Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
CAFESTOL is a ERK inhibitor for AP-1-targeted activity against PGE2 production and the mRNA expression of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells. Cafestol has strong inhibitory activity on PGE2 production by suppressing the NF-kB activation pathway.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $32 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $52 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $85 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $162 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $238 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | CAFESTOL is a ERK inhibitor for AP-1-targeted activity against PGE2 production and the mRNA expression of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells. Cafestol has strong inhibitory activity on PGE2 production by suppressing the NF-kB activation pathway. |
| In vitro | The precise molecular mechanism of the antiinflammatory activity of cafestol in terms of prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) production, a critical factor involved in inflammatory responses. Cafestol inhibited both PGE(2) production and the mRNA expression of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated RAW264.7 cells. This compound strongly decreased the translocation of c-Jun into the nucleus and AP-1 mediated luciferase activity. In kinase assays using purified extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) or immunoprecipitated ERK prepared from LPS-treated cells in the presence or absence of cafestol, it was found that this compound can act as an inhibitor of ERK2 but not of ERK1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (MEK 1). Suggest that cafestol may be a novel ERK inhibitor with AP-1-targeted inhibitory activity against PGE(2) production in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells[1]. |
| In vivo | CAFESTOL possesses antidiabetic properties in KKAy mice. Consequently, cafestol may contribute to the reduced risk of developing T2D in coffee consumers and has a potential role as an antidiabetic drug[2]. |
| Animal Research | Cafestol can postpone development of T2D in KKAy mice. Forty-seven male KKAy mice were randomized to consume chow supplemented daily with either 1.1 (high), 0.4 (low), or 0 (control) mg of cafestol for 10 weeks. Collected blood samples for fasting glucose, glucagon, and insulin as well as liver, muscle, and fat tissues for gene expression analysis. Isolated islets of Langerhans and measured insulin secretory capacity. After 10 weeks of intervention, fasting plasma glucose was 28-30% lower in cafestol groups compared with the control group (p < 0.01). Fasting glucagon was 20% lower and insulin sensitivity improved by 42% in the high-cafestol group (p < 0.05). Cafestol increased insulin secretion from isolated islets by 75-87% compared to the control group (p < 0.001)[2]. |
| Molecular Weight | 316.43 |
| Formula | C20H28O3 |
| Cas No. | 469-83-0 |
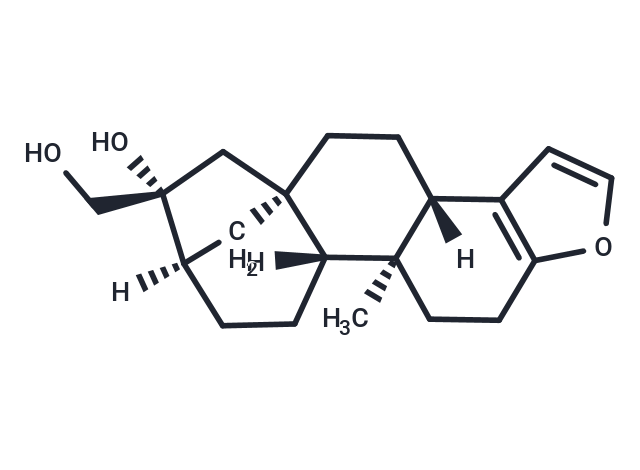
| Smiles | [H][C@@]12C[C@]3(C[C@]1(O)CO)CC[C@]1([H])c4ccoc4CC[C@@]1(C)[C@]3([H])CC2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.23 g/cm3 at 20℃ |
| Color | Yellow |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 5 mg/mL (15.8 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.