Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Rotenone is a natural plant-derived insecticide that acts as an inhibitor of mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I. It promotes the generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, induces apoptosis, and is commonly used to establish Parkinson's disease models.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $42 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $50 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $89 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $46 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Rotenone is a natural plant-derived insecticide that acts as an inhibitor of mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I. It promotes the generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, induces apoptosis, and is commonly used to establish Parkinson's disease models. |
| Targets&IC50 | A549 cells (24 h):26 μM (ED50), A549 cells:0.04 μg/mL, 697 cells (72 h):0.3 μM, A549 cells:0.901 μg/mL, 697 cells (48 h):0.3 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human leukemia cells HL-60 were treated with Rotenone (0-1000 nM) for 30 min and oxygen consumption was measured using a Clark oxygen electrode. RESULTS: Rotenone dose-dependently inhibited HL-60 cell respiration. Rotenone inhibited cellular respiration by more than 96% at 500 nM. [1] METHODS: 10th DIV cells were treated with Rotenone (20 nM) for 48 h. LDH levels were measured by LDH release assay. RESULTS: LDH release can be used as an indicator of general cytotoxicity. rotenone induced an increase in LDH release, and LDH activity increased more than 6-fold compared to the control group. LDH activity increased more than 6-fold compared to the control group.[2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To establish a reproducible mouse model of Rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease (PD), Rotenone (2.5 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to C57Bl/6 mice once daily for two weeks. RESULTS: Systemic exposure of mice to Rotenone resulted in progressive accumulation and regional spread of p129 aggregates, which preceded the maximal loss of DAn. [3] METHODS: To study neurotoxicity, Rotenone (30-100 mg/kg) was administered orally to C57BL/6 mice once daily for fifty-six days. RESULTS: The survival of Rotenone-treated mice at 30 mg/kg was unchanged from 28-56 days, although the survival of Rotenone-treated mice was reduced to approximately 70% within one week. 100 mg/kg Rotenone-treated mice showed a sudden decrease in survival after 28 days, and ultimately to approximately 15% after 56 days. A regimen of Rotenone given chronically at 30 mg/kg for 56 days is more useful for understanding the mechanisms of DA neurodegeneration. [4] |
| Synonyms | Rotocide, Rotenon, Paraderil, Dactinol, Barbasco |
| Molecular Weight | 394.42 |
| Formula | C23H22O6 |
| Cas No. | 83-79-4 |
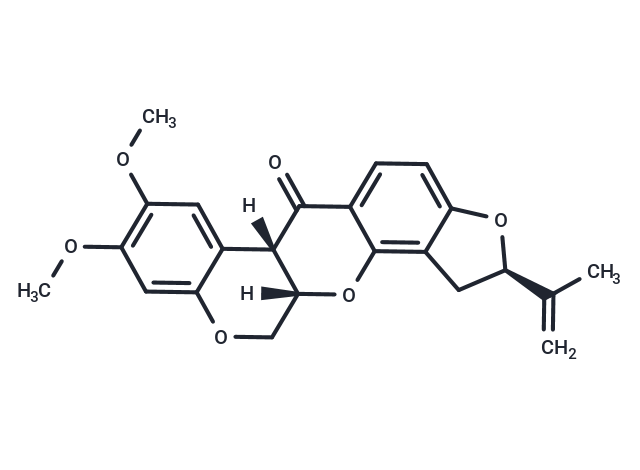
| Smiles | O=C1C=2C(=C3C(O[C@@H](C(C)=C)C3)=CC2)O[C@]4([C@@]1(C=5C(OC4)=CC(OC)=C(OC)C5)[H])[H] |
| Relative Density. | 1.27(20°C) |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,store under nitrogen | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (253.54 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 3.95 mg/mL (10.01 mM), Suspension. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.