Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

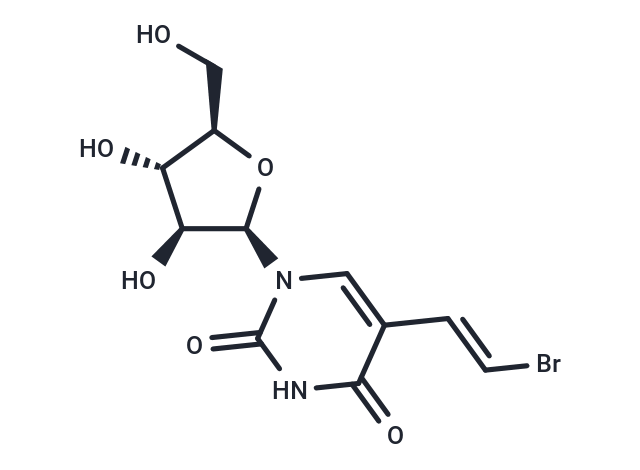
Sorivudine (BV-araU) has antiviral activity against several viruses including varicella zoster virus, herpes simplex type 1 virus, and Epstein-Barr virus by interfering with viral DNA synthesis.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $54 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $129 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $192 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $329 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $488 | In Stock |
| Description | Sorivudine (BV-araU) has antiviral activity against several viruses including varicella zoster virus, herpes simplex type 1 virus, and Epstein-Barr virus by interfering with viral DNA synthesis. |
| In vitro | Sorivudine inhibits strains of HSV-1 and HSV-2 (ID50s (50% inhibitory dose): 0.39 and 0.67 μM, respectively). Sorivudine has antiviral activity against several viruses including varicella-zoster virus, herpes simplex type 1 virus, and Epstein-Barr virus. Sorivudine has in vitro inhibitory activity against the varicella-zoster virus at concentrations of 00001-0.004 mg/ml. These concentrations are over 1000-fold lower than those which are required for the inhibition of VZV replication by acyclovir 3 Sorivudine also inhibits HSV-I replication at concentrations ranging from 0.03-0.1 mg/ml [1][2]. |
| In vivo | Sorivudine has been evaluated in the treatment of HSV-l encephalitis when administered orally to mice. The survival of treated mice is prolonged at dosages in excess of 12.5 mg/kg. A significant decrease in mortality was achieved as well with doses in excess of 50 mg/kg. Sorivudine therapy at dosages as low as 20 mg/kg per day given intramuscularly or 100 mg/kg per day administered orally completely protected against viremia and mortality. There was no evidence of neurotoxicity or abnormalities in hematology or clinical chemistries. Doses as low as 0.2 mg/kg per day were effective; however, breakthrough viremia was noted at lower dosages [2]. |
| Alias | BV-araU |
| Molecular Weight | 349.13 |
| Formula | C11H13BrN2O6 |
| Cas No. | 77181-69-2 |
| Smiles | OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)n1cc(\C=C\Br)c(=O)[nH]c1=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.31g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 125 mg/mL (358.03 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.