Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

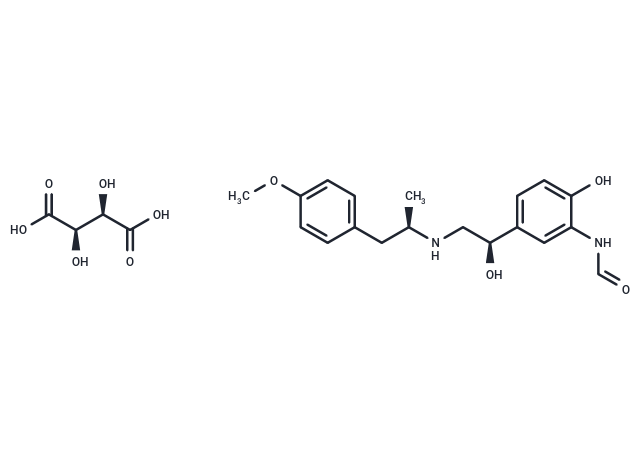
Arformoterol Tartrate ((R,R)-Formoterol tartrate) is the tartrate salt of arformoterol. Arformoterol is a long-acting beta-2 adrenergic agonist with bronchodilator activity[2].
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | 52 € | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | 75 € | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | 145 € | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | 221 € | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | 328 € | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | 487 € | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | 73 € | In Stock |
| Description | Arformoterol Tartrate ((R,R)-Formoterol tartrate) is the tartrate salt of arformoterol. Arformoterol is a long-acting beta-2 adrenergic agonist with bronchodilator activity[2]. |
| Targets&IC50 | β2-adrenoceptor:2.9 nM (Kd) |
| In vivo | Arformoterol (R,R-formoterol) is a active isomer of racemic formoterol and is indicated for the long-term, maintenance treatment of bronchoconstriction in patients with COPD including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is a potent and selective agent which causes bronchial smooth muscle relaxation and inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators. Its pharmacological effects can be attributed to the increased intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels that result from the stimulation of intracellular adenyl cyclase. Arformoterol tartrate is well absorbed through lungs when administered by a nebulizer. The mean peak plasma concentration (Cmax) and systemic exposure (AUC0-12h) are 4.3 pg/mL and 34.5 pg.h/mL, respectively, when 15 μg arformoterol is administered every 12 h for 14 days in COPD patients. The time to achieve median steady state peak plasma concentration (tmax) is approximately half an hour after drug administration. The mean terminal half-life is 26 h in COPD patients when treated with 15 μg inhaled arformoterol twice daily for 14 days. The binding of arformoterol to human plasma proteins in vitro is 52-65% at concentrations of 0.25, 0.5 and 1.0 ng/mL of radiolabeled arformoterol. Metabolism occurs primarily by direct conjugation (glucuronidation) and secondary route of metabolism is via O-demethylation. Metabolism is mediated by atleast five human uridine diphosphoglucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isozymes as well as CYP2D6 and CYP2C19. After administration of a single oral dose of radiolabeled arformoterol, 63% of the radioactive amount was recovered in urine and 11% in feces within 48 h. A total of 89% of the total radioactive dose was recovered within 14 days, with 67% in urine and 22% in faeces[1]. |
| Animal Research | Exposure of C57BL/6 mice(8 wk old) to 400 ppm Cl(2) for 30 minutes increased respiratory system resistance and airway responsiveness to aerosolized methacholine. Intranasal administration of arformoterol mitigated the Cl(2) effects on airway reactivity and AFC, presumably by increasing lung cyclic AMP level. Arformoterol did not modify the inflammatory responses, as evidenced by the number of inflammatory cells and concentrations of IL-6 and TNF-α in the bronchoalveolar lavage. NF-κB activity (assessed by p65 Western blots and electrophoretic mobility shift assay) remained at control levels up to 24 hours after Cl(2) exposure. Our results provide mechanistic insight into the effectiveness of long-term β(2)-agonists in reversing Cl(2)-induced reactive airway dysfunction syndrome and injury to distal lung epithelial cells[2]. |
| Alias | (R,R)-Formoterol tartrate |
| Molecular Weight | 494.49 |
| Formula | C23H30N2O10 |
| Cas No. | 200815-49-2 |
| Smiles | O[C@H]([C@@H](O)C(O)=O)C(O)=O.COc1ccc(C[C@@H](C)NC[C@H](O)c2ccc(O)c(NC=O)c2)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (111.23 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.