 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

AICAR (Acadesine) is an AMPK activator. AICAR has the functions of metabolic regulation, muscle function regulation, anti-cancer effect, neuroprotection and anti-aging.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $30 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | AICAR (Acadesine) is an AMPK activator. AICAR has the functions of metabolic regulation, muscle function regulation, anti-cancer effect, neuroprotection and anti-aging. |
| Targets&IC50 | Autophagy (rat hepatocytes):0.3 mM |
| In vitro | METHODS: CCRF-CEM, HeLa, and L1210 cells were treated with different concentrations of AICAR for 3 days. particle counting analysis was used to evaluate the inhibition of cell growth. RESULTS: AICAR inhibited the growth of CCRF-CEM cells (IC50=210 μM) and HeLa cells (IC50=165 μM), but did not inhibit the growth of L1210 cells (IC50≥ 250 μM). [1] METHODS: HCT-116 and HEK293 cells were treated with AICAR for 48 hours, and cytotoxicity was detected by the MTT method. RESULTS: AICAR is non-toxic to HCT-116 (EC50> 100 μM) and HEK293 (EC50> 100 μM) cells. [2] METHODS: K562 and K-562R cells were treated with AICAR for 48 hours, and the cytotoxicity was detected by the XTT method. RESULTS: AICAR showed cytotoxicity to K562 (IC50=800 μM) and K-562R (IC50=800 μM). [3] METHODS: K562 cells were treated with AICAR for 48 hours, and the anti-leukemia activity was detected by the XTT method. RESULTS: AICAR exhibited anti-leukemia activity against K562 (IC50=800 μM). [4] METHODS: MDA-MB-231 and RCC4 cells were treated with AICAR for 48 hours, and the anti-tumor activity was detected by the XTT method. RESULTS: AICAR exhibited anti-tumor activity against MDA-MB-231 cells (IC50=1000 μM) and RCC4 cells (IC50=250 μM). [5] METHODS: MDA-MB-453 and SK-BR-3 cells were treated with AICAR for 4 days, and their antiproliferative activity was detected by the Celltiter-glo luminescent cell viability assay. RESULTS: AICAR exhibited anti-tumor activity against MDA-MB-453 cells (IC50=1700 μM) and SK-BR-3 cells (IC50=180 μM). [6] METHODS: HepG2 cells were treated with AICAR (0.1-1.0 mM) for 12, 24 and 48 hours, and the protein levels were detected by western blot. RESULTS: The expression levels of IR-β in 0.25, 0.5 and 1.0 mM AICAR significantly decreased to 50%, 53% and 46% of the control at 48 h. [7] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the anti-tumor activity of AICAR, AICAR was subcutaneously injected (300 mg/kg/ day) into xenograft tumor mice derived from the H1975 cell line. RESULTS: AICAR significantly inhibited tumor growth, and the tumor weight decreased by 47% (p<0.05). The expression level of Ki-67 in tumor tissues treated with AICAR decreased, indicating a reduction in cell proliferation, while the expression levels of DNA damage markers γ-H2AX and p21Cip1 increased. [8] METHODS: To study the anti-tumor activity of AICAR, xenograft mice of MG63 and KHOS osteosarcoma cell lines were administered with AICAR (450 mg/kg/ day). RESULTS: AICAR treatment significantly inhibited tumor growth, and the tumor volume decreased by 14.1% and 35.4% respectively (p<0.05). Mitochondrial proliferation and apoptotic activities increased in tumor tissues treated with AICAR. [9] |
| Cell Research | Acadesine is added to K562 cell lines or primary cells (103 CD34+ cells/mL) growing in semisolid methyl cellulose medium. MethoCult H4100 or H4236 are used for cell lines and primary CD34+ cells respectively. Colonies are detected after 10 days of culture by adding 1 mg/mL of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reagent and are scored by Image J quantification software. (Only for Reference) |
| Synonyms | NSC105823, AICAR (Acadesine), AICA Riboside, Acadesine |
| Molecular Weight | 258.23 |
| Formula | C9H14N4O5 |
| Cas No. | 2627-69-2 |
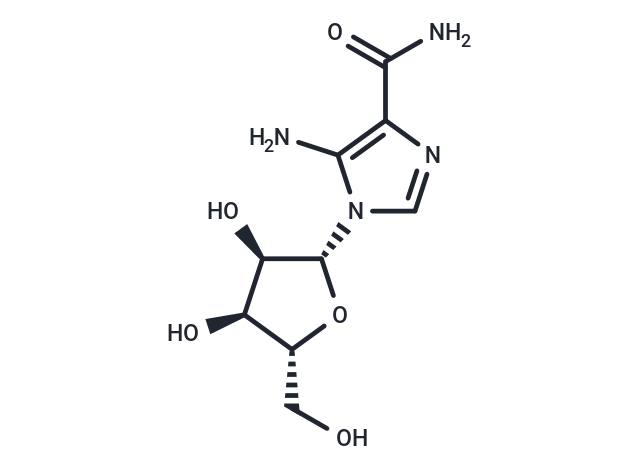
| Smiles | NC(=O)c1ncn([C@@H]2O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)c1N |
| Relative Density. | 2.06 g/cm3 |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 19.4 mg/mL (75.13 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 163.3 mg/mL (632.38 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 5 mg/mL (19.36 mM), Sonication is recommended. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.