Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Tiplaxtinin (Tiplasinin)(PAI-039) is a selective and orally efficacious inhibitor of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) with IC50 of 2.7 uM.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $37 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $59 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $87 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $156 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $273 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $538 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,150 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $66 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Tiplaxtinin (Tiplasinin)(PAI-039) is a selective and orally efficacious inhibitor of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) with IC50 of 2.7 uM. |
| Targets&IC50 | PAI1:2.7 μM |
| In vitro | In a panel of human bladder cell lines, PAI-1 results in the reduction of cellular proliferation, cell adhesion, and colony formation, and the induction of apoptosis and anoikis. [4] |
| In vivo | In a rat carotid thrombosis model, Tiplaxtinin (1 mg/kg, p.o.) increases time to occlusion and prevents the carotid blood flow reduction. [1] In C57BL/6J mice, (1 mg/g chow) attenuates Ang II-induced aortic remodeling. [2] In untreated type 1 diabetic mice, Tiplaxtinin (p.o.) restores skeletal muscle regeneration. [3] In athymic mice bearing human cancer cell line T24 and HeLa xenografts, Tiplaxtinin (1 mg/kg, p.o.) reduces tumor xenograft growth, associated with a reduction in tumor angiogenesis, a reduction in cellular proliferation, and an increase in apoptosis. [4] |
| Kinase Assay | Direct PAI-I in vitro activity assays : The chromogenic assay is initiated by the addition of tiplaxtinin (10 – 100 μM final concentration, maximum DMSO concentration of 0.2%) to recombinant human PAI-1 (140 nM in pH 6.6 buffer). After a 15 minute incubation at 25°C, 70 nM of recombinant human t-PA is added, and the combination of tiplaxtinin, PAI-1 and tPA are incubated for an additional 30 minutes. After the second incubation, Spectrozyme tPA, is added and absorbance read at 405 nm at 0 and 60 minutes. Relative PAI-1 inhibitory activity is equal to the residual tPA activity in the tiplaxtinin / PAI-1 treatment. Control treatments include the complete inhibition of tPA by PAI-1 at the molar ratio employed (2:1), and the absence of any effect of the tiplaxtinin on t-PA alone. The immunofunctional assay is based upon the non-SDS dissociable interaction between tPA and active PAI-1. Assay plates are coated with 100 μl of a solution of t-PA (10 μg/ml in TBS), and kept at 4 °C overnight. Tiplaxtinin is dissolved in DMSO and diluted to a final concentration of 1-100 μM as described above. Tiplaxtinin is then incubated with human PAI-1 (50 ng/ml) for 15 minutes, and an aliquot of this solution added to the t-PA-coated plate for 1 h. The solution is aspirated from the plate, which is then washed with a buffer consisting of 0.05% Tween 20 and 0.1% BSA in TBS. This assay detects only active inhibitory PAI-1 (not latent or substrate) bound to the plate, and is quantitated using a monoclonal antibody against human PAI-1 (MA33B8). A 1000X dilution of MA33B8 is added to the plate and incubated at for one hour, aspirated and washed. A secondary antibody consisting of goat anti-mouse IgG (H+L)-AP alkaline phosphatase conjugate is added, incubated for one hour, aspirated and washed. A 100 μl aliquot of alkaline phosphatase solution is added, followed by determination of absorbance at 405 nm 60 minutes later.The quantitation of residual active PAI-1 bound to t-PA at varying concentrations of tiplaxtinin is used to determine the IC50 by fitting the results to a logistic dose-response program, with the IC50 defined as the concentration of compound required to achieve 50% inhibition of PAI-1 activity. The assay sensitivity is 5 ng/ml of human PAI-1 as determined from a standard curve ranging from 0-100 ng/ml of human PAI-1. |
| Cell Research | Briefly, cell lines, T24, UM-UC-14, UROtsa, and HeLa cells are plated in 96-well dishes in triplicate at 1×103 cells per well and allowed to adhere for 24 hours. Subsequently, tiplaxtinin is added to the wells and allowed to incubate at the indicated concentrations. Cellular proliferation is determined by CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay according to manufacturer's instructions at 24 hours, and IC50 of tiplaxtinin is determined in Graphpad Prism. Luminescence was measured using a FLUOstar OPTIMA Reader.(Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | Tiplasinin, PAI-039 |
| Molecular Weight | 439.38 |
| Formula | C24H16F3NO4 |
| Cas No. | 393105-53-8 |
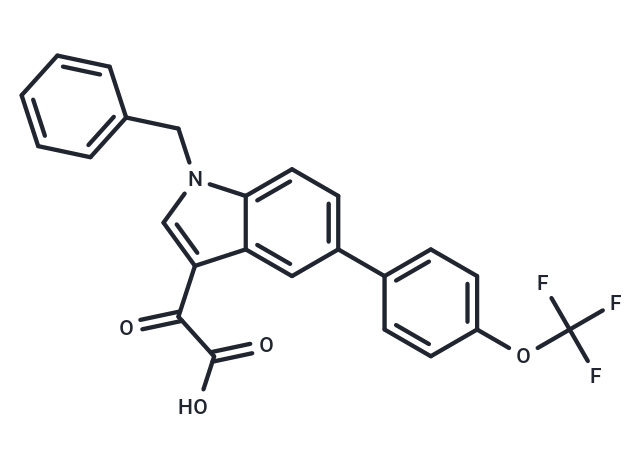
| Smiles | OC(=O)C(=O)c1cn(Cc2ccccc2)c2ccc(cc12)-c1ccc(OC(F)(F)F)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.34 g/cm3 |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: 15 mg/mL (34.14 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (113.8 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2 mg/mL (4.55 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.