Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Amlodipine Besylate(Amlodipine benzenesulfonate) is a long-lasting calcium channel blocker.
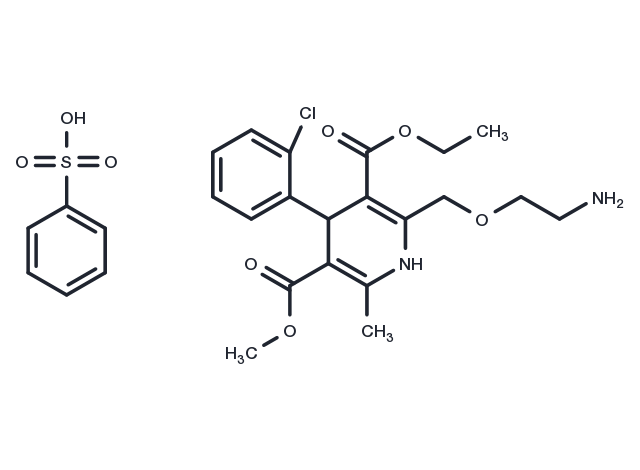
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 33.00 | |
| 1 g | In stock | $ 50.00 | |
| 5 g | In stock | $ 98.00 | |
| 1 mL * 10 mM (in DMSO) | In stock | $ 37.00 |





| Description | Amlodipine Besylate(Amlodipine benzenesulfonate) is a long-lasting calcium channel blocker. |
| Targets&IC50 | Ca2+ channel:1.9 nM |
| In vitro | Amlodipine is a safe and effective oral medication for treating systemic hypertension in cats. In swine coronary arteries with intact endothelium, Amlodipine notably reduces mean indirect systolic pressure, from 198 mmHg to 155 mmHg. |
| In vivo | In mice infused with angiotensin II, Amlodipine significantly reduced systolic blood pressure, LOX-1 expression, endothelial dysfunction, aortic hypertrophy, and the production of aortic O2(-) and ONOO(-), alongside a decrease in plasma levels of free 8-F(2)α-isoprostanes. In isolated pre-contracted endothelium-intact porcine coronary arteries, Amlodipine induced NO-mediated relaxation, resulting in a leftward shift of the concentration-relaxation curve toward bradykinin. Electron spin resonance spectroscopy in native endothelial cells revealed that Amlodipine increased NO production and stimulated an 8-fold rise in endothelial cyclic GMP levels. Furthermore, Amlodipine induced NO-mediated relaxation in isolated rat aortic rings, leading to downregulation of B2 receptor expression. In endothelial cells, Amlodipine time-dependently attenuated protein kinase C phosphorylation, similar to endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation, and also prevented phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced PKC activation. Amlodipine besylate reduced p85αPI3K, phosphorylated GSK-3β, phosphorylated Akt, Bcl-2, and heat shock transcription factor 1 induced H2O2 content, and inhibited Cyclooxygenase-2, cytosolic cytochrome c, cleaved caspase9, and the increase of cleaved caspase3 in neuronal cell apoptosis. |
| Synonyms | Amlodipine benzenesulfonate |
| Molecular Weight | 567.05 |
| Formula | C26H31ClN2O8S |
| CAS No. | 111470-99-6 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: 5.7 mg/mL (10 mM)
DMSO: 56.7 mg/mL (100 mM)
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Amlodipine Besylate 111470-99-6 Membrane transporter/Ion channel Metabolism Calcium Channel Inhibitor hypertension antianginal Amlodipine benzenesulfonate Amlodipine Ca channels dihydropyridine inhibit oral Ca2+ channels inhibitor
