 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Eicosapentaenoic Acid is an ω-3 fatty acid and an inhibitor of fatty acid synthase (FASN). Eicosapentaenoic Acid promotes DNA demethylation in the reexpression of the tumor suppressor gene CCAAT/ enhancer-binding protein δ (C/EBPδ). Eicosapentaenoic Acid activates the RAS/ERK/C/EBPβ pathway in U937 leukemia cells through demethylation of the CpG island of H-RAS intron 1. Eicosapentaenoic Acid promotes the relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells and vasodilation.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $36 | - | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $48 | - | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $68 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $159 | - | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | - | In Stock |

| Description | Eicosapentaenoic Acid is an ω-3 fatty acid and an inhibitor of fatty acid synthase (FASN). Eicosapentaenoic Acid promotes DNA demethylation in the reexpression of the tumor suppressor gene CCAAT/ enhancer-binding protein δ (C/EBPδ). Eicosapentaenoic Acid activates the RAS/ERK/C/EBPβ pathway in U937 leukemia cells through demethylation of the CpG island of H-RAS intron 1. Eicosapentaenoic Acid promotes the relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells and vasodilation. |
| Targets&IC50 | RBL-2H3 cells:> 50 μM, MDA-MB-468 cells:> 100 μM, MDA-MB-468 cells:> 100 μM (EC50) |
| In vitro | METHODS: HepG2 cells were treated with Eicosapentaenoic Acid (0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 mM) for 12 hours, and the inhibitory effect on cell growth was detected by the MTT assay. RESULTS: Eicosapentaenoic Acid inhibited the growth of HepG2 cells (IC50=50 µM). [1] METHODS: N2a cells were treated with Eicosapentaenoic Acid (1.5 µM-200 µM). The fluorescence intensity of fluorescin was measured by 485 nm excitation and 528 nm emission using a microplate reader to quantify the number of viable cells. RESULTS: Eicosapentaenoic Acid at 25 µM was considered to have no significant effect on cell viability and was used in subsequent cell protection experiments, indicating that its toxicity to cells was relatively low at this concentration. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the protective effect of Eicosapentaenoic Acid on the cardiovascular system, a diet rich in Eicosapentaenoic Acid was fed to spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) for 20 weeks. RESULTS: Rats in the Eicosapentaenoic Acid diet group showed a reduction in interstitial cardiac fibrosis and an improvement in left ventricular diastolic function, despite persistently elevated blood pressure. The Eicosapentaenoic Acid diet increased the mRNA expression of M2-type macrophage marker Mrc1 and anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10) in cardiac tissue. It indicates that the anti-fibrotic effect of EPA is partially achieved by promoting the polarization of macrophages to the anti-inflammatory M2 type and increasing IL-10. [3] METHODS: To study the antiviral efficacy of Eicosapentaenoic Acid, Eicosapentaenoic Acid (10, 50, and 100 mg/kg) was orally administered to C57 mice for 2 consecutive days. RESULTS: There was no significant difference in the serum ALT and urine CRE levels of mice in the Eicosapentaenoic Acid administration group compared with the control group, indicating that EPA had no hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity to mice at the given dose. HE staining also showed that EPA did not cause tissue damage in the liver and kidney tissues of mice. [4] |
| Molecular Weight | 302.45 |
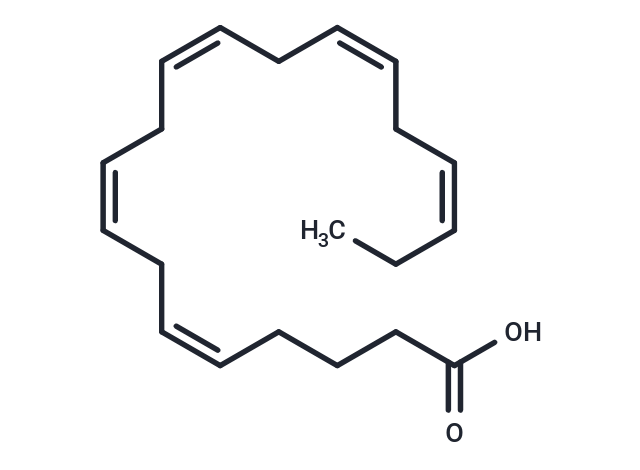
| Formula | C20H30O2 |
| Cas No. | 10417-94-4 |
| Smiles | CC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCC(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 0.943g/mLat 25°C(lit.) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Pure form: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (330.63 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 50 mg/mL (165.32 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.