |
| In vivo | Chlorthalidone is a thiazide-like diuretic. After oral intake, peak serum concentrations are achieved in 2-6 hours. The half-life of Chlorthalidone is approximately 42 (range 29-55) hours, reaching 45-60 hours after long-term dosing. However, interindividual variability in the half-life of Chlorthalidone is wide. Chlorthalidone is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. The natriuretic effect of Chlorthalidone is maximal at 18 hours and lasts more than 48 hours. Comparing different doses of Chlorthalidone, it has been observed that 25 mg daily is nearly as effective as higher doses, but with less risk of hypokalemia[1]. Chlorthalidone reduces calcium oxalate calculous recurrence but magnesium hydroxide does not. The effectiveness of Chlorthalidone or magnesium hydroxide is examined in the prevention of recurrent calcium oxalate kidney calculi. In a double-blind random allocation design daily dosages of 25 or 50 mg. Chlorthalidone, 650 or 1,300 mg. magnesium hydroxide, or an identical placebo are administered. All groups showed significantly decreased calculous events compared to the pretreatment rates. During the trial 56.1 per cent fewer calculi than predicted developed in the placebo group (p less than 0.01), whereas the groups receiving low and high dosage magnesium hydroxide showed 73.9 and 62.3 per cent fewer calculi, respectively (p less than 0.001 and less than 0.01, respectively). Chlorthalidone treatment results in a 90.1 per cent decrease from predicted rates and both dosages yielded similar results. When the treatments are compared Chlorthalidone is significantly better than the placebo or magnesium hydroxide (p less than 0.01). The large decreases in calculous events seen when placebo or ineffective therapy is given underscore the positive treatment bias that occurs when historical controls are used and they demonstrate the need for proper experimental design[2]. |
| Synonyms | E-Mycin |
| Molecular Weight | 733.93 |
| Formula | C37H67NO13 |
| Cas No. | 114-07-8 |
| Smiles | O([C@@H]1[C@@H](C)[C@H](O[C@H]2C[C@](OC)(C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)O2)[C@@H](C)C(=O)O[C@H](CC)[C@@](C)(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](C)C(=O)[C@H](C)C[C@@]1(C)O)[C@H]3[C@H](O)[C@@H](N(C)C)C[C@@H](C)O3 |
| Relative Density. | 1.2g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (340.63 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 3 mg/mL (4.09 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 136 mg/mL (185.3 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 5 mg/mL (6.81 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/Ethanol/DMSO
Ethanol/DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.