Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

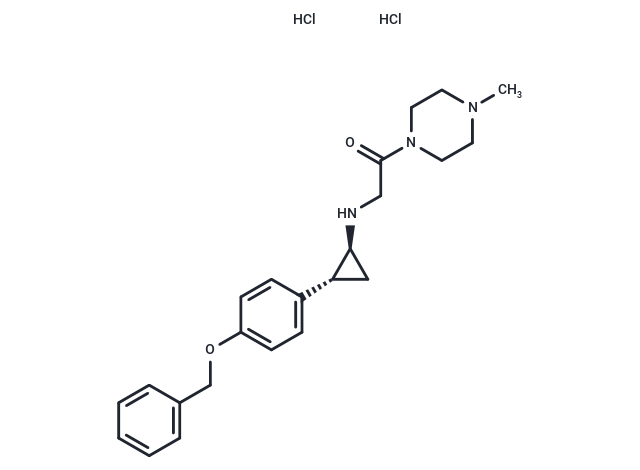
RN-1 dihydrochloride is an effective and selective irreversible inhibitor of lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1, IC50 = 70 nM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $42 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $98 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $158 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $269 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $392 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $569 | In Stock |
| Description | RN-1 dihydrochloride is an effective and selective irreversible inhibitor of lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1, IC50 = 70 nM). |
| Targets&IC50 | MAO-B:2.785 μM, MAO-A:0.51 μM, LSD1:70 nM |
| In vitro | RN-1 dihydrochloride exhibits selectivity for LSD1 over MAO-A and MAO-B with IC50 values of 0.51 μM and 2.785 μM respectively[3]. |
| In vivo | In sickle cell disease (SCD) mice, RN-1 dihydrochloride (3-10 mg/kg; i.p.) effectively induces fetal hemoglobin (HbF) levels in red blood cells and reduces disease pathology[1]. In C57BL/6 male mice, after administration of RN-1 dihydrochloride (10 mg/kg, i.p.), concentrations are detectable up to 24 h post dose in both plasma and brain tissues. RN-1 dihydrochloride significantly impairs long-term memory, but not short-term memory. The brain/plasma exposure ratio is 88.9[3]. |
| Molecular Weight | 452.42 |
| Formula | C23H31Cl2N3O2 |
| Cas No. | 1781835-13-9 |
| Smiles | Cl.Cl.CN1CCN(CC1)C(=O)CN[C@H]1C[C@@H]1c1ccc(OCc2ccccc2)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 18 mg/mL (39.79 mM), Sonication and heating to 60℃ are recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.