Shopping Cart
Remove All Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
PTUPB is a potent dual inhibitor of sEH and COX-2 enzymes with IC50 values of 0.9 nM and 1.26 μM, respectively.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $74 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $179 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $289 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $538 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $859 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $1,280 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $216 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | PTUPB is a potent dual inhibitor of sEH and COX-2 enzymes with IC50 values of 0.9 nM and 1.26 μM, respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | sEH:0.9 nM, COX-1:1.26 μM, COX-1:100 μM |
| In vitro | PTUPB has minimal inhibitory effects on cell proliferation in multiple cancer cell lines, including human melanoma cell and a transformed endothelial cell, whereas it potently inhibits HUVEC proliferation after 3 days of application[1]. |
| In vivo | PTUPB inhibits LLC tumor growth by 70-83% and exhibits with no overt toxicity, such as any weight loss when it is compared with the control group. After a period of treatment, the peak plasma concentration of PTUPB is high[1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 543.56 |
| Formula | C26H24F3N5O3S |
| Cas No. | 1287761-01-6 |
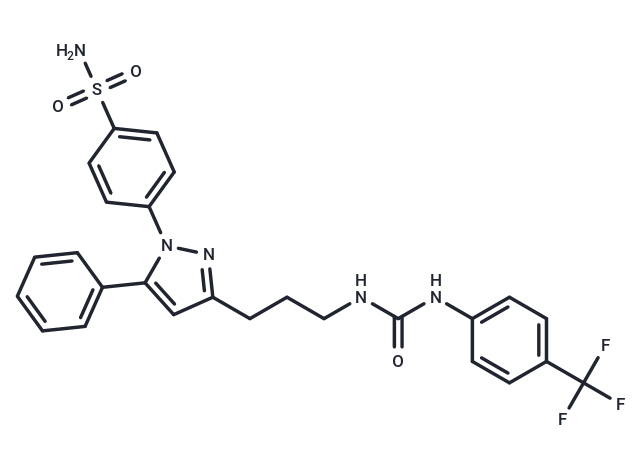
| Smiles | NS(=O)(=O)c1ccc(cc1)-n1nc(CCCNC(=O)Nc2ccc(cc2)C(F)(F)F)cc1-c1ccccc1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (183.97 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.