Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid is an amino acid that, as the D-isomer, is the defining agonist for the NMDA (N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid) receptor subtype of glutamate receptors.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $35 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $50 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $68 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $117 | In Stock |
| Description | N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid is an amino acid that, as the D-isomer, is the defining agonist for the NMDA (N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid) receptor subtype of glutamate receptors. |
| In vitro | NMDA is an excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter, which only binds to the NMDA receptor without effecting other glutamate receptors (such as those for AMPA and kainate). NMDA specifically binds to the NR2 subunits of NMDA receptor, and then stimulates the open of non-specific cation channel which can allow the passage of Ca2+ and Na+ into the cell and K+ out of the cell. Activation of the NMDA receptor is able to produce the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP), and trigger the increase of intracellular Ca2+ content which may further take participating in various signaling pathways. NMDA receptor plays a key role in a wide range of physiological (e.g. long-term potentiation and neuronal plasticity) and pathological processes (e.g. excitotoxicity and epilepsy). [1] |
| In vivo | Microinjection of NMDA (0.2 nM) significantly impacts male sexual behaviors, notably reducing both mount and intromission frequencies, while also shortening the latencies to intromission and ejaculation. Furthermore, NMDA markedly enhances, whereas AP-5 distinctly inhibits, ejaculatory behavior when observed during a 30-minute copulation test. When NMDA is bilaterally microinjected into the paraventricular nucleus (PVN), there is a notable increase in baseline lumbar sympathetic nerve activity (LSNA), with the peak increment of LSNA manifesting within 5 minutes of the procedure[3]. |
| Kinase Assay | Adrenal membranous homogenate suspensions are incubated with 10 nM [3H]Glu in 500/zl 50 mM Tris-acetate buffer (pH 7.4) at 2°C or 30°C in the presence and absence of various compounds. Incubation is terminated by the addition of 3 mL ice-cold buffer and subsequent filtration through a Whatman GF/B glass filter under a constant vacuum of 15 mm Hg. After washing the filter 4 times with 3 mL icecold buffer, the radioactivity trapped on the filter is measured by a liquid scintillation spectrometer using 5 mL modified Triton-toluene scintillant at a counting efficiency of 40-42%. The radioactivity found in the presence of 1 mM non-radioactive Glu is subtracted from each experimental value to obtain the specific binding of [3H]GIu in accordance with the y-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding assay system. The kinetic parameters of [3H]GIu binding, Kd and Bma x, are calculated by Scatchard analysis of the specific binding using a personal computer with a programme for non-linear regression analysis developed in our own laboratory. |
| Alias | N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 147.13 |
| Formula | C5H9NO4 |
| Cas No. | 6384-92-5 |
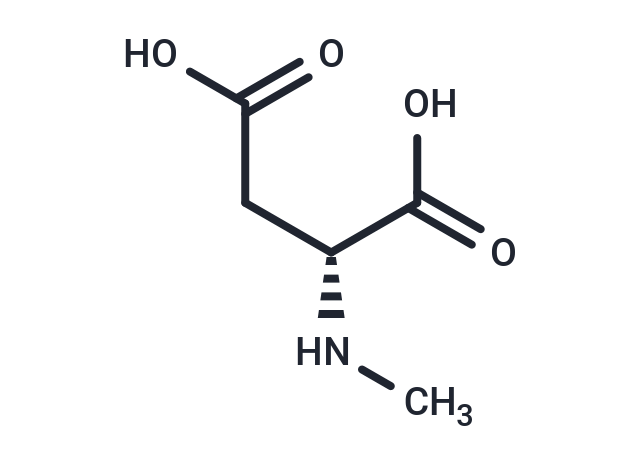
| Smiles | CN[C@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.4285 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 30 mg/mL (203.9 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 15 mg/mL (101.95 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.