Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Levofloxacin ((-)-Ofloxacin) is a synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic that inhibits the superhelical activity of bacterial DNA rotamase and prevents DNA replication. Levofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used for the treatment of a wide range of bacterial infections.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $76 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Levofloxacin ((-)-Ofloxacin) is a synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic that inhibits the superhelical activity of bacterial DNA rotamase and prevents DNA replication. Levofloxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic used for the treatment of a wide range of bacterial infections. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Bladder cell lines SV-HUC-1 and T24 were treated with Levofloxacin (25-800 µg/mL) for 24-48 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. RESULTS: Levofloxacin is cytotoxic in a dose- and time-dependent manner. [1] METHODS: IL-1β-stimulated inflammatory FLS cells were treated with Levofloxacin (14-224 µM) for 24 h, and gene expression levels were measured by RT-qPCR. RESULTS: When IL-1β-stimulated inflammatory FLS were treated with Levofloxacin for 24 h, the mRNA levels of MMP-1 and MMP-3 were increased in a concentration-dependent manner, and the mRNA expression level of TIMP-1 was also increased accordingly. In addition, the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and COX-2 decreased in a concentration-dependent manner, while PGE2 did not show any significant changes. In addition, the expression levels of Caspase-3 and Caspase-8 increased in a concentration-dependent manner. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study in vivo antimicrobial activity, Levofloxacin (100 mg/kg) and Imipenem (100 mg/kg) were administered intraperitoneally four times at 3 h intervals in the Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia mouse model. RESULTS: For Levofloxacin-sensitive strains, Levofloxacin and Imipenem were less bactericidal, with a slight reduction in lung bacterial counts compared to values at the start of treatment. The combination of Levofloxacin and Imipenem did not increase bactericidal activity. All regimens tested significantly reduced mortality compared to controls. [3] |
| Alias | Tavanic, Levaquin, Fluoroquinolone, Cravit, (-)-Ofloxacin |
| Molecular Weight | 361.37 |
| Formula | C18H20FN3O4 |
| Cas No. | 100986-85-4 |
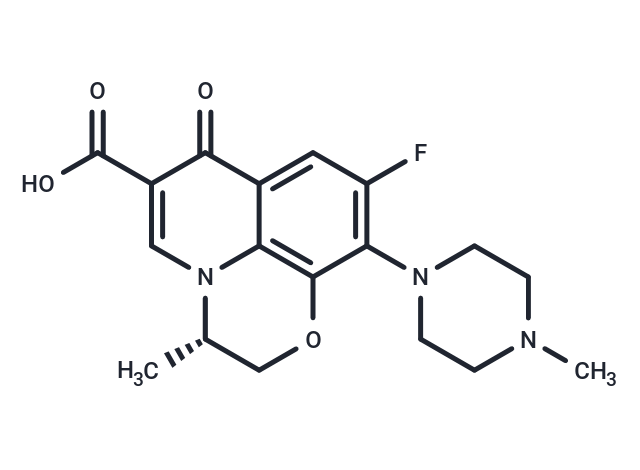
| Smiles | O=C1C=2C3=C(C(=C(F)C2)N4CCN(C)CC4)OC[C@H](C)N3C=C1C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.48 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 12.5 mg/mL (34.59 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 2 mg/mL (5.53 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 9 mg/mL (24.91 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/H2O/DMSO
H2O/DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.