 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Busulfan is an alkylating antineoplastic agent derived from dimethane sulfonate, with cytotoxic and immunosuppressive properties. It primarily acts by forming carbonium ions in vivo, which induce cross-linking between DNA strands or between DNA and proteins, leading to DNA damage, inhibition of DNA replication, and suppression of RNA transcription. In addition, Busulfan can inhibit thioredoxin reductase and induce apoptosis. It is commonly used as a myeloablative agent in preconditioning regimens for bone marrow transplantation and can also be used to establish anemia models.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $45 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $62 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Busulfan is an alkylating antineoplastic agent derived from dimethane sulfonate, with cytotoxic and immunosuppressive properties. It primarily acts by forming carbonium ions in vivo, which induce cross-linking between DNA strands or between DNA and proteins, leading to DNA damage, inhibition of DNA replication, and suppression of RNA transcription. In addition, Busulfan can inhibit thioredoxin reductase and induce apoptosis. It is commonly used as a myeloablative agent in preconditioning regimens for bone marrow transplantation and can also be used to establish anemia models. |
| In vitro | Mice transplanted with busulfan exhibit slow and incomplete lymphoid engraftment. Mice treated with busulfan demonstrate a significant increase in apoptosis and a reduction in testicular weight. In NOD/SCID mice, busulfan treatment combined with irradiation achieves a detection sensitivity similar to that of limiting dilution assays. A dose-dependent lymphoid tissue reconstitution is provided in mice with 20 mg/kg to 100 mg/kg of busulfan. At 40 mg/kg, busulfan induces the maximum number of apoptotic cells while minimizing the number of necrotic cells. |
| In vivo | Busulfan, an alkylating agent that induces DNA damage through cross-linking DNA with DNA and proteins, triggers senescence in normal human diploid WI38 fibroblast cells via a cascade mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), independent of the p53-DNA damage pathway. Busulfan causes a transient reduction in glutathione levels, followed by a sustained increase in ROS production. The hypophosphorylation of Rb induced by Busulfan inhibits the expression of PCNA in testicular cells, preventing apoptosis of spermatogonial stem cells. Moreover, while Busulfan reduces the frequency of cobblestone area-forming cells, it does not significantly increase apoptosis in hematopoietic stem cells (HSC)-like cells and progenitor cells with similar phenotypes. Busulfan suppresses the hematopoietic function of HSC-like cells and progenitor cells through an apoptosis-dependent mechanism. Additionally, Busulfan-induced senescence in bone marrow hematopoietic cells correlates with a time-dependent increase in the expression of p16Ink4a and p19Arf. |
| Synonyms | Sulphabutin, Myleran, Busulphan |
| Molecular Weight | 246.30 |
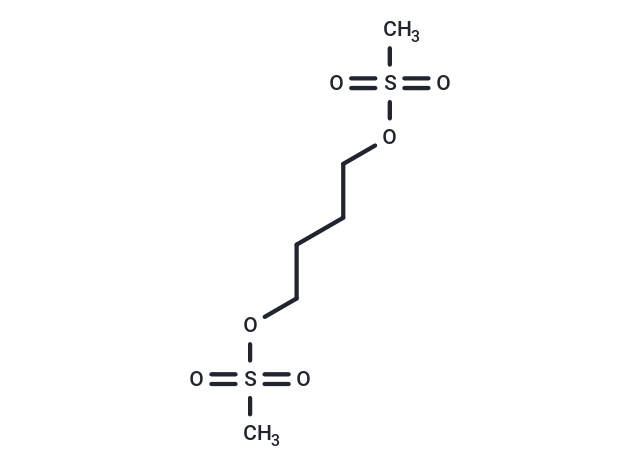
| Formula | C6H14O6S2 |
| Cas No. | 55-98-1 |
| Smiles | CS(=O)(=O)OCCCCOS(C)(=O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.35 g/cm3 |
| Storage | store under nitrogen | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 50.00 mg/mL (203.00 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 3.00 mg/mL (12.18 mM) Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.