Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

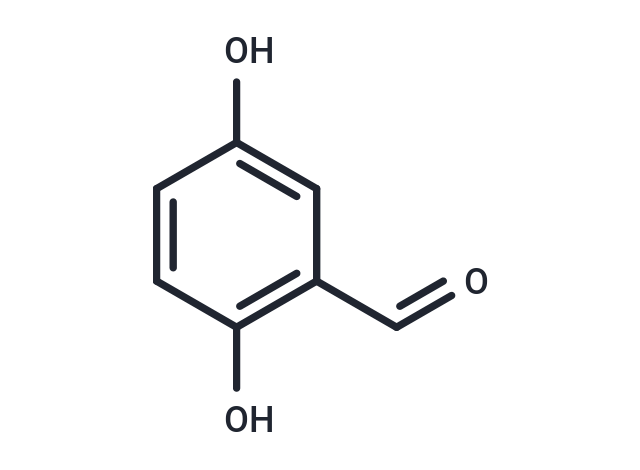
2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde (Gentisaldehyde) has antioxidant activity against Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis. 2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde also inhibits S. aureus strains(MIC50: 500 mg/L).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $29 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $30 | In Stock |
| Description | 2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde (Gentisaldehyde) has antioxidant activity against Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis. 2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde also inhibits S. aureus strains(MIC50: 500 mg/L). |
| Targets&IC50 | S. aureus:500 mg/L(MIC50) |
| In vitro | 2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde modified the three lipid monolayer structures by integrating into the monolayer, forming aggregates of antimicrobial -lipid complexes, reducing the packing effectiveness of the lipids, increasing the membrane fluidity, and altering the total dipole moment in the monolayer membrane model. The interactions of 2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde with bacterial phospholipids depended on both the structure of the antimicrobials and the composition of the monolayers[1]. |
| Alias | Gentisaldehyde |
| Molecular Weight | 138.12 |
| Formula | C7H6O3 |
| Cas No. | 1194-98-5 |
| Smiles | OC1=CC(C=O)=C(O)C=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.2667 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 30 mg/mL (217.2 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.