 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Fisetin belongs to a group of natural flavonols with a variety of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-tumor, anti-aging and neuroprotective effects.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $41 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $45 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Fisetin belongs to a group of natural flavonols with a variety of biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-tumor, anti-aging and neuroprotective effects. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human pancreatic cancer cells PANC-1 were treated with Fisetin (25-400 µM) for 24-48 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK-8 assay. RESULTS: Low concentrations of Fisetin (25-50 µM) did not significantly inhibit the viability of PANC-1 cells, and high concentrations inhibited it. [1] METHODS: HeLa cells were treated with Fisetin (20-50 µM) for 24-48 h. Cell cycle was detected by Flow cytometry. RESULTS: Cells treated with 20/30/50 µM Fisetin resulted in a high accumulation of G2/M phase cells. The proportion of G2/M-arrested cells increased from 10.1% to 16.2%, 18.9% and 25.1%, respectively, at 24 h, whereas the proportion of G2/M-blocked cells increased to 30.9%, 36.2% and 56.2%, respectively, at 48 h. Meanwhile, at 48 h, 50 µM of Fisetin put a large proportion of cells in Go/G1 phase. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To detect anti-tumor activity in vivo, Fisetin (300 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally every two days for 20 days to BALB/c nude mice bearing PANC-1 xenografts. RESULTS: Tumor size was significantly reduced in Fisetin-treated mice. proliferation-associated protein proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) was significantly reduced in the Fisetin-treated group. fisetin treatment reduced the expression of proteins associated with cell growth and proliferation, including PCNA, Ki67, and phosphorylated histone H3. [1] |
| Molecular Weight | 286.24 |
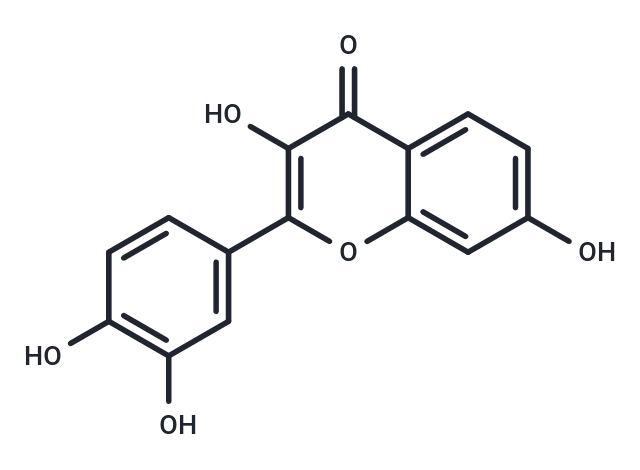
| Formula | C15H10O6 |
| Cas No. | 528-48-3 |
| Smiles | OC1=C(OC=2C(C1=O)=CC=C(O)C2)C3=CC(O)=C(O)C=C3 |
| Relative Density. | 1.688g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 28.6 mg/mL (99.92 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 2.9 mg/mL (10.13 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 2.87 mg/mL (10.03 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.