Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year


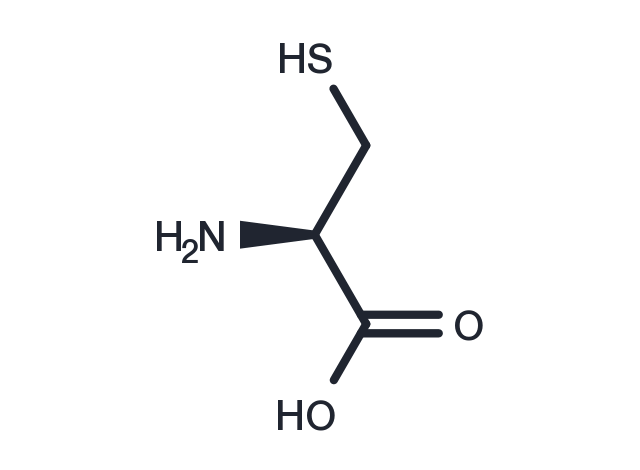
L-Cysteine (L-(+)-Cysteine) is a non-essential sulfur-containing amino acid in humans. L-Cysteine is important for protein synthesis, detoxification, and diverse metabolic functions. Found in beta-keratin, the main protein in nails, skin, and hair, L-Cysteine is important in collagen production, as well as skin elasticity and texture. Also required in the manufacture of amino acid taurine, L-Cysteine is a component of the antioxidant glutathione, and plays a role in the metabolism of essential biochemicals such as coenzyme A, heparin, and biotin.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | In stock | $ 41.00 | |
| 1 g | In stock | $ 48.00 |





| Description | L-Cysteine (L-(+)-Cysteine) is a non-essential sulfur-containing amino acid in humans. L-Cysteine is important for protein synthesis, detoxification, and diverse metabolic functions. Found in beta-keratin, the main protein in nails, skin, and hair, L-Cysteine is important in collagen production, as well as skin elasticity and texture. Also required in the manufacture of amino acid taurine, L-Cysteine is a component of the antioxidant glutathione, and plays a role in the metabolism of essential biochemicals such as coenzyme A, heparin, and biotin. |
| Synonyms | Thioserine, cysteine, L-(+)-Cysteine |
| Molecular Weight | 121.16 |
| Formula | C3H7NO2S |
| CAS No. | 52-90-4 |
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
DMSO: Insoluble
H2O: 10 mM
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
L-Cysteine 52-90-4 Metabolism Endogenous Metabolite taurine Thioserine Inhibitor hydrogen ghrelin glutathione conditionally cysteine L Cysteine LCysteine H2S inhibit sulphide L-(+)-Cysteine appetite inhibitor
