 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Hydralazine hydrochloride (Apresoline) is the hydrochloride salt of hydralazine, a phthalazine derivative with antihypertensive and potential antineoplastic activities. Hydralazine alters intracellular calcium release and interferes with smooth muscle cell calcium influx, resulting in arterial vasodilatation. This agent also inhibits the phosphorylation of myosin protein and chelation of trace metals required for smooth muscle contraction, resulting in an increase in heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output. In addition to its cardiovascular effects, hydralazine inhibits DNA methyltransferase, which may result in inhibition of DNA methylation in tumor cells.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 mg | $36 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $73 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $106 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Hydralazine hydrochloride (Apresoline) is the hydrochloride salt of hydralazine, a phthalazine derivative with antihypertensive and potential antineoplastic activities. Hydralazine alters intracellular calcium release and interferes with smooth muscle cell calcium influx, resulting in arterial vasodilatation. This agent also inhibits the phosphorylation of myosin protein and chelation of trace metals required for smooth muscle contraction, resulting in an increase in heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output. In addition to its cardiovascular effects, hydralazine inhibits DNA methyltransferase, which may result in inhibition of DNA methylation in tumor cells. |
| In vitro | Hydralazine impairs up-regulation of RAG-2 gene expression and reduces secondary Ig gene rearrangements. Hydralazine subverts B lymphocyte tolerance to self and contributes to generation of pathogenic autoreactivity by disrupting receptor editing. [1] Hydralazine directly scavenges free acrolein, decreasing intracellular acrolein availability and thereby suppressing macromolecular adduction. Hydralazine inhibits cross-linking if adding 30 min after commencing acrolein exposure but is ineffective if added after a 90-min delay. [2] Hydralazine (0.1-10 mM) inhibits both extracellular and intracellular ROS production by inflammatory macrophages, by a ROS-scavenging mechanism probably affecting superoxide radical (O(2)(*-))-generation by xanthine oxidase (XO) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADH/NADPH) oxidase. Hydralazine (0.1-10 mM) significantly reduces NO(*) generation, and this effect is attributable to an inhibition of NOS-2 gene expression and protein synthesis. Hydralazine also effectively blocks COX-2 gene expression which perfectly correlated with a reduction of protein levels and PGE(2) synthesis. [3] Hydralazine protects against not only acrolein-mediated injury, but also compression in guinea pig spinal cord ex vivo. Hydralazine can significantly alleviate acrolein-induced superoxide production, glutathione depletion, mitochondrial dysfunction, loss of membrane integrity, and reduces compound action potential conduction. [4] |
| In vivo | Hydralazine affords strong, dose-dependent protection against the increases in plasma marker enzymes but not the hepatic glutathione depletion produced by allyl alcohol in mice. [5] |
| Synonyms | Hydralazine HCl, Apresoline |
| Molecular Weight | 196.64 |
| Formula | C8H9ClN4 |
| Cas No. | 304-20-1 |
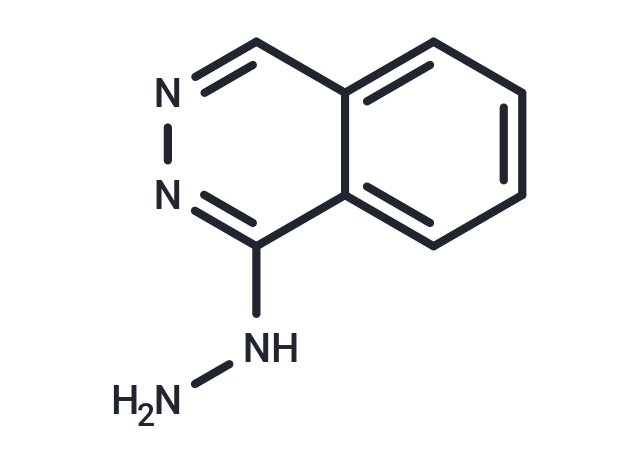
| Smiles | NNC1=NN=CC2=CC=CC=C12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.2961 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Color | White |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 10 mM, Sonication is recommended. DMSO: Insoluble | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.