 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) mainly targets bacterial DNA Gyrase (IC50=0.22-0.31 µM) and topoisomerase IV (IC50=0.3-1.9 µM). Ciprofloxacin is a highly active fluoroquinolone antibiotic.
| Pack Size | Price | USA Warehouse | Global Warehouse | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $41 | In Stock | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $59 | In Stock | In Stock |
| Description | Ciprofloxacin (Bay-09867) mainly targets bacterial DNA Gyrase (IC50=0.22-0.31 µM) and topoisomerase IV (IC50=0.3-1.9 µM). Ciprofloxacin is a highly active fluoroquinolone antibiotic. |
| Targets&IC50 | Korschikov:6700 μg/L, B. anthracis:0.12 μg/mL (MIC90), Y. pestis:0.03 μg/mL (MIC90), GABAA:250 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Prostate cancer cells (LNCaP and DU145) were treated with Ciprofloxacin, and the cytotoxicity was detected by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay. RESULTS: Ciprofloxacin showed low cytotoxicity to DU145 cells, with a LDH release rate of 23.3%. The release rate of LDH to LNCaP cells was 22.1%. [1] METHODS: Tenocytes were treated with Ciprofloxacin (5-50 μg/mL) for 0-24 hours, and MTT assay was used to detect cell growth inhibition. RESULTS: Ciprofloxacin inhibited cell proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. [2] METHODS: Minimum inhibitory concentrations of Yersinia pestis and Bacillus anthracis were determined after treatment with Ciprofloxacin. RESULTS: Ciprofloxacin showed potent activity against Yersinia pestis and Bacillus anthracis with MIC90 of 0.03 μg/mL and 0.12 μg/mL, respectively. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the preventive effect of Ciprofloxacin against plague, mice were intraperitoneally injected with Ciprofloxacin (30 mg/kg) for 24 hours. RESULTS: Ciprofloxacin could prevent Yersinia pestis in a mouse model of pneumonic plague. [4] METHODS: To investigate the effect of Ciprofloxacin on the susceptibility to aortic dissection and rupture in mice, Ciprofloxacin (100 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally once daily for 4 weeks. RESULTS: Ciprofloxacin accelerated aortic root dilation and increased the incidence of aortic dissection and rupture by decreasing LOX levels and increasing MMP levels and activity in the aortic wall. Ciprofloxacin induces DNA damage and release of DNA into the cytoplasm, mitochondrial dysfunction, and activation of cytoplasmic DNA sensor signals. Ciprofloxacin increased apoptosis and necroptosis in the aortic wall. [5] |
| Kinase Assay | The in vitro kinase assays is performed by incubating purified kinase (IKKε or TBK1) in kinase buffer containing 25 mM Tris (pH7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, and 10 μM ATP for 30 minutes at 30°C in the presence of 0.5 μCi γ-[32P]-ATP and 1 μg MBP per sample as a substrate. The kinase reaction is stopped by adding 4x sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer and boiling for 5 minutes at 95°C. Supernatants are resolved by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose, and analyzed by autoradiography using a Typhoon 9410 phosphorimager. |
| Synonyms | Ciproxan, Ciprobay, Bay-09867, Bay o 9867 |
| Molecular Weight | 331.34 |
| Formula | C17H18FN3O3 |
| Cas No. | 85721-33-1 |
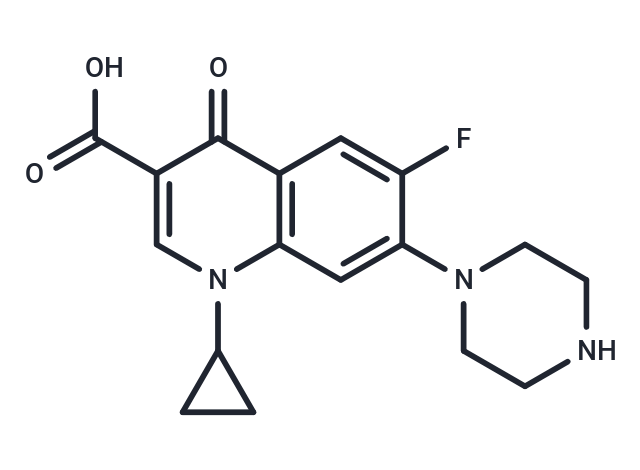
| Smiles | OC(=O)C1=CN(C2CC2)C2=C(C=C(F)C(=C2)N2CCNCC2)C1=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.461 g/cm3 |
| Storage | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: Insoluble DMSO: 0.33 mg/mL (1 mM), Sonication is recommended. 0.1 M HCl: 55 mg/mL (165.99 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended.The compound is unstable in solution. Please use sonn. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/0.1 M HCl
0.1 M HCl
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dissolve 2 mg of the compound in 100 μL DMSO![]() to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
to obtain a stock solution at a concentration of 20 mg/mL . If the required concentration exceeds the compound's known solubility, please contact us for technical support before proceeding.
1) Add 100 μL of the DMSO![]() stock solution to 400 μL PEG300
stock solution to 400 μL PEG300![]() and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
and mix thoroughly until the solution becomes clear.
2) Add 50 μL Tween 80 and mix well until fully clarified.
3) Add 450 μL Saline,PBS or ddH2O![]() and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
and mix thoroughly until a homogeneous solution is obtained.
| Size | Quantity | Unit Price | Amount | Operation |
|---|

Copyright © 2015-2026 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.