Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


Phosphorylethanolamine (O-Phosphorylethanolamine) is a phosphomonoester metabolite of the phospholipid metabolism. Phosphorylethanolamine is a precursor of phospholipid synthesis and a product of phospholipid breakdown. Phosphomonoesters are present at much higher levels in the brain than in other organs. In developing the brain, phosphomonoesters are normally elevated during the period of neuritic proliferation. This also coincides with the occurrence of normal programmed cell death and synaptic pruning in developing the brain. These findings are consistent with the role of phosphomonoesters in membrane biosynthesis. Phosphorylethanolamine shows a strong structural similarity to the inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA, and the GABAB receptor partial agonist, 3-amino-propylphosphonic acid. Phosphorylethanolamine is a phosphomonoester which is decreased in post-mortem Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | In stock | $ 29.00 |


| Description | Phosphorylethanolamine (O-Phosphorylethanolamine) is a phosphomonoester metabolite of the phospholipid metabolism. Phosphorylethanolamine is a precursor of phospholipid synthesis and a product of phospholipid breakdown. Phosphomonoesters are present at much higher levels in the brain than in other organs. In developing the brain, phosphomonoesters are normally elevated during the period of neuritic proliferation. This also coincides with the occurrence of normal programmed cell death and synaptic pruning in developing the brain. These findings are consistent with the role of phosphomonoesters in membrane biosynthesis. Phosphorylethanolamine shows a strong structural similarity to the inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA, and the GABAB receptor partial agonist, 3-amino-propylphosphonic acid. Phosphorylethanolamine is a phosphomonoester which is decreased in post-mortem Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain. |
| Synonyms | O-Phosphorylethanolamine |
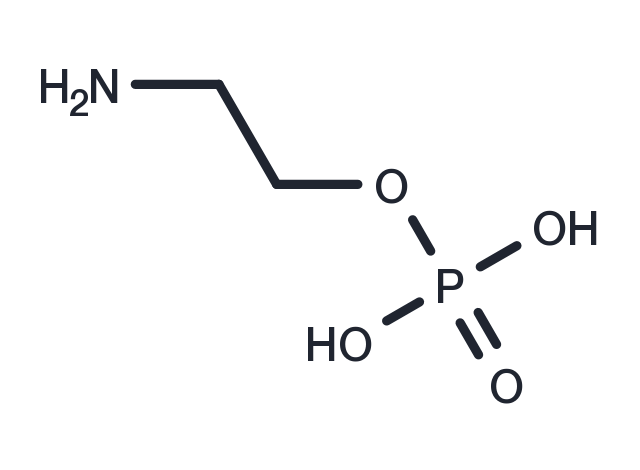
| Molecular Weight | 141.06 |
| Formula | C2H8NO4P |
| CAS No. | 1071-23-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: Slightly soluble
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
Phosphorylethanolamine 1071-23-4 Metabolism Others Endogenous Metabolite O-Phosphorylethanolamine inhibit NSC254167 Inhibitor NSC 254167 Monoaminoethyl O-Phosphoethanolamine NSC-254167 inhibitor
